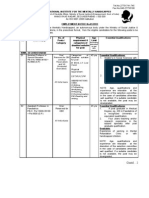
ACTIVITY REACTION OBSERVATION COLOR CONCLUSION
CHANGE
1 1.1 2Mg + O2 -> 2MgO Bright white flame, Silver to white Magnesium reacts
Burning of white powder (powder). with oxygen.
magnesium ribbon (MgO) formed. Combination
dazzling white reaction.
flame
2 1.2 Pb(NO3)2+2KI→PbI2+2KNO A bright yellow Formation of a This is a double
Lead nitrate and 3 precipitate of lead bright yellow displacement
potassium iodide (II) iodide (PbI₂) precipitate of reaction where
forms. lead(II) iodide ions exchange
The solution may (PbI₂) in a partners, forming
appear cloudy due colorless an insoluble
to the solution. precipitate.
precipitation. Lead(II) iodide
(PbI₂) is insoluble
in water, leading to
its precipitation.
3 1.3 Zn+H2SO4→ZnSO4+H2↑ Effervescence is No significant This is a single
The reaction of observed as color change in displacement
sulphuric acid with bubbles of the solution, reaction
Zn hydrogen gas are but the zinc The reaction
released. metal demonstrates the
The solution diminishes activity series of
remains colorless over time. metals, with zinc
because both being more reactive
sulfuric acid and than hydrogen.
zinc sulfate are
colorless in
solution.
�4 1.4 CaO+H2O→Ca(OH)2 Exothermic No color Calcium oxide
Reaction of calcium Reaction: The change reacts with water to
oxide in water mixture becomes form calcium
hot due to the hydroxide (slaked
release of heat. lime),
The reaction demonstrating an
accompany hissing exothermic
sound and bubbles reaction.
A clear solution of
lime water forms
at the top.
5 1.5 2FeSO4 Ferrous sulfate Light green to Heating ferrous
Heating of ferrous Fe2O3+SO2+SO3 crystals are light white then to sulfate is a thermal
sulphate crystals. green. reddish brown. decomposition
The crystals lose reaction, where
water of ferrous sulfate
crystallization and breaks down into
turn white. ferric oxide, sulfur
A pungent smell of dioxide, and sulfur
sulfur dioxide trioxide.
(SO₂) and sulfur
trioxide (SO₃)
gases is observed.
Further heating
produces a brown
residue of ferric
oxide
(Fe2O3Fe_2O_3Fe2
O3)
6 1.6 2Pb(NO3)22PbO+4NO2+O2 Lead nitrate White lead Heating lead
crystals are white. nitrate changes nitrate is athermal
� Heating of lead The crystals into yellow decomposition
nitrate decompose, precipitate of reaction where the
producing a lead oxide compound breaks
brown gas A brown gas down into lead
(nitrogen dioxide) (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen
with a dioxide) is dioxide, and
characteristic evolved. oxygen.
pungent smell.
A glowing splint
reignites,
indicating the
release of oxygen
gas
A yellow residue
of lead(II) oxide
remains in the
container.
7 1.7 2H2O Bubbles of gas are No color Water undergoes
Electrolysis of water 2H2+O2 observed forming change electrolysis,
at both electrodes. splitting into
The volume of gas hydrogen and
collected at the oxygen gases in a
cathode (hydrogen 2:1 volume ratio.
gas) is double the
volume of gas
collected at the
anode (oxygen
gas).
8 1.8 2AgCl Silver chloride White silver This is a
Silver chloride in 2Ag+Cl2 (AgCl) is a white chloride to photochemical
sunlight solid. grey decomposition
reaction,’ where
� The white color silver chloride
gradually turns decomposes in the
gray due to the presence of
formation of sunlight into
metallic silver metallic silver and
Chlorine gas (Cl2) chlorine gas.
is released but may
not be visually
noticeable.
9 1.9 Fe+CuSO4→FeSO4 +Cu blue color of the Blue to green This is a
Reaction of Iron solution gradually displacement
with Copper fades as iron reaction where
Sulphate Solution displaces copper iron, being more
from copper reactive than
sulfate, forming copper, displaces
ferrous sulfate copper from its
which is pale sulfate solution.
green. The reaction
A reddish-brown illustrates the
layer of copper reactivity series of
metal gets metals and the
deposited on the formation of new
surface of the iron substances.
nail.
10 1.10 BaCl2(aq)+Na2SO4(aq)→BaS A white, insoluble white This is double
Reaction between O4(s)+2NaCl (aq) precipitate forms precipitate of displacement
sodium sulpate and immediately after barium sulfate reaction
bareium chloride the solutions are (BaSO₄) is
mixed. clearly visible.
�11. 1.1 Formation of Copper Oxide: Copper powder is Reddish brown Heating copper in
Heating Copper in a 2Cu (s)+O2(g)→2CuO (s) reddish-brown to black again the presence of
China Dish and Reduction of Copper Oxide: color. to reddish oxygen forms black
Passing Hydrogen CuO (s)+H2(g)→Cu (s)+H2O While the heating brown copper(II) oxide.
Gas color changes to When hydrogen
black gas is passed over
After passing hot copper(II)
hydrogen the red oxide, it reduces
color is regained the oxide back to
reddish-brown
copper.
This reaction
demonstrates a
redox process,
where copper
oxide is reduced to
copper (gain of
electrons), and
hydrogen is
oxidized to water
(loss of electrons).