0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views4 pagesLead Acid Accumulator Assignment
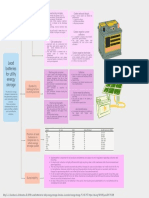
The assignment discusses the factors affecting the life and efficiency of lead-acid accumulators, including cycle life, operating conditions, and the impact of acid concentration and temperature. It also covers trickle charging advantages with plante plates, practical limits of plate separation, and methods to enhance performance. Additionally, it identifies factors causing inefficiency and suggests ways to mitigate these issues.
Uploaded by
Fabiha SattaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views4 pagesLead Acid Accumulator Assignment
The assignment discusses the factors affecting the life and efficiency of lead-acid accumulators, including cycle life, operating conditions, and the impact of acid concentration and temperature. It also covers trickle charging advantages with plante plates, practical limits of plate separation, and methods to enhance performance. Additionally, it identifies factors causing inefficiency and suggests ways to mitigate these issues.
Uploaded by
Fabiha SattaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd