Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Robotics 2mark
Uploaded by
isirajudeen17Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Robotics 2mark
Uploaded by
isirajudeen17Copyright:
Available Formats
SELVAM COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY, NAMAKKAL DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
SUBJECT: INDUSTRAIL ROBOTICS SEMESTER / YEAR : VII / IV
Prepared by, I.Sirajudeen, Asst. Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering
Checked & Verified by, S. Malik Raj, Professor & Head of Dept, Department of Mechanical Engineering
Unit-I: 1. Name the FOUR basic robot configurations. a) Cartesian coordinate system b) Cylindrical coordinate system c) Polar or spherical coordinate system d) Revolute coordinate system 2. List out the types of joint Notation. (a) Linear joint, (b) Rotational joint, (c) Twisting joint, (d) Revolving joint. 3. What is meant by a work envelope? The work envelope is described by the surface of the work space. It depends upon the number of types of joints, physical types of joints and links and the range of various joints. 4. Sketch a robot and name its parts. 1. Manipulator (Robot arm) 2. End effector 3. Controller 4. Gripper 5. Actuator 5. What is meant by workspace? The space in which the end point of the robot arm is capable of operating is called as workspace in other words, reach ability of robot arm is known as workspace. 6. What is meant by degeneracy? Some robots, though, do have a certain joint arrangement in their final orientation joints that can lead to redundancy for certain orientations. Most industrial robots have 6 or less joints, thus, redundancy is not inherent to their design. 7. List the various types of robot drive system for industrial robots 1. Electric drive: (a) DC motor; (b) Servomotor; (c) Stepper motor 2. Pneumatic drive 3. Hydraulic drive 8. Sketch and indicate the type of any rotating joints used in robots. (or) Sketch a twisting joint. Rotational (R):
9. What are the types of hydraulic actuators used in robotics? (i) Piston cylinder, (ii) Swing motor, (iii) Hydraulic motor
10. What is meant by robot anatomy? The robot anatomy is the study of structure of robot that is physical construction of the manipulator's structure. The mechanical structure of manipulator that consists of rigid bodies (links) connected by means of joints, is segmented into arm that ensures mobility and reachability, a wrist that confers orientation, and an end effectors that performs the required task 11. What are the three degrees of freedom associated with the arm and body motion? Three degrees of freedom associated with the arm and body motion are: Right (or) Left movement (X-axis motion) In and out movement (Y -axis motion) Vertical movement (Z-axis motion)
12. Define the term work envelope. Work envelop is defined as the envelope (or) space within which the robot can manipulate the end of the wrist. A robot's work envelope is the range of movement 13. Give some application of robots in industries. (a) Material Handling Application (i) Material transfer application (ii) Machine loading/unloading application. (b) Process Application (i) Welding (ii) Painting (iii) Assembly (iv) Machining (v) Inspection 14. How do you specify a robot? (i) Speed; (ii) Actuator (iii) Payload; (iv) Repeatability (v) Accuracy; (vi) Reliability (vii) Manipulator; (viii) End effector ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Unit-II: 1. State any two techniques used for object recognition. a) Template matching b) Structural Technique
2. Write about Hall Effect sensors. When a beam of charged particles passes through a magnetic field forces act on the particles and the beam is deflected from the straight line path a current flowing in a conductor is like a beam of moving charges and thus can be defined by magnetic field
3. Classify the robots according to the drive system. 1. Pneumatic drive 2. Hydraulic drive 3. Electric drive (a)DC Motor (b) Servo motor (c) Stepper motor 4. List any two important advantages and disadvantages of a pneumatic gripper. Advantages of pneumatic gripper: 1. Its light weight design. 2. It is possible to distribute the pressure uniformly the entire area. 3. Control is simple 4. Pick up time is very fast. Disadvantages: 1. It is not suitable for heavy loads. 2. Sometime is required to build the pressure. 5. What is inverse Kinematics? It is a scheme to determine joint angles of robot by knowing its position in the world coordinate system. Pjoint = (1, 2, 3) 6. Name any four proximity sensors used in robotics Sensor, which senses the presence or absence of the object without having physical contact between the objects I) Inductive Sensor 2) Capacitive Sensor 3) Ultrasonic Sensor 4) Magnetic Sensor 7. Sketch the screw-actuated mechanical gripper.
8. What are the limitations of adhesive grippers? (i) Adhesive substances losses his tackiness on repeated usage. (ii) Reliability is diminished with successive operations 9. Distinguish between direct and inverse kinematics. (i) Reverse kinematics: It is a scheme to determine joint angles of a robot by knowing its Position in the world coordinate system. PJOINT = (1, 2, 3) (ii) Direct kinematics: It is a scheme to determine the position of the robot in the world coordinate system by knowing the joint angles and the link parameters of the robot. PWORLD = ( x, y, z )
10. Differentiate between touch and force sensors. Touch sensor: It senses the presence or absence of the object by having physical contact between the objects. Force sensors: Force sensors are used primarily for measuring the reaction forces developed at the interface between mechanical assemblies 11. List the types of drives used in robots. Electric drives Hydraulic drives Pneumatic drives 12. What is a RCC device? For what purpose is it used in a robot? RCC device means Remote. Center Compliance devices. Uses: (i) RCC device are commonly used in automated assembly applications to provide Compliance for misalignment during assembly. (ii) The compensator is a .compliance device that enhances the flexibility and reliability of a robot 13. What is a mechanical gripper? A mechanical gripper is an end effector that uses mechanical finger actuated by mechanism to grasp an object. Mechanical grippers are used to transfer parts from one location to another or to assemble parts. 14. What is the properties 0f stepper motor? Stator wiring (number of coils and wire loads). Number of steps in a complete rotation. Operating voltage and current. Amount of force generated (torque). Maximum rotation speed (steps per second). 15. State the advantage and limitation of hydraulic drive. Advantage: 1. Robust 2. Self lubrication 3. It can also provide precise control at low speeds. 4. High efficiency and high power to size ratio. 5. Hydraulic robots are more capable of withstanding shock loads. Disadvantage: 1. Expensive 2. High maintenance 3. Not energy efficient 4. Noisy 5. Not suited for clean air environments 16. Write the basic principle of servo motor. A servomotor is used within position control (or) speed control feedback control system. An electrostatic motor is based on the attraction and repulsion of electrical charge. 17. Give some examples of robot end effector. 1. Gripper 2. Tools 3. Welding equipment 4. End of arm tooling
18. What are the types of grippers?' 1. Mechanical finger grippers. 2. Pneumatic grippers. 3. Hydraulic grippers. 4. Collect gripper. 5. Magnetic gripper. 6. Vacuum gripper. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Unit-III: 1. Define a tactile sensor and list the types. Tactile sensor is device that indicates the contact between themselves and some other solid objects. 1. Digital (Touch) Sensor 2. Analogue (Force) Sensor 2. List the two basic types of robot programming method. a. Lead through methods b. Textual robot languages c. Mechanical Programming 3. State the working principle of a touch sensor. Touch sensors in sensors, which senses the presence or absence of the object by having physical contact between the objects. When the button is pressed, an electrical circuit is closed inside the sensors. This lets electricity flow. When the button is released, the circuit is broken and no electricity flows. Touch sensors send a signal when physical contact is made. 4. What is the function of a frame grabber? A frame grabber is an electronic device that captures individual, digital still frames from an analog video signal or a digital video stream. It is hardware device used to capture and store the digital image. 5. What are the limitations of hydraulic drive systems? 1) Expensive 2) High maintenance 3) Not energy efficient 4) Noisy 5) Not suited for clean-air environments. 6. What is the purpose of thresholding in analysis? Thresholding is a binary conversion technique in which each pixel is converted into a binary value either black or white.
7. Mention use of machine vision system. (i) This can be used to replace, machining for applications like welding, machining to maintain relationship between tool and work. (ii) Machine vision systems are used for printed circuit board. (iii) This is for the recognition of object from its image. (iv) Achieve 100% accuracy.
8. Enumerate the difference between open loop and closed loop control system Open loop control system It is being relatively simple Low cost Good reliability The disadvantage is that they are often inaccurate since there are no correction for error Closed loop control system More complex More cost Greater chance of breakdowns as a consequence of the greater number of components Relatively accurate in matching the actual to the required values
9. What is meant by template matching? Templates of the parts to be recognized are stored in the vision system memory. The images recorded by the vision camera are compared with the templates stored in memory to determine if a matching part is present. 10. What is a teach pendant? The teach pendant is usually a small handheld control box with combinations of toggle switches, dials and buttons to regulate the robot's physical movement's and program capabilities 11.Classify the position sensors. Main types of position sensors are: Incremental Absolute Some other devices which are used as position sensors. Resistive position sensors. Linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) Encoders. Potentiometer. Resolver 12. Brief on the working of inductive type proximity sensor. Inductive proximity sensors operate under the electrical principle of inductance. Inductance is the phenomenon where fluctuating current, which by definition has a magnetic component induces an electromotive force (emf) is a target object. To amplify a devices inductance effect, a sensor manufacturer twists wire into a tight coil and runs a current through it. 13. What is triangulation? Triangulation is a process by which the location of radio transmitter can be determined by measuring either the radial distance, or the direction of the received signal from two (or) three different points. Triangulation is sometimes used in cellular communication to pin point the geographic position of a user. 14. What is smoothing in vision system? Smoothing in vision system is often used to reduce noise within an image (or) to produce a less pixelated image. Most smoothing methods are based on low pass filter
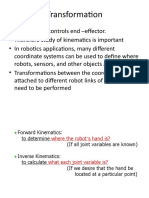
15. What are the desirable features of sensor? 1. Cost 2. Ease of operation 3. Operating range 4. Accuracy 5. Precision 6. Reliability' 7. Speed of response 8. Calibration 16. List the different types of tactile sensor. Digital (Touch) Sensor Analogue (Force) Sensor 17. What are the applications of Machine Vision System? Inspection Identification Visual serving and navigation 18. What are the various techniques in image processing and analysis? Image data reduction Segmentation Feature extraction Object recognition ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Unit-IV: 1. What are Actuators? Actuators are the devices used for converting hydraulic energy (or) electrical energy into mechanical energy. In other words, actuators perform a function just opposite to that of the pumps. The pressurized hydraulic fluid delivered by the hydraulic pump is supplied to the actuators, which converts the energy of the fluid into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is used to get the work done. The hydraulic actuators produce linear, rotary, or oscillating motion. 2. What is transformation? Transformations of frames introduced to make modeling the relocation of objects easier.An object is described with respect to a frame located in the object, and this frame is relocated with a transformation. The transformation is the result of a sequence of rotations and translations, which are recorded with a transformation equation 3. What is meant by a teach pendent? The teach pendent is usually a small hand held control box with combination of toggle switches, dials and buttons to regulate the robot's physical movements and program capabilities. 4. Explain any two commands associated with programming of an end effector. 1. OPEN 2. CLOSE. 3. OPEN I 4. CLOSE I OPEN I: These instructions cause the pneumatic control valves to receive a signal to open the gripper immediately. CLOSE I: These instruction cause the pneumatic control valves to receive a signal to close the gripper.
5. Define the term 'feature extraction Transforming the input data into the set of feature is called feature extraction. A feature area, diameter, perimeter, is a single parameter that permits ease of comparison and identification. 6. State any two techniques used for object recognition. a) Template matching b) Structural Technique 7. What the benefits of this off line programming? Reduced down time for programming. Programming tools make programming easier. Enables concurrent engineering and reduces product lead time. Assists cell design and allows process optimization. 8. Explain the reasons for defining points in a program. To define a working position for the end-effector To avoid obstacles 9. What is A GV? Automated guided vehicle (AGV) is an independently operated self-propelled vehicle guided along defined pathways in the floor. It is normally powered with batteries. It is mainly used for handling material from one place to other place. 10. List out different types of image compression technique. Discrete image transforms in image data compression Hierarchical and progressive compression techniques Comparison of compression methods 11. Perform the following transformation on point (25, 10, and 20): Trans (8, 5, and 0). Solution: Case 1:
12. What is the command used to execute the speed of the robot in VAL programming? Speed command is used to define the velocity with which the robot's arm is moved. SPEED 90: Indicates that the robot should operate at 90% of normal speed during program execution. SPEED 50 Ips: Which indicates the speed of the end effector during program execution would be 50 in/sec.
13 .Determine the translated vector for the given vector = v = 25 i + 10 j + 20 k, perform a translation by a distance of 8 units in "x" direction, 5 units in 'y" direction and 0 units in "z" direction. Given that: v = 25 i + 10 j+ 20 k; x = 25, Y = 10, and z = 20 x direction (a) = 8 units; y direction (b) = 5 units; Solution: The translation transformation
z direction (c) = 0 units
14. Write the meaning of the following command: DMOVE (1, 10) DMOVE (< 4, 5, 6> < 30, - 45, 90>) Solution: DMOVE is the motion command for an Incremental (or) Delta.move. In parenthesis the joint and the distance of incremental move are specified. Example 1: DMOVE (1, 10) Ist IInd Ist position indicates the joint number. IInd position indicates the distance of the incremental moves. Joint 1 moves by 10 inch. Example 2: DMOVE (< 4, 5, 6> < 30, - 45, 90>) The motion commands an incremental move of axes 4, 5, 6 and by 30, - 45 and 90 respectively. 15. What is reverse kinematics? It is a scheme to determine joint angles of robot by knowing its position; in the world coordinate system.
16. Define degrees of freedom It is defined as one of the variables required to define the motion of a body in space. Each joint in a robotic system gives the robot one degrees of freedom. 17. Show the relation usd in forward & reverse transformation of 2degrees of freedom manipulator
18. What is teach pendant? The teach pendant is usually a small handheld control box with combination of toggle switches, dials and buttons to regulate the robot's physical movements and program capabilities. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Unit-V: 1. What is continuous path programming? It is the types of programming were the motion cycle involves smooth complex Curvilinear movements of robot arm. 2. What is teach pendant? The teach pendant is usually a small handheld control box with combinations of toggle switches, dials and buttons to regulate the robot's physical movements and program capabilities. 3.List any two important considerations for robot safety. Environmental condition. Location and installation requirement. , Human errors. Mode of operation 4. How do you calculate the robot economics by return of investment method?
5. What is the purpose of structured lighting? The intersection of the sheet with objects in the work space yields a light stripe which is viewed through 'a television camera displaced a distance from the light source. The stripe pattern is easily analyzed by a computer to obtain range information. 6. What are the different methods of economic analysis? 1) Payback method 2) Equivalent uniform annual cost (EUAC) method 3) Return on investment (ROI) method 7. What are the general characteristics that make potential robot application technically practical and economically feasible? Hazardous or uncomfortable working conditions Repetitive operations Difficult handling jobs Multicast operation 8. What are the steps to be followed by the company in order to implement robot programs in its operations? Initial familiarization with the technology. Plant survey to identify potential applications. Selection of the application. Selection of the robot. Detailed economic analysis and capital authorization. Planning and engineering the installation. Installation.
9. What is meant by image analysis? Image analysis ids the collection of processes in which a captured image that is prepared by image processing is analyzed in order to extract information about the image and to identify objects or facts about the object or its environment.
10. Give two applications of robot in machining. Drilling; Grinding; Reaming; Tapping Deburring 11. Calculate the payback period for a robot project with the following data: Net annual cash flow Rs. 45,000, Investment cost Rs. 1, 00,000 Given: Net annual cash flow = Rs. 45,000; To find: Pay back period Solution: Investment cost Rs. 1,00,000
12. Which data are required to perform economic analysis of a robot project? Expected rate of return. Payout and investment's expected life. Risk is not making investment. Cost and risk incase of failure. Opportunity cost that is the return from alternative investment. 13. What are the three levels of safely sensor systems in robotics defined by National Bureau of Standards? The National Bureau of standards defines three levels of safely sensor system in robotics. Level 1 - Perimeter penetration detection Level 2 - Intruder detection inside the work cell Level 3 Intruder detection in the immediate vicinity of the robot. 14. Total investment cost is estimated as Rs. 5 lakhs for a robot project. The total operating costs are expected to be Rs. 20,000 per year. The expected revenues from the robot installation are Rs. 1,00,000 annually. It is expected that the robot project will have a service life of 5 years. Determine the payback period that is expected of the investment. Given that: Total investment cost estimated = Rs.5,00,000 Total operating cost/year = Rs.20,000 The expected revenue and from = Rs.1,00,000 the robot installation Expect service life n = 5 years
To find: Pay back period Solution:
15. List the typical MOTION command. 1. MOVE 2. APPRO 3. DEPART 4. DMOVE 16. List out types of A GV vehicles. 1. To wing vehicles 2. Unit load vehicles 3. Pallet truck vehicles 4. Fork truck vehicles 5. Light load vehicles 6. Assembly line vehicles 17. What are types of robots commonly used for machine loading and unloading operation? 1. Servo control robot (point to point) 2. Non-servo robot (pick and place robot) 18. Write two aspects of the safety issue in robotics. 1. Redundancy 2. Back up system -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You might also like
- Books Download: Screenshots of Web Pages Goo - GL QR Codes Qclock Google MapDocument6 pagesBooks Download: Screenshots of Web Pages Goo - GL QR Codes Qclock Google Mapisirajudeen17No ratings yet
- Books Download: Screenshots of Web Pages Goo - GL QR Codes Qclock Google MapDocument6 pagesBooks Download: Screenshots of Web Pages Goo - GL QR Codes Qclock Google Mapisirajudeen17No ratings yet
- RBE2 Vs RBE3 Rigid Finite ElementDocument20 pagesRBE2 Vs RBE3 Rigid Finite ElementAnonymous umabEI6No ratings yet
- EE2023-Robotics and Automation PDFDocument13 pagesEE2023-Robotics and Automation PDFveerapandianNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Analysis of Structures PDFDocument755 pagesDynamic Analysis of Structures PDFJardeyFrancisVallejo0% (1)
- Chapter 7 Robot and Other Motion Control SystemsDocument15 pagesChapter 7 Robot and Other Motion Control SystemsMohith SNo ratings yet
- Robotics Lab Manuals Final PDFDocument38 pagesRobotics Lab Manuals Final PDFravihbti100% (1)
- Robotics Unit-5 Question BankDocument6 pagesRobotics Unit-5 Question BankveerapandianNo ratings yet
- OIE751-Robotics Question Bank PDFDocument12 pagesOIE751-Robotics Question Bank PDFmaragatharaj100% (1)
- Robotics, Industrial Robotics, Question BankDocument13 pagesRobotics, Industrial Robotics, Question Banksiraj100% (5)
- Robotics and Automations Material - M - Vinoth KumarDocument63 pagesRobotics and Automations Material - M - Vinoth Kumartumati venkata vinayNo ratings yet
- Problemas de Dinamica de MaquinasDocument60 pagesProblemas de Dinamica de MaquinasUlises Castillo FloresNo ratings yet
- (MT8701)Document2 pages(MT8701)Johnson Paul100% (2)
- Kinematic Fundamentals Chapter-2Document58 pagesKinematic Fundamentals Chapter-2Anand KesarkarNo ratings yet
- STS121 M3L3 - Automation and RoboticsDocument8 pagesSTS121 M3L3 - Automation and RoboticsJusteene SaysonNo ratings yet
- Robotics NotesDocument22 pagesRobotics NotesUpendra020% (1)
- Robotics Part3Document87 pagesRobotics Part3Dheeraj RajNo ratings yet
- RObotics and Automation Question Bank AnDocument19 pagesRObotics and Automation Question Bank AnSharmila83No ratings yet
- rOBOTICS NOTESDocument14 pagesrOBOTICS NOTESdsathiya100% (4)
- Me 1008 - RoboticsDocument10 pagesMe 1008 - RoboticsmaverickhydronNo ratings yet
- Sudharsan Engineering College: UNIT I Fundamentals of RobotsDocument7 pagesSudharsan Engineering College: UNIT I Fundamentals of RobotsmetkarthikNo ratings yet
- 05 JacobianDocument82 pages05 JacobianTonny ThanhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: 6 HRS: Introduction: Basic Concepts, Laws of Robotics, RobotDocument69 pagesUnit 1: 6 HRS: Introduction: Basic Concepts, Laws of Robotics, Robotvithal100% (1)
- Industrial Robotics AssignmentDocument3 pagesIndustrial Robotics Assignmentpikaboo1No ratings yet
- Question Bank RoboticsDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank RoboticslakshmigsrNo ratings yet
- 056 - ME8099, ME6010 Robotics - Question BankDocument6 pages056 - ME8099, ME6010 Robotics - Question BanksathishskymechNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument5 pagesMCQprabhaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Stress Analysis PaperDocument2 pagesExperimental Stress Analysis PaperAbdul FattahNo ratings yet
- IC6003-Principles of RoboticsDocument15 pagesIC6003-Principles of Roboticsrajemtech100% (1)
- Robotics Unit-3 2-MarksDocument17 pagesRobotics Unit-3 2-Marksveerapandian100% (1)
- Robotics, Laboratory ManualDocument26 pagesRobotics, Laboratory ManualManu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 (Trajectory Planning)Document24 pagesChapter 5 (Trajectory Planning)Saurabh ThakurNo ratings yet
- rOBOTICS Unit-2,3Document2 pagesrOBOTICS Unit-2,3dsathiyaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 1st UnitDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank 1st UnitAlapati RajasekharNo ratings yet
- Robotics ProperDocument182 pagesRobotics PropermacxNo ratings yet
- VAL ProgrammingDocument1 pageVAL ProgrammingabhijithNo ratings yet
- 1406 Advanced Kinematics and Dynamics of MachineryDocument13 pages1406 Advanced Kinematics and Dynamics of MachineryChiranjeev JainNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii PDFDocument17 pagesUnit Ii PDFManojKumar MNo ratings yet
- Peak-And Average-Power Reduction in Check-Based BIST by Using Bit-Swapping LFSR and Check-Chain OrderingDocument7 pagesPeak-And Average-Power Reduction in Check-Based BIST by Using Bit-Swapping LFSR and Check-Chain OrderingInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- ROBOTICSQUESTION BANK Unit V, Vi, Vii, Viii by Mahendra Babu Mekala, PBRVITS, KavaliDocument10 pagesROBOTICSQUESTION BANK Unit V, Vi, Vii, Viii by Mahendra Babu Mekala, PBRVITS, KavaliMahendra Babu Mekala100% (2)
- Sathyabama Question PaperDocument3 pagesSathyabama Question PaperamiestudentNo ratings yet
- CD9211 Computer Applications in Design Jan-10 PDFDocument3 pagesCD9211 Computer Applications in Design Jan-10 PDFRajesh KannanNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.harikirthikaNo ratings yet
- Robot Actuators & Feed Back ComponentsDocument25 pagesRobot Actuators & Feed Back ComponentsANONYMOUS PDFSNo ratings yet
- ME 2028 ROBOTICS-Questionbank Unit1&2Document2 pagesME 2028 ROBOTICS-Questionbank Unit1&2Karthick RamNo ratings yet
- Lec02 ManipulatorsDocument7 pagesLec02 ManipulatorsMohamad YazidNo ratings yet
- ROBOTICS Part4Document94 pagesROBOTICS Part4Sandeep GogadiNo ratings yet
- Robo VivaDocument3 pagesRobo VivaRAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Inverse Kinematic Control of A Prosthetic ArmDocument26 pagesInverse Kinematic Control of A Prosthetic Armodsnet100% (1)
- Robotics Question BankDocument1 pageRobotics Question Bankankieta10No ratings yet
- EC368 Robotics MODEL QUESTION PAPER WITH DETAILED ANSWER KEYDocument21 pagesEC368 Robotics MODEL QUESTION PAPER WITH DETAILED ANSWER KEYsavitha100% (2)
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsNel Sweetie0% (1)
- Lec4 Robot ClassificationDocument24 pagesLec4 Robot ClassificationMarghel Rañigo BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Me 2028 Robotics With QBDocument133 pagesMe 2028 Robotics With QBDharmendra Kumar0% (1)
- KOM Question BankDocument10 pagesKOM Question Banknsubbu_mitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SolutionDocument4 pagesChapter 2 SolutionEngr ShabirNo ratings yet
- 06 Question Bank MV 2018 Unit V Vibration Measurement PDFDocument1 page06 Question Bank MV 2018 Unit V Vibration Measurement PDFNABIL HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Agni College of Technology: Office of Examcell Model ExamDocument3 pagesAgni College of Technology: Office of Examcell Model ExamohmshankarNo ratings yet
- Principles of RoboticsDocument13 pagesPrinciples of RoboticsMahendran MahiNo ratings yet
- Part A Ans Key 1,2,4Document3 pagesPart A Ans Key 1,2,4VenkadeshNo ratings yet
- IV Year 2 Marks 16 Marks MechDocument108 pagesIV Year 2 Marks 16 Marks Mechjagadeeshwar vasudevanNo ratings yet
- Robotics - 2 MarksDocument10 pagesRobotics - 2 MarksVijayNo ratings yet
- Robotics UNIT-I Two Marks With AnswersDocument3 pagesRobotics UNIT-I Two Marks With AnswersAnonymous ZB6qyhD6No ratings yet
- Introduction To Robotics 1 2 Marks Questions & AnswersDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Robotics 1 2 Marks Questions & AnswersSeshaiah TurakaNo ratings yet
- Robotics - Automation-Question BankDocument10 pagesRobotics - Automation-Question BankMansi PatelNo ratings yet
- 2028 RoboticsDocument13 pages2028 Roboticsrgopi_83No ratings yet
- PDF 1Document427 pagesPDF 1isirajudeen17No ratings yet
- Mini Project CarbonDocument44 pagesMini Project Carbonisirajudeen17No ratings yet
- Nano Coating For Cutting ToolDocument15 pagesNano Coating For Cutting Toolisirajudeen17No ratings yet
- Nano Coating For Cutting ToolDocument5 pagesNano Coating For Cutting Toolisirajudeen17No ratings yet
- Boron Nano TubeDocument5 pagesBoron Nano Tubeisirajudeen17100% (2)
- Nano Coating For Cutting ToolDocument26 pagesNano Coating For Cutting Toolisirajudeen17100% (1)
- Boron CarbonDocument4 pagesBoron Carbonisirajudeen17100% (2)
- DDFFFDocument4 pagesDDFFFAnonymous 2Dz4Kq9M7No ratings yet
- Delta Robots For High Speed ManipulationDocument11 pagesDelta Robots For High Speed Manipulationakti gonzoNo ratings yet
- DYNAMIC MODELLING AND CONTROL OF A 3-DOF PLANAR PARALLEL ROBOTIC (XYthetaZ MOTION) PLATFORMDocument10 pagesDYNAMIC MODELLING AND CONTROL OF A 3-DOF PLANAR PARALLEL ROBOTIC (XYthetaZ MOTION) PLATFORMVinoth VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Module 5, Week 5, CE-301, Dr. Bashir AlamDocument51 pagesModule 5, Week 5, CE-301, Dr. Bashir AlamMohd IdreesNo ratings yet
- New FeatDocument100 pagesNew FeatΈνκινουαν Κόγκ ΑδάμουNo ratings yet
- Robotics ch5Document39 pagesRobotics ch5Waseem AbbasNo ratings yet
- Truss Analysis OutputDocument11 pagesTruss Analysis OutputMary Joy AzonNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Analysis of Stanford ArmDocument31 pagesKinematic Analysis of Stanford ArmabhishekNo ratings yet
- Gandarias 2020Document8 pagesGandarias 2020duonglacbkNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 Introduction of Machines and Mechanisms: TheoryDocument23 pagesAssignment - 1 Introduction of Machines and Mechanisms: TheoryAman AmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture PDF IIT BombayDocument593 pagesLecture PDF IIT BombayKhan SalimNo ratings yet
- Park LynchDocument542 pagesPark LynchLe Dinh Phong0% (1)
- 12113-STAADPro V8i Verification ManualDocument168 pages12113-STAADPro V8i Verification ManualEugene AfableNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Robust Control of Quadruped RobotDocument5 pagesModeling and Robust Control of Quadruped RobotMer FroNo ratings yet
- Plantwide ControlDocument72 pagesPlantwide ControlAtaíde NetoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Robotics LabDocument35 pagesLaboratory Manual: Robotics LabTeja's SecondaryNo ratings yet
- Degrees of Freedom Analysis For Process ControlDocument6 pagesDegrees of Freedom Analysis For Process Controlal-hadad100% (1)
- Flight MechanicsDocument536 pagesFlight MechanicsArpit Dodia100% (2)
- Analysis of Structure and Kinematics of Four-Bar Crank-Rocker Walking MechanismDocument14 pagesAnalysis of Structure and Kinematics of Four-Bar Crank-Rocker Walking MechanismVitaliyNo ratings yet
- MCE 312 Lecture Note (Module 2)Document29 pagesMCE 312 Lecture Note (Module 2)jagpreetNo ratings yet
- Tensegrity Literature StudyDocument62 pagesTensegrity Literature StudyLeonid BlyumNo ratings yet
- ETABS Joint RestraintsDocument2 pagesETABS Joint RestraintsBunkun15100% (3)
- Robotics 7Document17 pagesRobotics 7nadiaNo ratings yet
- The MathWorksDocument9 pagesThe MathWorksEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- The Analysis of R-S-S-R Spatial Four-Bar MechanismDocument56 pagesThe Analysis of R-S-S-R Spatial Four-Bar MechanismBenny SavioNo ratings yet