0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views16 pagesMatricesUO1.3.2 MSBTE - FORMAT (Autosaved)
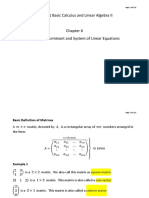
The document is a mathematics lecture on matrices, focusing on matrix multiplication, transposition, and properties of symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices. It includes definitions, conditions for multiplication, and step-by-step solutions to example problems. The content is aimed at teaching students how to solve systems of linear equations using matrix inversion and other matrix operations.
Uploaded by
Ayush ShindeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views16 pagesMatricesUO1.3.2 MSBTE - FORMAT (Autosaved)
The document is a mathematics lecture on matrices, focusing on matrix multiplication, transposition, and properties of symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices. It includes definitions, conditions for multiplication, and step-by-step solutions to example problems. The content is aimed at teaching students how to solve systems of linear equations using matrix inversion and other matrix operations.
Uploaded by
Ayush ShindeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd