0% found this document useful (0 votes)
275 views29 pagesTQM Chapter 6
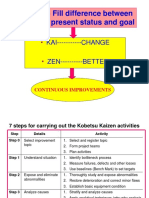
Kaizen is a Japanese philosophy emphasizing continuous improvement through small, incremental changes involving all employees. It focuses on enhancing productivity, quality, and employee satisfaction while reducing waste and standardizing processes. Key methodologies include the PDCA cycle, 5S, and value stream mapping, which collectively foster a culture of ongoing enhancement in organizations.
Uploaded by
pjy8nfkjtqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
275 views29 pagesTQM Chapter 6
Kaizen is a Japanese philosophy emphasizing continuous improvement through small, incremental changes involving all employees. It focuses on enhancing productivity, quality, and employee satisfaction while reducing waste and standardizing processes. Key methodologies include the PDCA cycle, 5S, and value stream mapping, which collectively foster a culture of ongoing enhancement in organizations.
Uploaded by
pjy8nfkjtqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd