Created by Turbolearn AI
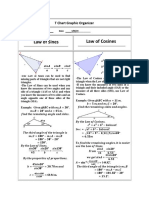
Law of Cosines
The Law of Cosines is used to solve oblique triangles (triangles with no right angle)
when given:
Two sides and an included angle (SAS)
Three sides (SSS)
When to Use Law of Cosines
Unlike the Law of Sines, the Law of Cosines is applied specifically when you have
either two sides and the included angle (SAS) or three sides (SSS) of a triangle.
Steps for Solving Oblique Triangles Using the Law of
Cosines
SAS Case
1. Find the side opposite the given angle using the Law of Cosines.
2. Find the measure of one of the remaining angles by applying either the Law of
Sines or the Law of Cosines.
3. Find the measure of the third angle by applying the Triangle Sum Theorem.
SSS Case
1. Find the angle opposite the longest side using the Law of Cosines.
2. Find one of the remaining angles using either the Law of Sines or the Law of
Cosines.
3. Find the third angle by applying the Triangle Sum Theorem.
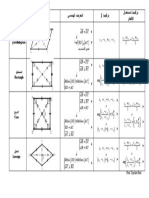
Formulas
Finding Sides
Page 1
� Created by Turbolearn AI
For any triangle ABC with sides a, b, and c:
To find side a: a 2
= b
2
+ c
2
− 2bc × cos(A)
To find side b: b 2 2
= a
2
+ c − 2ac × cos(B)
To find side c: c 2
= a
2
+ b
2
− 2ab × cos(C)
Finding Angles
To find angle A: cos(A) =
2 2 2
b +c −a
2bc
To find angle B: cos(B) =
2 2 2
a +c −b
2ac
2 2 2
To find angle C : cos(C) = a +b −c
2ab
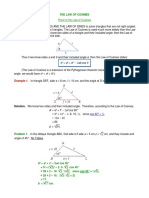
Example 1: Solving an SAS Triangle
Given: Triangle ABC with b = 6.83 inches, c = 9 inches, and A = 102.38 . ∘
Goal: Solve the triangle (find all missing sides and angles).
Step 1: Find Side a
2 2
a = √ b + c − 2bc × cos(A)
Substitute the given values:
2 2 ∘
a = √ (6.83) + (9) − 2 × 6.83 × 9 × cos(102.38 )
a ≈ 12.41 inches
Step 2: Find Angle B (Using Law of Sines)
Using the Law of Sines:
sin(B) sin(A)
=
b a
∘
sin(B) sin(102.38 )
=
6.83 12.41
∘
sin(102.38 )×6.83
sin(B) =
12.41
sin(B) ≈ 0.5376
Page 2
� Created by Turbolearn AI
∘
B = arcsin(0.5376) ≈ 32.52
Alternatively, using the Law of Cosines:
2 2 2 2 2 2
a +c −b (12.41) +(9) −(6.83)
cos(B) = = ≈ 0.8432
2ac 2×12.41×9
∘
B = arccos(0.8432) ≈ 32.50
Step 3: Find Angle C
Using the Triangle Sum Theorem:
∘
C = 180 − (A + B)
∘ ∘ ∘
C = 180 − (102.38 + 32.52 )
∘
C ≈ 45.10
Example 2: Solving another SAS Triangle
Given: Triangle ABC where b = 10 inches, a = 7.98 inches, and C = 100.67 .
∘
In this case, you have two sides and an included angle (SAS). The first step is to find
the side opposite the given angle, which is side c.
2 2
c = √ a + b − 2ab × cos(C)
Substitute the values: c = √(7.98) 2
+ (10)
2 ∘
− (2 × 7.98 × 10 × cos(100.67 ))
Law of Cosines Examples
Example 2
Given a triangle where side a = 7.98 inches, side b = 10 inches, and side c = 13.9
inches, find the measures of the angles.
Page 3
� Created by Turbolearn AI
1. Find angle A using the Law of Cosines:
2 2 2
b +c −a
cos(A) =
2bc
2. Substitute the given values:
2 2 2
10 +13.9 −7.98
cos(A) =
2×10×13.9
3. Calculate the value:
100+193.21−63.6804
cos(A) = = 0.8256
278
4. Find angle A by taking the inverse cosine:
−1 ∘
A = cos (0.8256) = 34.35
5. Using the Triangle Sum Theorem, the measure of angle C can be found by
subtracting the sum of angles A and B from 180 degrees. Angle C is
approximately 44.98 degrees.
Example 3
Given a triangle with sides a = 6, b = 4, and c = 7, find the measures of the angles.
Page 4
� Created by Turbolearn AI
1. Find angle C using the Law of Cosines:
2 2 2
a +b −c
cos(C) =
2ab
2. Substitute the given values:
2 2 2
6 +4 −7
cos(C) =
2×6×4
3. Calculate the value:
36+16−49 3
cos(C) = = = 0.0625
48 48
4. Find angle C by taking the inverse cosine:
−1 ∘
C = cos (0.0625) = 86.42
5. Find angle A using the Law of Cosines:
2 2 2
b +c −a
cos(A) =
2bc
6. Substitute the given values:
2 2 2
4 +7 −6
cos(A) =
2×4×7
7. Calculate the value:
16+49−36 29
cos(A) = = = 0.5179
56 56
8. Find angle A by taking the inverse cosine:
−1 ∘
A = cos (0.5179) = 58.81
9. To find angle B, subtract angles A and C from 180 degrees:
∘ ∘ ∘ ∘
B = 180 − (58.81 + 86.42 ) = 34.77
Page 5