LESSON 6
TOPIC: DRAWING OF PLANS
AND BLUE PRINTS
At the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
sketch and identify architectural symbols
identify and explain building blue prints
explain the different types of building components
mention types of foundations, walls, doors, windows and roofs.
INTRODUCTION
Building is a complex structural work that requires the expertise and experience of building
professionals. Building plan is a detailed drawing of building that shows its size, shape and
measurements.
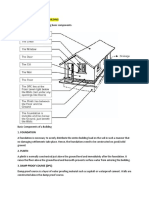
ARCHITECTURAL SYMBOLS
Building plan and Blue-prints symbols are called architectural symbols. They are used to
represent building components, fittings, materials, etc used in building construction.
The following are common architectural symbols used in building.
P a g e 1 | 14
�BUILDING BLUE-PRINT
The blue print is the architectural design and drawings of a building on paper. It is designed
and prepared by an architect before physical construction work commences.
The purpose of blue print is to provide an effective means of communication in the building
industry, it also provides information required to erect a building to the contractor and
other members of the building team.
Blue-print is a photographic print of a plan for a building. The blue print is also known as
“working drawing”. The various drawings that constitute the blue prints are:
1. LAYOUT DRAWING: this will show the length and breadth of the plot of land, the
size of the proposed building, assess road etc.
P a g e 2 | 14
�2. FLOOR PLAN: A building floor plan represents a view from above the building
projected onto a horizontal plane with the absence of the roof. The floor plan shows
all the necessary features of the building like: walls , door openings, window
openings, the foundation and partition of the building into apartments
3. ELEVATIONS: This shows the views of the front, the side or the back of the building
as seen from distance.
FRONT ELEVATION
P a g e 3 | 14
�4. SECTIONS: This is the view obtained when the building floor plan is assumed to be
sliced through by a cutting plane. The purpose of sectioning is to reveal hidden
details of most structural details of most elements in the substructure and
superstructure such as thickness of walls, floors, beams, columns and roof trusses.
P a g e 4 | 14
�5. PERSPECTIVE: The perspective drawing shows the real (actual) and clearer picture of
a proposed building when viewed from a particular angle or location by an observer.
Other drawings included on the working drawings are: electrical installation,
plumbing works, structural details, site location etc.
P a g e 5 | 14
�IDENTIFICATION OF BUILDING COMPONENETS
Buildings are generally divided into two major parts, these are:
Substructure – these are parts of building below ground level e.g foundation,
foundation block work and ground floors.
Superstructure – these are part of buildings above the ground level. These includes
walls, doors, windows, roof etc.
A. FOUNDATION
Foundation is the sub-structural part of a building buried below the ground. It supports the
building and transfer the weight of the building to the ground. The type of foundation used
for a building depends on the nature of site ground and the type of building to be erected.
The materials used for the foundation constructions are concrete, cement, blocks, sand,
water, hardcore, granite, reinforcements (iron rods) etc.
FUNCTIONS OF FOUNDATION
a. It bears the load of the building.
b. It transmit the building loads to the solid part of the ground.
c. Protects the building from upward moisture movement.
d. It makes the building rigid.
TYPES OF FOUNDATION
1. STRIP FOUNDATION: This is the most widely use type of foundation. The depth of
the foundation could range from 600mm to 1200mm. It is mainly used where you
have strong soil base and non-waterlogged areas.
2. PAD FOUNDATION: This is where separate standing columns (pillars) are erected
from the foundation to carry a slab at the top of the ground. It is widely used when
you want to make use of the ground floor of building as a parking space or when the
ground space is not conducive to have foundation.
3. RAFT FOUNDATION: This is mostly used where the building is on very soft natural
ground or fill. The foundation concrete is spread up to the ground floor. It is used in
areas where the soil is sandy and loose.
4. PILE FOUNDATION: These are recommended for buildings which are to be erected
on a shrinkable clay soils and where the foundations need not be more than 900mm.
It is used mostly for skyscrapers and high-rise building, it is also used in waterlogged
areas and island whereby the ground is dug to remove the weak soil.
P a g e 6 | 14
� PILE FOUNDATON
B. WALLS
The wall is a vertical solid part of a building through which the load from the roof is
transmitted to the foundation.
FUNCTIONS OF WALL
To oppose the passage of noise.
It encloses and protects the building.
It bears the roof’s load and transmits it to the foundation.
It protects the occupant of a building against unfavorable weather conditions.
TYPES OF WALLS
1. PARTITION WALLS: It is used for the purpose of separating rooms, or dividing a
room.
2. SHARED WALLS: This is a type of wall shared by neighbours and may also separate
apartment or hotel rooms from each other.
P a g e 7 | 14
� 3. PORTABLE WALLS: These are cubicle walls, room dividers or portable partitions,
which are used to take a large open space and divide it into smaller rooms. They are
commonly found inside schools, hotels, convention centers etc.
4. BOUNDARY WALLS: These include privacy walls, boundary-marking walls on
property and town walls also known as fences.
5. SEPARATION WALL: Some walls are designed to formally separate one population
from another. An example is a wall that separates a country that split into two.
6. MOVABLE PARTITIONS: These are used where the walls of a room are frequently
opened to form one large floor area. There are several types of partition; sliding,
sliding and folding and screens.
MATERIALS FOR MAKING WALLS
Timber products
Glass
Metal
Asbestos sheet
Leaves
Tree trunks and branches
Blocks
Stone
Bricks
C. FLOORS
A floor is a continuous horizontal surface designed and constructed between walls to
support people and their furnitures, equipment and machinery including the self-weight of
the building. The floor can be concrete or timber floor with different finfishes such as motar
screed, terrazzo, tiles, etc
P a g e 8 | 14
�FUNCTIONS OF FLOORS
It makes building rigid and stable.
It prevents underground water and heat from rising into the building.
It prevents the transmission of sound from one dwelling to another.
It provides support for people and their furnitures, equipment and machinery
including the self-weight of the building.
To accommodate services easily e.g conduit piping.
TYPES OF FLOORS
Solid floor
Pre-cast concrete floor
Suspended floor
Concrete slab floor
OPENINGS IN WALLS
These means part of wall not covered by walling materials. It is allowed to provide windows,
doors and ventilation spaces. It must be spanned on top by the lintel.
LINTEL: These are horizontal components built above openings such as windows and doors
to withstand the load from the wall above it.
DOORS
A door is a solid barrier to a door opening. To every building or room is an entrance or an
exit usually covered by a door made of different types of materials such as wood, steel,
aluminum, glass or two or more combination of the materials.
FUNCTIONS OF DOORS
i. Provides exit and entrance to the building
ii. It provides security to the building
iii. Provides improved appearance to the building
iv. To guide against harsh weather conditions
TYPES OF DOORS
1. Panel door (one panel door, two panel door, three panel door etc.)
2. Flush door
3. Sliding doors
4. Revolving doors
5. Ledged and braced battened door
6. Framed ledged and braced battened door
7. Folding door (roller shutter used for garage)
8. Louvre door e.t.c
P a g e 9 | 14
�WINDOWS
These are fixed to the window openings in a wall to let in light and air. Windows are usually
either side-hinged or vertically hinged and are called casement windows or slide up and
down and are called cash windows. Others are sliding sashes, pivoted sashes, night vents
etc.
FUNCTIONS OF WINDOWS
Letting in and out air (ventilation).
Letting in light.
P a g e 10 | 14
� Providing outside view for occupants.
Providing security to the building.
Providing improved appearance to the building.
TYPES OF WINDOWS
1. Louvre window
2. Sliding window
3. Casement window
4. Panel window etc.
P a g e 11 | 14
�ROOFS
Roof is the uppermost part of a building which provides coverage for the building structure.
It protects the occupants from weather conditions such as rain, snow, sun etc. Some
examples of roofing materials are; grass, zinc, aluminium, slates, asbestos, concrete etc.
FUNCTIONS OF ROOFS
To prevent penetration of rain and snow.
To prevent direct radiation of sun into the building.
To improve the aesthetic (appearance) of the building.
To accommodate services such as overhead tanks, conduit pipes, ceiling fans etc.
TYPES OF ROOF
1. Lean-to roof
2. Gable or pitched roof
3. Hip roof
4. Combination or couple roof
5. Arched roof
6. Butterfly roof
7. Half monitor roof
8. Monitor roof
9. Mansard roof etc.
P a g e 12 | 14
�CLASS ACTIVITY
Match the objects below with the appropriate corresponding names on the line provided.
1. Water closet
2. Mansard roof
3. Pile foundation
4. Wardrobe
5. bath tub
6. Shower drain
7. Gable roof
8. Raft foundation
9. Panel door
10. Louvre window
11. Casement window
12. lamp
13. Strip foundation
14. Concrete
15. Cell
16. Flush door
P a g e 13 | 14
�P a g e 14 | 14