Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photovoltaics
Photovoltaics
Uploaded by
Naresh ChowdaryCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Photovoltaics
Photovoltaics
Uploaded by
Naresh ChowdaryCopyright:
Available Formats
By V.
NARESH KUMAR
Photovoltaic's are best known as a method for generating electric power by using solar cells to convert energy from the sun into electricity The photovoltaic effect refers to photons of light knocking electrons into a higher state of energy to create electricity The term photovoltaic denotes the unbiased operating mode of a photodiode in which current through the device is entirely due to transduced light energy
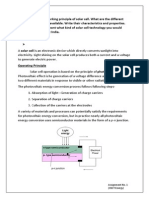
Photovoltaic system
Typical output of a module (~30 cells) is 15 V, with 1.5 A current
Copper Indium Diselinide CIS with band gap 1eV, high absorption coefficient 105cm-1 High efficiency levels PROS 18% laboratory efficiency >11% module efficiency CONS Immature manufacturing process Slow vacuum process
Solar cells produce direct current electricity from light, which can be used to power equipment or to recharge a battery. The first practical application of photovoltaic's was to power orbiting satellites and other spacecraft, but today majority of photovoltaic modules are used for grid connected power generation
Silicon deposited in a continuous on a base material such as glass, metal or polymers Thin-film crystalline solar cell consists of layers about 10m thick compared with 200300m layers for crystalline silicon cells
PROS Low cost substrate and fabrication process CONS Not very stable
Power stations In buildings In transport Standalone devices Rural electrification Solar roadways
You might also like
- Solar Cell: (Photovoltaics)Document37 pagesSolar Cell: (Photovoltaics)Muhammad FauzanNo ratings yet
- SolarDocument57 pagesSolarNag Y50% (2)
- Photovoltaic Effect: Solar CellDocument9 pagesPhotovoltaic Effect: Solar CellAbdullah MomtazNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Technologies Unit 2 LightingDocument111 pagesSolar Energy Technologies Unit 2 LightingTharun RagavNo ratings yet
- Abstract of Solar CellDocument7 pagesAbstract of Solar CellnuraleeeNo ratings yet
- What Is A Photovoltaic CellDocument13 pagesWhat Is A Photovoltaic CellZakaria SalemNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic (PV) : and Copper Indium Selenide/sulfideDocument6 pagesPhotovoltaic (PV) : and Copper Indium Selenide/sulfidetroy_asubNo ratings yet
- Solar Panel: Solar PV Modules Mounted On A RooftopDocument17 pagesSolar Panel: Solar PV Modules Mounted On A RooftopMaria Sweetlin DNo ratings yet
- Solar Panel - WikipediaDocument77 pagesSolar Panel - WikipediaAnilNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell - PPTDocument33 pagesSolar Cell - PPTThomas Wayne100% (3)
- Solar + Wind EnergyDocument232 pagesSolar + Wind EnergyJames BondNo ratings yet
- Xid-7772938 2Document26 pagesXid-7772938 2kefeinzelNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument54 pagesLectureMO 2004No ratings yet
- Solar PVDocument84 pagesSolar PVNaveena ShreeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document58 pagesChapter 3digiy40095No ratings yet
- Ec ProjectDocument13 pagesEc ProjectSurya KotamrajaNo ratings yet
- Supervisor: Dr. Shah Alam Mentor: Dr.M.J.Siddiqui Presented By: Surbhi AgarwalDocument27 pagesSupervisor: Dr. Shah Alam Mentor: Dr.M.J.Siddiqui Presented By: Surbhi AgarwalMr. K.S. Raghul Asst Prof MECHNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell: (Photovoltaics)Document37 pagesSolar Cell: (Photovoltaics)Akshay PabbathiNo ratings yet
- Supervisor: Dr. Shah Alam Mentor: Dr.M.J.Siddiqui Presented By: Surbhi AgarwalDocument27 pagesSupervisor: Dr. Shah Alam Mentor: Dr.M.J.Siddiqui Presented By: Surbhi AgarwalMr. K.S. Raghul Asst Prof MECHNo ratings yet
- PV PresentationDocument21 pagesPV Presentationمحمد الرشدانNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Introduction To Roof Top Solar SystemDocument47 pagesChapter - 1 Introduction To Roof Top Solar Systemjonnalagadda harithaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals and Application of Solar PhotovoltaicsDocument24 pagesFundamentals and Application of Solar PhotovoltaicsEmmanuel OgoloNo ratings yet
- Ee 147Document3 pagesEe 147Menchie LabadanNo ratings yet
- Solar Panel: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument18 pagesSolar Panel: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchEr Dinesh TambeNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 IntroductionDocument24 pagesChapter-1 IntroductionNaveenNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Plant: Government Engineering College BharatpurDocument29 pagesSolar Power Plant: Government Engineering College BharatpurHinduja KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- PV Technology - LatestDocument21 pagesPV Technology - LatestZaferullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Solar CellDocument33 pagesSolar CellSumit BansalNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 (CBCT Energy)Document8 pagesAssignment No. 1 (CBCT Energy)Mallika P. ShivamNo ratings yet
- Effect of Shading On Photovoltaic Cell: Ekpenyong, E.E and Anyasi, F.IDocument6 pagesEffect of Shading On Photovoltaic Cell: Ekpenyong, E.E and Anyasi, F.IM VetriselviNo ratings yet
- ApuntesDocument28 pagesApuntesFrancisco RamosNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell: Name Batc H Roll NO. Official Email IDDocument21 pagesSolar Cell: Name Batc H Roll NO. Official Email IDAjinkya GholveNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell - RTF 0Document3 pagesSolar Cell - RTF 0MaryamKianiNo ratings yet
- Basics of Photovoltaics AND Solar CellDocument19 pagesBasics of Photovoltaics AND Solar CellCYCLONE GamingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2Ravi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 516538596-Seminar - PPTX 20231124 092231 0000Document15 pages516538596-Seminar - PPTX 20231124 092231 0000KIRUBAHARAN MANIVASAGANNo ratings yet
- Solar For StudentsDocument8 pagesSolar For StudentsAbhishek ChauhanNo ratings yet
- EsquivelVilchisA TermoApl 36 PhotovoltaicSystem Nov152014Document9 pagesEsquivelVilchisA TermoApl 36 PhotovoltaicSystem Nov152014EsquivelAndiieNo ratings yet
- Solar Photvoltaics: Dr.A.M.Surendra KumarDocument31 pagesSolar Photvoltaics: Dr.A.M.Surendra KumarHarish A.P.No ratings yet
- PV Plants (1200)Document82 pagesPV Plants (1200)Yasmeen MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Part E - SOLAR PV CELLDocument10 pagesPart E - SOLAR PV CELLshashanknaikat5No ratings yet
- Ganesh SeminarDocument19 pagesGanesh SeminarRohithNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Solar Panel Efficiency Using Solar Concentration by Simple Mirrors and by Cooling 2014Document4 pagesImprovement in Solar Panel Efficiency Using Solar Concentration by Simple Mirrors and by Cooling 2014cmhg1982No ratings yet
- JurnalDocument4 pagesJurnalzamzul ariefNo ratings yet
- Res PresentationDocument15 pagesRes PresentationKIRUBAHARAN MANIVASAGANNo ratings yet
- MLE4208 Lecture 1 PDFDocument31 pagesMLE4208 Lecture 1 PDFhikolNo ratings yet
- Open Ended Lab RESDocument6 pagesOpen Ended Lab RESmuhammad Ehsan UllahNo ratings yet
- Solar Unit 2 &3Document60 pagesSolar Unit 2 &3richaadlakhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Solar EnergyDocument33 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Solar EnergyNathan EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- RW 0004PhotovoltaicsRev5Document4 pagesRW 0004PhotovoltaicsRev5Olawale John AdeotiNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic System: Camilo Peñaranda Rincon 1092156401Document3 pagesPhotovoltaic System: Camilo Peñaranda Rincon 1092156401Camilo PeñarandaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Layout of DC MicrogridDocument14 pages1.3 Layout of DC MicrogridBiswaranjan MahantaNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaics: What Is Photovoltaic Solar Energy (PV) ?Document4 pagesPhotovoltaics: What Is Photovoltaic Solar Energy (PV) ?Dawit TilahunNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Fabrication of An Active Cooling System For Reducing Photovoltaic Module TemperatureDocument7 pagesAnalysis and Fabrication of An Active Cooling System For Reducing Photovoltaic Module TemperaturecarlosNo ratings yet
- Solar Power GenerationDocument35 pagesSolar Power GenerationMyxtèrîoux Punk100% (2)
- Project1 DoneDocument15 pagesProject1 DoneDr-naser MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Solar Power System Structure and Working PrincipleDocument6 pagesSolar Power System Structure and Working PrincipleAriel CatapalNo ratings yet
- Ec 6016Document46 pagesEc 60161987parthi100% (1)
- Solar Tracking System 14012013065504 Solar Tracking SystemDocument25 pagesSolar Tracking System 14012013065504 Solar Tracking SystemMUHAMMED FAISALNo ratings yet
- INSTALL YOUR OWN Photovoltaic System: Hybrid, Stand Alone and Battery StorageFrom EverandINSTALL YOUR OWN Photovoltaic System: Hybrid, Stand Alone and Battery StorageNo ratings yet