0% found this document useful (0 votes)
591 views7 pagesAlgebra 2/Trig Cheat Sheet
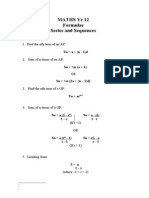
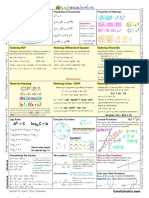
This document is a comprehensive cheat sheet for Algebra 2 and Trigonometry, covering essential topics such as the unit circle, trigonometric functions, identities, distance formula, law of sines, and logarithmic rules. It includes formulas, identities, and methods for solving equations, as well as concepts related to probability, statistics, and polynomial division. The cheat sheet serves as a quick reference for key mathematical principles and problem-solving techniques.
Uploaded by
sasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
591 views7 pagesAlgebra 2/Trig Cheat Sheet
This document is a comprehensive cheat sheet for Algebra 2 and Trigonometry, covering essential topics such as the unit circle, trigonometric functions, identities, distance formula, law of sines, and logarithmic rules. It includes formulas, identities, and methods for solving equations, as well as concepts related to probability, statistics, and polynomial division. The cheat sheet serves as a quick reference for key mathematical principles and problem-solving techniques.
Uploaded by
sasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd