Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Ckts Lab Manual (A.c)
Uploaded by
Karn SudhanshOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Ckts Lab Manual (A.c)
Uploaded by
Karn SudhanshCopyright:
Available Formats
www.jntuworld.
com
COMPENSATION THEOREM Aim: To verify Compensation theorem. Apparatus: S.No 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Equipment RESISTORS MULTIMETER RPS BREADBOARD Fuse CONNECTING WIRES Type WW 0-20A 0-30V TCC AS REQUIRED Range Quantity
Circuit Diagram:
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
Theory:
The compensation theorem states that any element in the network either linear or non linear may be replaced by a voltage source of magnitude equal to the current passing through the element multiplied by the value of element provide the currents and voltages in other parts of the circuit remain unaltered. Procedure: 1. 2. 3. 4. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram. Calculate valus of I, I1,I. Current values are taken from the fig. Compare theoretical and practical values.
Observations: parameter I I1 I theoretical practical
Model calculations: From the fig: I = V/R I1 = V/(R+R) I = I- I1 Precautions: 1. All connections should be tight. 2. All reading should be taken with out parallax error. 3. Before giving are removing the connections, supply should be switched off. Result: Thus the Compensation theorem is verified.
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
MAXIMUM POWER TRANSFER THEOREM Aim: To verify Maximum power transfer theorem. Apparatus: S.No 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Equipment Voltmeter Ammeter Rheostats Variacs Knife switches Fuse Type MI MI WW 1- DPDT TCC Range Quantity
Circuit diagram for Maximum Power Tranfer Theorem:
Theory: In any linear network containing an independent voltage source in series with the resistance Rs or an independent current source in parallel with a resistance rs, delivers maximum power to that load resistance RL for which RL = RS.
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
Procedure for Maximum Power Transfer theorem: 1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram.
2. 3. 4. 5.
20V of input voltage is applied to the given circuit By varying RL note down the corresponding VL , IL
Calculate the power in each case Draw the graph between maximum power verses load resistance and indicate the maximum.
Observations for Maximum Power Transfer Theorem: S.No 1. 2. 3. 4. . . . . . . RL VL(V) IL(A) PL = VLIL(W)
Theoretical calculations: Pmax =Vth2/4Rth Model Graph:
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
Precautions: 4. All connections should be tight. 5. All reading should be taken with out parallax error. 6. Before giving are removing the connections, supply should be switched off. Result: 1. Maximum power was transferred when RL = _________(ohms) 2. Actual Source resistance RS = ________(ohms)
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
RECIPROCITY & MILLIMANS THEOREMS Aim: a) To verify Reciprocity theorem. b) To verify Millimans theorem. Apparatus: S.No 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Equipment Voltmeter Ammeter Rheostats Variacs Knife switches Fuse Type MI MI WW 1- DPDT TCC Range Quantity
Circuit Diagram for Reciprocity Theorem:
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
Circuit Diagram for Millimans Theorem:
Theory: Reciprocity theorem: It states that in any linear network containing two or more sources, if we apply some input to the circuit, the ratio of the response in any element to input is constant even when the position of the input and outputs are interchanged. Millimans Theorem: This theorem states that when a number of voltage sources(V1, V2..Vn) are in parallel having internal resistances (R1, R2, R3 Rn) respectively, the arrangement can be replaced by a single equivalent voltage source V in series with an equivalent series resistance R.
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
Procedure for Reciprocity Theorem: 1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram. 2. Keep the varic is in mnimum output position, supply is taken. 3. Keep the switch S1 is in position A and switch S2 is in position X, all meter readings are noted. 4. Keep the switch S1 is in position A and switch S2 is in position Y, all meter readings are noted. 5. Keep the switch S1 is in position B and switch S2 is in position X, all meter readings are noted. Procedure for Millimans Theorem: 1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram. 2. Keep the variacs in minimum output position and switch is in postion-2, supply is taken. 3. Adjust the variac such that desired voltage is obtained. 4. Note down the meter readings. 5. Keep the switch is in open position, note down the meter readings. 6. Again keep the switch is in position-1, note down the meter readings. Observations for Reciprocity Theorem: S.No 1. 2. 3. Model Calculations: V1 / I21 = ____________ V1(V) I1(A) V2(V) I2(A) Test condition Both sources are active Source 1 only active Source 2 only active
V2 / I111 = _____________ Observations for Millimans theorem: S.No 1. 2. 3. V(V) I(A) Test condition Switch is in position 2 Switch is in open position Switch is in position 1
Model calculations:
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
V = ( V1G1 V2G2 ..) / ( G1 + G2+.) R = 1 / ( G1 + G2 +) REQ = VOC / ISC Precautions: 7. All connections should be tight. 8. All reading should be taken with out parallax error. 9. Before giving are removing the connections, supply should be switched off. Result: Thus Reciprocity Theorem and Millimans Theorem is verified .
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
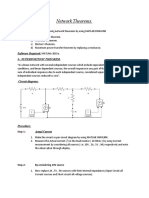
THEVENINS, NORTONS AND MAXIMUM POWER TRANSFER THEOREM Aim: a) To verify Thevenins theorem. b) To verify Nortons theorem c) To verify Maximum power transfer theorem. Apparatus: S.No 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Equipment Voltmeter Ammeter Rheostats Variacs Knife switches Fuse Type MI MI WW 1- DPDT TCC Range Quantity
Circuit diagram for Thevenins & Nortons Theorem:
Theory: Thevenins theorem: Thevenins theorem states that any linear network with terminals could be replaced by a single voltage source Vth in series with a single
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
resistance Rth. The Thevenins equivalent voltage Vth is the open circuit voltage measured at the terminals. The resistance Rth is the driving point resistance of the network at the terminals when all the internal sources are set equal to zero. Nortons theorem: Nortons theorem states that any linear active network with output terminals can be replaced by a single current source in parallel with a single resistance. The Nortons equivalent current source In is the current through a short circuit applied to terminals. The shunt resistance RN is the driving point resistance of the network seen through the points when all the internal sources are set to zero. Procedure fro Thevenins& Nortons Theorems: 1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram. 2. Keep the variac is in minimum output position and supply is taken. 3. Keeping the SPDT switch in position-1, supply is taken. Voltmeter and Ammeter readings are noted. 4. Keeping the SPDT switch is in open position, Voltmeter readings are noted. 5. Keeping the SPDT switch is in position-2, Ammeter readings are noted.
Observations for Thevenins & Nortons theorems: At Vs = S.No I(A) V(V) Test condition Load present Load removed Load is replaced by short
Rth = Voc / Isc = _____________ ohms IL (From thevenins theorem) = Voc / ( Rth + RL) = ____________ Amps. IL( From Nortons theorem) = INRN / ( RN+ RL) = ____________ Amps.
www.jntuworld.com
www.jntuworld.com
10. All connections should be tight. 11. All reading should be taken with out parallax error. 12. Before giving are removing the connections, supply should be switched off. Result: 3. IL from Thevenins Theorem = _______________ (amps) 4. IL from Nortons theorem = ___________(amps)
www.jntuworld.com
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Google Analytics Certification Test QuestionsDocument36 pagesGoogle Analytics Certification Test QuestionsRoberto Delgato100% (1)
- Pee Lab ManualDocument77 pagesPee Lab ManualRajendraTuraka100% (1)
- Manufacturing Egg Trays from Waste PaperDocument17 pagesManufacturing Egg Trays from Waste Paperravibarora86% (7)
- Question BankDocument11 pagesQuestion BankRohini MukunthanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Transformer Parameters from Open Circuit TestDocument7 pagesDetermination of Transformer Parameters from Open Circuit TestSur ShriNo ratings yet
- Circular Tank Radius CalculationDocument25 pagesCircular Tank Radius CalculationQamar AbbasNo ratings yet
- BS 5896 2010Document33 pagesBS 5896 2010shashiresh50% (2)
- Circuit Analysis and Design Manual FinalDocument65 pagesCircuit Analysis and Design Manual Finalصدام حسینNo ratings yet
- 6655 Lab Manual 2Document162 pages6655 Lab Manual 2Brett Hendricks100% (1)
- ET Lab ManualDocument52 pagesET Lab Manualcholleti sriram100% (1)
- Digital Logic Design Lab RecordDocument7 pagesDigital Logic Design Lab RecordBiftu ShibbireNo ratings yet
- Electrical Science Manual 2023Document55 pagesElectrical Science Manual 2023ANSHUL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Experiment ManualDocument17 pagesExperiment ManualKavita BishtNo ratings yet
- III I PE Lab Manual PDFDocument28 pagesIII I PE Lab Manual PDFSwaranjali RawatNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Lab FileDocument44 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Lab File032AkritiNo ratings yet
- NT Lab MannualDocument31 pagesNT Lab MannualsagarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument23 pagesLaboratory ManualAnmol AhsaasNo ratings yet
- EE2155 Electrical Circuits Lab Manual PDFDocument38 pagesEE2155 Electrical Circuits Lab Manual PDFSymmer CulNo ratings yet
- Networl Manual (PTDC)Document28 pagesNetworl Manual (PTDC)sadeeskumar.dNo ratings yet
- Superposition and Norton Theorems PresentationDocument24 pagesSuperposition and Norton Theorems PresentationMahmudul AlamNo ratings yet
- Circuits and NetworksDocument23 pagesCircuits and NetworksDei PehNo ratings yet
- BEEE Lab Manual CSVTUDocument44 pagesBEEE Lab Manual CSVTUMulty TalantedNo ratings yet
- Verifying Electrical Theorems ExperimentDocument37 pagesVerifying Electrical Theorems Experimentakashdeep tickooNo ratings yet
- Exp3 Sem2 Edit 0506Document9 pagesExp3 Sem2 Edit 0506shavin699100% (1)
- EEE Network LabDocument14 pagesEEE Network LabPradeep SinglaNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesDocument18 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesVK DNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesDocument18 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & Drivesshashi kumarNo ratings yet
- Basic DC Circuits - Learn Kirchhoff's Rules for Circuit AnalysisDocument2 pagesBasic DC Circuits - Learn Kirchhoff's Rules for Circuit AnalysisTez HarrietNo ratings yet
- Half-Wave Rectification LabDocument6 pagesHalf-Wave Rectification LabRafeyNo ratings yet
- 6655 Lab Manual PDFDocument160 pages6655 Lab Manual PDFkL10111No ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 3 (C) To Verify Maximum Power Transfer TheoremDocument13 pagesLab Report Experiment 3 (C) To Verify Maximum Power Transfer TheoremArif Zain75% (12)
- Eee ManualDocument53 pagesEee ManualplsmcokNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab ManualDocument62 pagesBee Lab ManualSwetha VanamNo ratings yet
- Learning Element 3Document17 pagesLearning Element 3niel lunaNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits: DC, Ac Power Systems Electrical Machines Drives SystemsDocument36 pagesElectric Circuits: DC, Ac Power Systems Electrical Machines Drives SystemsMatthew 'moka' BlandNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab ManualDocument60 pagesBee Lab Manualravi828No ratings yet
- Electric Machines LaboratoryDocument44 pagesElectric Machines Laboratory11mustafa.mNo ratings yet
- Exp. 5 - Terminal Characteristis and Parallel Operation of Single Phase Transformers.Document7 pagesExp. 5 - Terminal Characteristis and Parallel Operation of Single Phase Transformers.AbhishEk SinghNo ratings yet
- TH TH TH THDocument8 pagesTH TH TH THSrinivasa Reddy Devi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual BTY309 Biomedical Circuits and Networks LaboratoryDocument45 pagesLaboratory Manual BTY309 Biomedical Circuits and Networks LaboratoryRiya KumariNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Lab (Ice) : Experiment No: 3Document4 pagesCircuit Theory Lab (Ice) : Experiment No: 3D V AnshuNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Thevenin's & Norton's Theorem and Maximum Power TransferDocument5 pagesExperiment: Thevenin's & Norton's Theorem and Maximum Power TransferMunir Izkandaryan ZX'zNo ratings yet
- Network TheoremsDocument14 pagesNetwork TheoremsruduitududtNo ratings yet
- PHY CourseworkDocument8 pagesPHY CourseworkLIANG HUI YI MoeNo ratings yet
- Ee602 Circuit AnalysisDocument55 pagesEe602 Circuit AnalysisArryshah DahmiaNo ratings yet
- Network Theory Lab ManualDocument31 pagesNetwork Theory Lab ManualkondraguntajbNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument56 pagesLab ManualNishant AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument37 pagesBasic Electrical EngineeringCharles SandersNo ratings yet
- Experriment 1 009Document7 pagesExperriment 1 009MOHAMMAD FARDEEN SUMAIR 160419735020No ratings yet
- ElectricalCircuitsLab EE0211Document30 pagesElectricalCircuitsLab EE0211jhapte02No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines I29012020Document73 pagesElectrical Machines I29012020fake1542002No ratings yet
- Chapter 4.2Document42 pagesChapter 4.2Muhd RzwanNo ratings yet
- Leybold Práctica3 TrafoMonofásicoDocument8 pagesLeybold Práctica3 TrafoMonofásicoNOGRACIASNo ratings yet
- EE536 ManualDocument67 pagesEE536 Manualciraj123456No ratings yet
- Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: Name of The Experiment: Verification of KVL & Voltage Devider RuleDocument7 pagesBangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: Name of The Experiment: Verification of KVL & Voltage Devider RuleSayeed Mohammed100% (1)
- Work TheoremsDocument45 pagesWork TheoremsSaikat LayekNo ratings yet
- EE LAB ManualDocument48 pagesEE LAB ManualManu anandNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 1: TheoryDocument6 pagesExperiment - 1: TheoryKiran Kumar KandregulaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Lotus Leaf by NanocastingDocument4 pagesArtificial Lotus Leaf by Nanocastinganon_527700070No ratings yet
- Allcargo Corporate BrochureDocument12 pagesAllcargo Corporate BrochureallinonecargologisticsNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic and Microprocessor Design With Interfacing 2nd Edition Hwang Solutions ManualDocument27 pagesDigital Logic and Microprocessor Design With Interfacing 2nd Edition Hwang Solutions Manualdacdonaldnxv1zq100% (27)
- FC Vs FBDocument8 pagesFC Vs FBMiguel SanchesNo ratings yet
- TOR Admin Assistant SC - 4Document1 pageTOR Admin Assistant SC - 4newarakanNo ratings yet
- Performance Estimation of Ofdm-Wimax Network: Vishal Sharma & Navneet KaurDocument8 pagesPerformance Estimation of Ofdm-Wimax Network: Vishal Sharma & Navneet KaurTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- PLCDocument16 pagesPLCMohit Kinger100% (1)
- 6303A HP Flare Drain DrumDocument16 pages6303A HP Flare Drain DrumMohammad MohseniNo ratings yet
- Item No. Specification Requested Offered Specifications 1.1. 1.1 Law and CertificatesDocument23 pagesItem No. Specification Requested Offered Specifications 1.1. 1.1 Law and CertificatesSaša StankovićNo ratings yet
- Siemens 1LE1 PDFDocument308 pagesSiemens 1LE1 PDFharold100% (1)
- Artikel Jurnal - Fundamental Differences of Transition To Industry 4.0 From Previous Industrial RevolutionsDocument9 pagesArtikel Jurnal - Fundamental Differences of Transition To Industry 4.0 From Previous Industrial RevolutionsJohny DoelNo ratings yet
- Amptec Issue 7Document8 pagesAmptec Issue 7Linda Turner-BoothNo ratings yet
- Industrial HygieneDocument31 pagesIndustrial HygieneGautam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Programmability in SPSS 16 & 17, Jon PeckDocument36 pagesProgrammability in SPSS 16 & 17, Jon PeckJasmin MaricNo ratings yet
- 1 Project ManagementDocument14 pages1 Project Managementyaswanth119No ratings yet
- Rc16-17 Etc Sem-IV, May 19Document5 pagesRc16-17 Etc Sem-IV, May 19Prasad KavthakarNo ratings yet
- Intermot Hydraulic Motors IAM+ Series Technical CatalogueDocument81 pagesIntermot Hydraulic Motors IAM+ Series Technical CatalogueeduardoraulNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument11 pagesRefrigerationBroAmirNo ratings yet
- X-Span & Setting ToolsDocument18 pagesX-Span & Setting ToolsDenier RubianoNo ratings yet
- Virginia Transformer - Developments in Traction TransformersDocument10 pagesVirginia Transformer - Developments in Traction TransformersTshepo Sharky SebeNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Week 8Document3 pagesQuarter 1 Week 8Geoffrey Tolentino-UnidaNo ratings yet
- MS 01 182Document5 pagesMS 01 182kicsnerNo ratings yet
- PERFAPPRAISAL Research proposal on performance appraisal practices at National Bank of Pakistan and United Bank LimitedDocument4 pagesPERFAPPRAISAL Research proposal on performance appraisal practices at National Bank of Pakistan and United Bank LimitedNadia KhanNo ratings yet
- V 2172 0020 0031 - Rev - 6 (3458748) PDFDocument262 pagesV 2172 0020 0031 - Rev - 6 (3458748) PDFLG Milton LuisNo ratings yet
- CSE 390 Bash Command ReferenceDocument3 pagesCSE 390 Bash Command Referencesam100% (1)
- Results Part III - Part III-March 2017 - ElectricalDocument3 pagesResults Part III - Part III-March 2017 - ElectricalTharaka MunasingheNo ratings yet