0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views3 pagesOptical Instruments
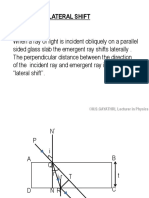
The document discusses various optical instruments, including simple and compound microscopes, and telescopes, detailing their image characteristics and magnification types. It also covers the principles of refraction through prisms, including conditions for emergence and maximum deviation. Key concepts include the relationship between aperture size and image brightness, as well as the behavior of light as it passes through different prism angles.
Uploaded by
Yogeswara Rao AraveetiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views3 pagesOptical Instruments
The document discusses various optical instruments, including simple and compound microscopes, and telescopes, detailing their image characteristics and magnification types. It also covers the principles of refraction through prisms, including conditions for emergence and maximum deviation. Key concepts include the relationship between aperture size and image brightness, as well as the behavior of light as it passes through different prism angles.
Uploaded by
Yogeswara Rao AraveetiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd