0% found this document useful (0 votes)
122 views14 pagesYour Complete Guide To Additional Mathematics (A-Math) Topics
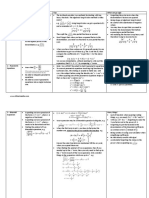
This guide provides an overview of challenging topics in O-level Additional Mathematics, including quadratic functions, surds, polynomials, binomial expansions, and more. Each section outlines common difficulties students face and offers practical tips and strategies to master the concepts. The document serves as a comprehensive resource for students seeking to improve their understanding and performance in A-Math.
Uploaded by
Fan HongCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
122 views14 pagesYour Complete Guide To Additional Mathematics (A-Math) Topics
This guide provides an overview of challenging topics in O-level Additional Mathematics, including quadratic functions, surds, polynomials, binomial expansions, and more. Each section outlines common difficulties students face and offers practical tips and strategies to master the concepts. The document serves as a comprehensive resource for students seeking to improve their understanding and performance in A-Math.
Uploaded by
Fan HongCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd