Name: Yanxi Chen
Class: 9-C
Topic: Quadratic Functions
Subject: Mathematics
Teacher: Ms. Osborne
Due Date: 11/3/2025
�1) Definition & General Form
a) General Form of a Quadratic Function:
The general form of a quadratic function is 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐, where a, b, and c are
numbers and a is not zero.
b) What is a Parabola?
A parabola is a set of points that are all equally spaced from a straight line known as the
directrix and a fixed point known as the focus. This implies that the distance to the focus and
the distance to the directrix are equal regardless of where you choose on the curve. The
vertex, which divides the curve into two mirror-image halves, is the centre of the parabola
where it turns.
c) What Shape does a Quadratic Function Graph form?
When you graph a quadratic function, it will always form a parabola which is a U-shaped
curve. The parabola will open either upward (if 𝑎 is positive) or downward (if 𝑎 is negative),
depending on the value of 𝑎 .
2) Key Characteristics of Quadratic Functions
a) What are the Key Characteristics of a Quadratic Function?
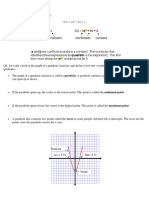
Vertex:
The vertex is the highest or lowest point in a quadratic function. The vertex is expressed as
(ℎ,𝑘) (h,k), where k is the function's lowest or highest point and h is the axis of symmetry.
The vertex is the lowest position if a > 0, and the highest point if a < 0.
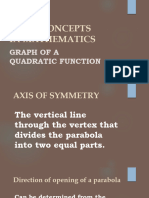
Axis of Symmetry:
The vertical line known as the axis of symmetry, is the line which splits the parabola in half.
−𝑏
Found using the formula 𝑥 = , the line will always pass through the vertex. This indicates
2𝑎
that the parabola's left and right sides are mirror images of one another.
Direction of Opening:
Depending on the value of a in the quadratic function, the parabola's opening direction
changes. The parabola widens upward and forms a U-shape if 𝑎 > 0 and opens downward
if 𝑎 < 0.
x-intercept:
The points where the parabola crosses the x-axis are called the x-intercepts, sometimes
referred to as roots or zeros. In order to find these, the equation 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 = 0 must be
solved. Depending on where the parabola is on the graph, some quadratic functions have two
x-intercepts, some have one, and some have none.
�y-intercept:
The parabola's intersection with the y-axis is known as the y-intercept. When 𝑥 = 0 , this
occurs. We may determine that the y-intercept is always at (0, 𝑐) by changing 𝑥 = 0 in the
quadratic equation.
b) Define the Vertex of a Parabola. How can you find the Vertex from the Quadratic
Equation?
The vertex of a parabola is its highest or lowest point, depending on the direction it opens. It
lies on the axis of symmetry, which divides the parabola into two equal halves. If the
quadratic function is in standard form:
𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐
The x-coordinate of the vertex is given by the formula:
−𝑏
𝑥=
2𝑎
where a and b are coefficients from the quadratic equation.
Once the x-coordinate is found, substitute it back into the equation to find the y-coordinate:
𝑦 = 𝑎(𝑥)2 + 𝑏(𝑥) + 𝑐
Thus, the vertex is the point (𝑥, 𝑦).Example:
Given the quadratic equation 𝑦 = 4𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 + 14 , find the vertex.
x-coordinate:
−(−4) 4 1
𝑥= = =
2(4) 8 2
y-coordinate:
1 2 1
𝑦 = 4 ( ) − 4 ( ) + 14
2 2
𝑦 = 1 − 2 + 14
𝑦 = 13
Vertex: (0.5,13)
c) On a Graph, show the Openings of a Quadratic Graph, Axis of Symmetry, Turning Point,
Roots, and y-intercept.
�3) Identifying Key Properties of Quadratic Functions
Given the quadratic function 𝑓(𝑥) = 2𝑥 2 + 7𝑥 + 3:
a) Axis of Symmetry:
−𝑏
𝑥=
2𝑎
−7
𝑥=
2(2)
−7
𝑥=
4
𝑥 = −1.75
b) Direction of Opening:
The parabola will be opening upwards because the coefficient of 𝑎 = 2 is positive.
c) y-intercept:
𝑓(0) = 2(0)2 + 7(0) + 3
=3
y-intercept: (0,3)
d) x-intercepts:
2𝑥 2 + 7𝑥 + 3 = 0
−7 ± √72 − 4(2)(3)
𝑥=
2(2)
−7 ± √49 − 24
𝑥=
4
−7 ± √25
𝑥=
4
−7 ± 5
𝑥 =
4
−7 + 5
𝑥 =
4
−2 1
𝑥 = =−
4 2
−7 − 5
𝑥 =
4
−12
𝑥 =
4
𝑥 = −3
x-intercepts: (−0.5,0), (−3,0)
�References
Cuemath. (n.d.). Quadratic Function - Formulas, Definition, Graphs, Examples. Cuemath.
https://www.cuemath.com/calculus/quadratic-functions/
5.2: Quadratic Functions. (2019, January 8). Mathematics LibreTexts.
https://math.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Algebra/College_Algebra_1e_(OpenStax)/05%3A_P
olynomial_and_Rational_Functions/502%3A_Quadratic_Functions
Quadratic Functions. (2024). Uncw.edu.
https://dl.uncw.edu/digilib/Mathematics/Algebra/mat111hb/PandR/quadratic/quadratic.html
Quadratic graphs | Lesson (article). (n.d.). Khan Academy.
https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/v2-sat-math/x0fcc98a58ba3bea7:advanced-math-
easier/x0fcc98a58ba3bea7:quadratic-graphs-easier/a/v2-sat-lesson-quadratic-graphs