Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CIEN 30043 Lecture No. 1a
Uploaded by
One Less than TwiceOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CIEN 30043 Lecture No. 1a
Uploaded by
One Less than TwiceCopyright:
Available Formats
STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
Introduction
Classification of Structures
Loads
Structural Design
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
Idealized Structure
Determinacy and Stability
Equations of Equilibrium
Application of the Equations of Static Equilibrium
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
3. Analysis of Statically Determinate Trusses
Common Types of Trusses
Classification of Coplanar Trusses
The Method of Joints
Zero-Force Members
The Method of Sections
Compound Trusses
Complex Trusses
Space Trusses
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
4. Internal Loadings Developed in Structural Members
Internal Loadings at a Specified Point
Shear and Moment Functions
Shear and Moment Diagrams for a Beam
Shear and Moment Diagrams for a Frame
Moment Diagrams Constructed by the Method of Superposition
5. Cables and Arches
Cables Subjected to Concentrated Loads
Cables Subjected to a Uniform Distributed Load
Three-Hinged Arches
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
6. Influence Lines for Statically Determinate Structures
Influence Lines
Influence Lines for Beams
Influence Lines for Trusses
Maximum Influence at a Point due to a Series of Concentrated Loads
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
1. TYPES OF STRUCTURES AND LOADS
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
INTRODUCTION
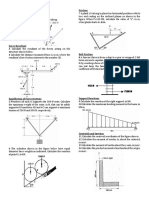
Structure - a system of connected parts used to support a load.
Important examples: Important to account:
‣ Buildings ‣ Safety
‣ Bridges ‣ Esthetics
‣ Towers ‣ Serviceability
‣ Economic constraints
‣ Environmental
constraints
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Structural Elements
TIE RODS
- structural members subjected to tensile force
rod bar
angle channel
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Structural Elements
TIE RODS
- structural members subjected to tensile force
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Structural Elements
BEAMS
- usually straight horizontal members used primarily to carry vertical
loads
simply supported beam cantilever beam
fixed-supported beam continuous beam
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Structural Elements
BEAMS
- usually straight horizontal members used primarily to carry vertical
loads
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Structural Elements
COLUMNS
- members that are generally vertical and resist axial compressive
loads (and bending)
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Structural Elements
COLUMNS
- members that are generally vertical and resist axial compressive
loads (and bending)
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Types of Structures
TRUSS
- structures that consist of two-force members only, where the
members are organized so that the assemblage as a whole behaves
as a single object.
compression
tension
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Types of Structures
TRUSS
- structures that consist of two-force members only, where the
members are organized so that the assemblage as a whole behaves
as a single object.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Types of Structures
CABLES
- structures that are usually flexible and carry their loads in tension.
Unlike tension ties, however, the external load is not applied along
the axis of the cable, and consequently the cable takes a form that
has a defined sag.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Types of Structures
CABLES
- structures that are usually flexible and carry their loads in tension.
Unlike tension ties, however, the external load us not applied along
the axis of the cable, and consequently the cable takes a form that
has a defined sag.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Types of Structures
ARCHES
- structures that achieve its strength in compression. Arches must be
rigid, however, in order to maintain their shape, and this results in
secondary loadings involving shear and moment.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Types of Structures
ARCHES
- structures that achieve its strength in compression. Arches must be
rigid, however, in order to maintain their shape, and this results in
secondary loadings involving shear and moment.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Types of Structures
FRAMES
- often used in buildings and re composed of beams and columns that
are either pin or fixed connected.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Types of Structures
FRAMES
- often used in buildings and are composed of beams and columns
that are either pin or fixed connected.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
CLASSIFICATION OF STRUCTURES
Types of Structures
SURFACE STRUCTURE
- made from a material having very small thickness compared to its
other dimensions.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Design Codes
National Structural Code of the Philippines (NSCP) 2015
Volume I – Buildings, Towers, and Other Vertical Structures
National Structural Code of the Philippines (NSCP)
Volume II – Bridges
DPWH Design Guidelines, Criteria, and Standards 2015
Volume 5 – Bridge Design
Volume 6 – Public Buildings and Other Related Structures
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Dead Loads
Dead loads consists of the weights of the various structural members
and the weight of any objects that are permanently attached to the
structure.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Dead Loads
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Dead Loads
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Sample Problem No. 1
A floor beam is used to support the 1.83 m width of a lightweight plain
concrete slab having a thickness of 102 mm. The slab serves as a
portion of the ceiling for the floor below, and therefore its bottom is
coated with plaster. Furthermore, a 2.44-m high, 305-mm thick
lightweight solid concrete block wall is directly over the top flange of
the beam. Determine the loading on the beam measured per meter
length of the beam.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Sample Problem No. 1
Concrete slab:
305 mm
(23.6 kN/m3) (0.102m) (1.83m) = 4.405 kN/m
Plaster ceiling:
(0.24 kN/m2) (1.83m) = 0.439 kN/m
2.44 m
Block wall:
(16.5 kN/m3) (2.44m) (0.305m) = 12.28 kN/m
__________
102 mm Total Load = 17.124 kN/m
0.915 m
0.915 m
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Live Loads
Live loads can vary both in their magnitude and location. They may be
caused by the weight of objects temporarily placed on a structure,
moving vehicles, or natural forces.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Wind Loads
When structures block the flow of wind, the wind’s kinetic energy is
converted into potential energy of pressure, which causes a wind
loading.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Wind Loads
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Earthquake Loads
Earthquakes produce loadings on a structure through its interaction
with the ground and its response characteristics. These loadings result
from the structure’s distortion caused by the ground’s motion and the
lateral resistance of the structure.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Earthquake Loads
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Hydrostatic and Soil Pressure
When structures are used to retain water, soil, or granular materials, the
pressure developed by these loadings becomes an important criterion
for their designs.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Hydrostatic and Soil Pressure
When structures are used to retain water, soil, or granular materials, the
pressure developed by these loadings becomes an important criterion
for their designs.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
LOADS
Other Natural Loads
Several other types of live loads may also have to be considered in the
design of a structure, depending on its location or use. These include
the effect of blast, temperature changes, and differential settlement of
the foundation.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
1. Types of Structures and Loads
STRUCTURAL DESIGN
Load Combinations
Whenever a structure is designed, it is important to give consideration
to both material and load uncertainties.
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
2. ANALYSIS OF STATICALLY
DETERMINATE STRUCTURES
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Support Connections
IDEALIZED MODELS
typical “pin-supported” typical “fixed-supported”
connection detail connection detail
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Support Connections
IDEALIZED MODELS
typical “roller-supported” typical “fixed-supported”
connection detail connection detail
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Support Connections
IDEALIZED MODELS
pin support pin-connected joint fixed support fixed-connected joint
torsional spring support torsional spring joint
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Support Connections
IDEALIZED MODELS
P
P
L/2 L/2
L/2 L/2
actual beam idealized beam
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Support Connections
SUPPORTS FOR COPLANAR STRUCTURES
Type of Connection Idealized Symbol Reaction
(1) light cable
(2)
rollers
rocker
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Support Connections
light cables
rollers & rocker
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Support Connections
SUPPORTS FOR COPLANAR STRUCTURES
Type of Connection Idealized Symbol Reaction
(3) smooth contact surface
(4) smooth pin-connected collar
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Support Connections
SUPPORTS FOR COPLANAR STRUCTURES
Type of Connection Idealized Symbol Reaction
(5) smooth pin or hinge
(6) fixed support
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Support Connections
smooth pin or hinge fixed support
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Support Connections
SUPPORTS FOR COPLANAR STRUCTURES
Type of Connection Idealized Symbol Reaction
(7)
slider
fixed-connected
collar
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Support Connections
fixed-connected collar
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Idealized Structure
IDEALIZED MODELS
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Idealized Structure
IDEALIZED MODELS
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Idealized Structure
IDEALIZED MODELS
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Idealized Structure
IDEALIZED MODELS
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Tributary Loadings
ONE-WAY SYSTEM
4.8 kN/m2
0.75m
0.75m
0.75m
3m 1.5m 0.75m
1.5m
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Tributary Loadings
ONE-WAY SYSTEM 7.2 kN/m
4.8 kN/m2
3m
10.8 kN 10.8 kN
10.8 kN
5.4 kN 5.4 kN
3m 1.5m
1.5m
1.5m 1.5m
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
2. Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures
IDEALIZED STRUCTURES
Tributary Loadings
TWO-WAY SYSTEM
3m
4.8 kN/m2
3m
1.5m
3m
3m
CIEN 3144 STRUCTURAL THEORY 1
You might also like
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Introduction to Design of Building StructuresFrom EverandIntroduction to Design of Building StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- CIEN 3144 Structural Theory 1Document172 pagesCIEN 3144 Structural Theory 1Andrei Alido100% (1)
- TOS I - Chapter 1Document27 pagesTOS I - Chapter 1michael jayNo ratings yet
- New Quiz Format Theory2Document27 pagesNew Quiz Format Theory2Adrian Neil PinedaNo ratings yet
- ConstructionDocument16 pagesConstructionasoomlayNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Module 2Document32 pagesEngineering Mechanics Module 2Abigail SiatrezNo ratings yet
- 01 - CIEN 30043 - Types of Structures and Loads-2Document21 pages01 - CIEN 30043 - Types of Structures and Loads-2Talentless SoooyaaaNo ratings yet
- CE 33 Structural Theory - I: - Time: - ProfessorDocument28 pagesCE 33 Structural Theory - I: - Time: - ProfessorGintokiNo ratings yet
- Class 01 Review of Structural Systems and Properties in ArchitectureDocument44 pagesClass 01 Review of Structural Systems and Properties in ArchitectureRadhi MajmudarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To Structural AnalysisDocument29 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To Structural AnalysisRu TandsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Structural AnalysisDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Structural Analysisroswel.ramiloNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Structural Theory PDFDocument37 pages1 Introduction To Structural Theory PDFKingJames De MattaNo ratings yet
- Module-1Document75 pagesModule-1pakistani challangeNo ratings yet
- Elementary Design of Structures Notes PDFDocument53 pagesElementary Design of Structures Notes PDFAsiimwe Moses Kasirika100% (7)
- 1 IntroductionDocument43 pages1 IntroductionWassan IdreesNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document85 pagesModule 1Syed WasimNo ratings yet
- W1 Chapter 1-Introduction (NF) 2022Document61 pagesW1 Chapter 1-Introduction (NF) 2022Nor HakimNo ratings yet
- Deadload LiveloadDocument37 pagesDeadload LiveloadVincent Nebria100% (1)
- tHEORY mODULEDocument34 pagestHEORY mODULEJorge DanielleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Limit State Design For Flexure: Reinforced Concrete Structures I (Ceng-3111)Document50 pagesChapter 2 Limit State Design For Flexure: Reinforced Concrete Structures I (Ceng-3111)Muaz HararNo ratings yet
- A. Struct 3 SillevaDocument4 pagesA. Struct 3 SillevaPatricia BraganzaNo ratings yet
- Video1.2 Introduction To StructuresDocument28 pagesVideo1.2 Introduction To StructuresNguyễn An KhoaNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis-I All NotesDocument185 pagesStructural Analysis-I All Notesug2319311No ratings yet
- BCO01-02 - Stability of Steel Arches PDFDocument25 pagesBCO01-02 - Stability of Steel Arches PDFSiva Prasad MamillapalliNo ratings yet
- Notes CE60StabilityDeterminacyDocument4 pagesNotes CE60StabilityDeterminacyMusicMeowNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Structural LoadsDocument19 pagesModule 1 - Structural LoadsJerico Pilapil NamucoNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures Course NotesDocument10 pagesTheory of Structures Course NotesT N Roland BourgeNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Intro To Structural AnaylsisDocument15 pagesModule 1 Intro To Structural AnaylsisVasquez Austine ThriceNo ratings yet
- Module+1.1+ (CE315) + +Review+of+Statics+and+Mechanics,+Introduction+to+TOS+ +LOWDocument42 pagesModule+1.1+ (CE315) + +Review+of+Statics+and+Mechanics,+Introduction+to+TOS+ +LOWKytts VhieNo ratings yet
- BEC6Document10 pagesBEC6Edelson RapadaNo ratings yet
- Structural SystemsDocument9 pagesStructural SystemsmartaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Intro To Structural AnaylsisDocument13 pagesModule 1 Intro To Structural AnaylsisshnslaveNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Structural AnalysisDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Structural AnalysisAlyssandra Beatriz AustriaNo ratings yet
- Name: Section: Schedule: Date:: Course Code: ES341 Module #1Document19 pagesName: Section: Schedule: Date:: Course Code: ES341 Module #1Cowar D. CourageNo ratings yet
- Struct Intro ReviewerDocument5 pagesStruct Intro ReviewerLine PestañoNo ratings yet
- Topic: Unit - 1: Medha Neetu Prathyush A Keerthi Maseeh Varun GouravDocument35 pagesTopic: Unit - 1: Medha Neetu Prathyush A Keerthi Maseeh Varun GouravtejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document16 pagesChapter 3Halina HamidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document44 pagesLecture 1Inam UllahNo ratings yet
- 02 Geenral Intro DuctionsDocument52 pages02 Geenral Intro Ductionsmuhammad irfanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Structural AnalysisDocument59 pagesIntroduction To Structural Analysisrio jay bananNo ratings yet
- ToS Lessons MergedDocument150 pagesToS Lessons MergedAlyssandra Beatriz AustriaNo ratings yet
- Sttheo IntroDocument6 pagesSttheo IntroRyke Ivan Sab-it BunolnaNo ratings yet
- CE131P E01 4Q 1920 Module 1Document23 pagesCE131P E01 4Q 1920 Module 1Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Advance Structural Systems: UNIT-1Document26 pagesAdvance Structural Systems: UNIT-1shipwreckwaveNo ratings yet
- Cie 063 Chapter OneDocument85 pagesCie 063 Chapter Onemark carloNo ratings yet
- L01 CSTRU133D-Introduction To Structural Analysis and Minimum Design LoadsDocument46 pagesL01 CSTRU133D-Introduction To Structural Analysis and Minimum Design LoadsGabriel JavelonaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Stability and Determinacy: Main Reference: Structural Analysis (R.C. Hibbeler)Document62 pagesIntroduction To Stability and Determinacy: Main Reference: Structural Analysis (R.C. Hibbeler)Study ChillNo ratings yet
- CE 111 - Civil Engineering Orientation - TOPIC NO.04Document10 pagesCE 111 - Civil Engineering Orientation - TOPIC NO.04Canilang KarelleNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis: TH THDocument6 pagesStructural Analysis: TH THleinad micosaNo ratings yet
- Steel Design Module 1 Tension and Compression MembersDocument26 pagesSteel Design Module 1 Tension and Compression Membersa.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Structural AnalysisDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Structural AnalysisCNo ratings yet
- Lec-1b - Types of StructuresDocument23 pagesLec-1b - Types of StructuresNouman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis ReviewerDocument14 pagesStructural Analysis ReviewerRyugi KamasakiNo ratings yet
- Ce 311-ST - M1 - T1 - W2 - LabDocument16 pagesCe 311-ST - M1 - T1 - W2 - LabCHEZANIE MIYA ASUNCIONNo ratings yet
- What Is Engineering?: - Form Function StructureDocument7 pagesWhat Is Engineering?: - Form Function StructureGabiNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Review of Statics and Mechanics Introduction To TOSDocument48 pagesWeek 1 Review of Statics and Mechanics Introduction To TOSJHON ROY OLIVANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document51 pagesChapter 1CE-Cret KuyaaDeeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - ToS 1 - Introduction - Structural Forms and Their IdentificationDocument38 pagesLecture 1 - ToS 1 - Introduction - Structural Forms and Their IdentificationIsaac OgolaNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Terminologies in Theory of Structures 1Document6 pagesDefinitions and Terminologies in Theory of Structures 1Lemuel John CristobalNo ratings yet
- CIEN 30043 Lecture No. 4Document24 pagesCIEN 30043 Lecture No. 4One Less than TwiceNo ratings yet
- CIEN 30043 Lecture No. 3Document32 pagesCIEN 30043 Lecture No. 3One Less than TwiceNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid Bodies ICDocument1 pageStatics of Rigid Bodies ICOne Less than TwiceNo ratings yet
- Dyna 1 VcaDocument2 pagesDyna 1 VcaIvan SantosNo ratings yet
- Bentone b55Document44 pagesBentone b55ardazerokNo ratings yet
- XII Notes WajahatDocument237 pagesXII Notes Wajahatsaim.akhtar.4.5.6No ratings yet
- ZS 4, ZS 4 VSD & ZS 4 VSD+ - enDocument32 pagesZS 4, ZS 4 VSD & ZS 4 VSD+ - enwael72No ratings yet
- How To Reset A CFMOTO 650NKDocument2 pagesHow To Reset A CFMOTO 650NKAdrian FernandezNo ratings yet
- Overload Relay: Quick Setup GuideDocument1 pageOverload Relay: Quick Setup Guidealejandro jimenezNo ratings yet
- Best Practice For Consigning Lithium Cells / Batteries in Hong KongDocument8 pagesBest Practice For Consigning Lithium Cells / Batteries in Hong KongPhilip LoNo ratings yet
- FPT Hoa Lac - EngReport V1Document30 pagesFPT Hoa Lac - EngReport V1Nguyên Trịnh CaoNo ratings yet
- English Kelas XII FixDocument14 pagesEnglish Kelas XII FixasrorNo ratings yet
- Life 2e Bre Pre-Inter SB U05 Preview VerDocument63 pagesLife 2e Bre Pre-Inter SB U05 Preview VerMinh Thu Pham NgocNo ratings yet
- 6CTA8.3-G2 Datasheet ENGINE CUMMINSDocument4 pages6CTA8.3-G2 Datasheet ENGINE CUMMINSluis perezNo ratings yet
- 2022 Acdelco Training Course CatalogDocument81 pages2022 Acdelco Training Course CatalogWilliam Orozco LópezNo ratings yet
- Unit-10-Our-houses-in-the-future-Lesson-3-A-closer-look-2 - Basic VerDocument22 pagesUnit-10-Our-houses-in-the-future-Lesson-3-A-closer-look-2 - Basic VerQuynh Thy DoNo ratings yet
- Sample Testing Performa: Total Parco Pakistan LTDDocument1 pageSample Testing Performa: Total Parco Pakistan LTDAdnanNo ratings yet
- Technical - Datasheet - Grid Power VRX-FT 12-180Document1 pageTechnical - Datasheet - Grid Power VRX-FT 12-180xuyen tranNo ratings yet
- RAC MCQ Set 1Document58 pagesRAC MCQ Set 1aditya NirmalNo ratings yet
- Perancangan Pengembangan Produk Powerbank Dengan Metode Quality Function Deployment (QFD)Document13 pagesPerancangan Pengembangan Produk Powerbank Dengan Metode Quality Function Deployment (QFD)TM AMarcellinus Tedy100% (1)
- Fuel System A5 B8Document69 pagesFuel System A5 B8ArturoRatierNo ratings yet
- ME - Example Lab ReportDocument20 pagesME - Example Lab ReportSunny KhadkaNo ratings yet
- 20 The Discovery of The 20th Century To Change The WorldDocument6 pages20 The Discovery of The 20th Century To Change The WorldanakramboengNo ratings yet
- Owners Manual MFL69168201Document20 pagesOwners Manual MFL69168201Clarissee VidalNo ratings yet
- Hdi DL08PDocument188 pagesHdi DL08Pq26n65hvfsNo ratings yet
- High-Speed DC Circuit Breakers For Fixed Installations (En / Iec) Type URDocument16 pagesHigh-Speed DC Circuit Breakers For Fixed Installations (En / Iec) Type URMouth GoonieNo ratings yet
- Engine Harness (W28) Component Location-6.8L Tier 2/stage IIDocument26 pagesEngine Harness (W28) Component Location-6.8L Tier 2/stage IIAbisay GuchaminNo ratings yet
- Turbine Auxilaries: Ranjeet Kumar Agrawal Assistant Manager NTPC KorbaDocument72 pagesTurbine Auxilaries: Ranjeet Kumar Agrawal Assistant Manager NTPC KorbaSourav Saha100% (1)
- Lightening Arrester 500kVTest Report EnglishDocument20 pagesLightening Arrester 500kVTest Report Englishashwani2101No ratings yet
- DoE Corporate Overview - en - PagesDocument16 pagesDoE Corporate Overview - en - Pageschand198No ratings yet
- Ficha Técnica Motor 1 11-16 Ss 2019Document1 pageFicha Técnica Motor 1 11-16 Ss 2019Gina Vanessa Quintero CruzNo ratings yet
- Three Phase C LLDR Ifi Controlled RectifierDocument28 pagesThree Phase C LLDR Ifi Controlled RectifierTuhin ShahNo ratings yet
- Export or Die!' British DieseDocument9 pagesExport or Die!' British Diesewellington freitasNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Determination of Tariff by Bidding Process For Procurement of Power by Distribution LicenseesDocument1 pageGuidelines For Determination of Tariff by Bidding Process For Procurement of Power by Distribution LicenseesKeerthi Vasan USNo ratings yet