Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Principal Working Advantages Application Conclusion
Uploaded by
Harshit AgarwalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Principal Working Advantages Application Conclusion
Uploaded by
Harshit AgarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION PRINCIPAL WORKING ADVANTAGES APPLICATION CONCLUSION
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert energy into useful mechanical motion. Heat engines, including internal combustion engines and external combustion engines (such as steam engines) burn a fuel to create heat which is then used to create motion. Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, pneumatic motors use compressed air and others, such as windup toys use elastic energy. In biological systems, molecular motors like myosins in muscles use chemical energy to create motion.
The six-stroke engine is a type of internal combustion engine based on the four-stroke engine, but with additional complexity to make it more efficient and reduce emissions. First concept of this engine are represent by Malcolm Beare.
The pistons in a six stroke engine goes up and down total six times for each injection of fuel. Designs either use steam or air as the working fluid for the additional power stroke. six-stroke engine with external and internal combustion and double flow is similar to the actual internal reciprocating combustion engine
1. Intake valve 2. Heating chamber valve 3. Combustion chamber valve 4. Exhaust valve 5. Cylinder 6. Combustion chamber 7. Air heating chamber 8. Wall of combustion chamber 9. Fuel injector 10. Heater plug
The intake valve (1) is open. Intake of pure air in the cylinder (5).
(1)
(5)
The heating chamber valve(2) is open. Compression of pure air in the heating chamber(7).
(7)
(2)
The Combustion chamber valve(3) is open. Release of combustion gases in the cylinder (5).
(3) (5)
The exhaust valve (4) is open. Exhaust of the combustion gases.
(4)
The heating chamber valve (2) is open. Release of hot pure air into the cylinder (5).
(2) (5)
The Combustion chamber valve(3) is open. Recompression of the pure air in the combustion chamber.
(3)
i.
ii.
iii.
Reduction in fuel consumption by at least 40%. Thermal efficiency reaching 50% . Two expansions (work) in six strokes.
IV.
Dramatic reduction in pollution up to 60% to 90% depend upon types of fuel and also reduce a noise pollution.
V.
Cooling system is not required so reduce engine weight.
VI.
The engine can run on a variety of fuels, ranging from diesel to LPG or animal grease.
VII.
Cost comparable to those of a four-stroke engine.
Motorboats might offer a big outlet for this type of engine Furthermore, the use of fuels other than gasoline would greatly reduce the risks of explosion. Motor-pumps, generator sets, stationary engines, etc....intended for agriculture and industry. Many more applications may also be envisaged.
Drastically reducing fuel consumption and pollution without radically affecting performances would allow the current concept of the automobile to be reassessed. There is, at this day, no wonder solution for the replacement of the internal combustion engine. Only improvements of the current technology can help it progress within reasonable time and financial limits. The six-stroke engine fits perfectly into this view.
You might also like
- Toyota Echo 1NZ-FE 1999 - 2001 Engine Management Wiring DiagramDocument2 pagesToyota Echo 1NZ-FE 1999 - 2001 Engine Management Wiring Diagramrodolfo paucara100% (1)
- Kta38 G3 PDFDocument2 pagesKta38 G3 PDFacere18100% (2)
- 4102 Series Diesel Engine: Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument16 pages4102 Series Diesel Engine: Operation and Maintenance ManualSteven J Baynes100% (1)
- Types of Six Stroke EngineDocument8 pagesTypes of Six Stroke EngineUmair SharifNo ratings yet
- Six Stroke EngineDocument17 pagesSix Stroke Enginekarunesh17No ratings yet
- Seminar Powerpoint Presentation On 6 Stroke EnginesDocument31 pagesSeminar Powerpoint Presentation On 6 Stroke EnginesVijay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Combustion Turbines: Five-Stroke EngineDocument3 pagesCombustion Turbines: Five-Stroke EngineWolfMensch1216No ratings yet
- 6stroke Engine Cahnder.Document26 pages6stroke Engine Cahnder.Rangappa swamyNo ratings yet
- 6 Stroke Petrol Engine: Mechvibes PresentationDocument18 pages6 Stroke Petrol Engine: Mechvibes PresentationHarjot SinghNo ratings yet
- Six Stroke EngineDocument36 pagesSix Stroke EngineAmandeep Tanwar100% (2)
- A Presentation On Six-Stroke EnginesDocument17 pagesA Presentation On Six-Stroke EnginesHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump ToDocument7 pagesInternal Combustion Engine: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump ToAbdullah KhaledNo ratings yet
- The Internal Combustion EngineDocument8 pagesThe Internal Combustion EngineRiko AidaNo ratings yet
- Ijaret 11 11 202Document7 pagesIjaret 11 11 202Abhisekh PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Hand Made CarDocument33 pagesHand Made CarSahil DhirNo ratings yet
- Paper Presentation Coe PandharapurDocument16 pagesPaper Presentation Coe PandharapurShrishant PatilNo ratings yet
- Siege Engine Electric Engine: NomenclatureDocument11 pagesSiege Engine Electric Engine: NomenclatureZülfüNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument13 pagesInternal Combustion EngineBichoo ArackalNo ratings yet
- 6-Stroke Engine1Document22 pages6-Stroke Engine1KumarVidyadharNo ratings yet
- EngineDocument19 pagesEngineSukumar PaniNo ratings yet
- 6 Stroke EngineDocument14 pages6 Stroke EngineMayank VyasNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines: Introduction Fuels Four Stroke Engine Parts of A Four Stroke EngineDocument17 pagesInternal Combustion Engines: Introduction Fuels Four Stroke Engine Parts of A Four Stroke EnginehitulparmarNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument16 pagesInternal Combustion EngineHamzeh Al-QaisiNo ratings yet
- Six Stroke Engine SeminarDocument37 pagesSix Stroke Engine SeminarShiv Raj KhojaNo ratings yet
- Review Six Stroke EngineDocument7 pagesReview Six Stroke EngineSuhas G FADNISNo ratings yet
- Six Stroke Engines - Velozeta Mod 2018-2019Document19 pagesSix Stroke Engines - Velozeta Mod 2018-2019BharathNo ratings yet
- Report On Six Stroke EnginDocument19 pagesReport On Six Stroke EnginBharathNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument13 pagesInternal Combustion EngineNAITAJINo ratings yet
- Term Paper ON I C Engine ThermodynamicDocument14 pagesTerm Paper ON I C Engine ThermodynamicSuresh SharmaNo ratings yet
- 6stroke EngineDocument5 pages6stroke EngineMitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- EncylopediaDocument9 pagesEncylopedianayanit044No ratings yet
- 6 STRK EngDocument6 pages6 STRK EngKarthik ChillaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report 2ND PartDocument19 pagesSeminar Report 2ND PartAshutosh RautNo ratings yet
- Six Strock EngineDocument4 pagesSix Strock EngineNani Srinu VasalaNo ratings yet
- Six Stroke EngineDocument14 pagesSix Stroke EnginePaarth JangraNo ratings yet
- Paper Title (Use Style: Paper Title) : Subtitle As Needed (Paper Subtitle)Document13 pagesPaper Title (Use Style: Paper Title) : Subtitle As Needed (Paper Subtitle)Vikas GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Six-Stroke EngineDocument3 pagesThe Six-Stroke EngineAmrut KarajagiNo ratings yet
- MD ProjectDocument35 pagesMD ProjectDar AkhtNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentSahil KalaNo ratings yet
- Six Stroke EnginesDocument18 pagesSix Stroke EnginesRamiNo ratings yet
- 6 Stroke EngineDocument16 pages6 Stroke EngineKongala Vamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- LkjhuDocument20 pagesLkjhuMohisinONajeebNo ratings yet
- Development of High Efficiency Engine by Combining I. C. Engine and E C EngineDocument4 pagesDevelopment of High Efficiency Engine by Combining I. C. Engine and E C EngineMuhammad Rifqi PinandhitoNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Six Stroke Internal Combustion EngineDocument4 pagesDesign and Analysis of Six Stroke Internal Combustion Engineabhijith thankachanNo ratings yet
- Ijett V34P243 PDFDocument7 pagesIjett V34P243 PDFBilyaminuNo ratings yet
- Multi Point Fuel Injection SystemDocument23 pagesMulti Point Fuel Injection SystemGoutham Reddy100% (2)
- Presentation On Petrol Engine: Presented By-Mridul Mudai Sec-B4004 Roll No-B64Document12 pagesPresentation On Petrol Engine: Presented By-Mridul Mudai Sec-B4004 Roll No-B64mridulmudai1991No ratings yet
- Mfpi & CrdiDocument18 pagesMfpi & CrdiAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Engines Work: Carburetor InjectorDocument2 pagesEngines Work: Carburetor InjectorAmirNo ratings yet
- 6 Stroke EngineDocument12 pages6 Stroke EngineVanam VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Direct Injection: o o o oDocument7 pagesDirect Injection: o o o opardeep4372No ratings yet
- A Review On Six Stroke CI Engine: Kuladeep Kumar PandeyDocument5 pagesA Review On Six Stroke CI Engine: Kuladeep Kumar PandeyKuldeep PandeyNo ratings yet
- Fuel InjectionDocument18 pagesFuel InjectionsavitagupNo ratings yet
- Communication Lab 4-Stroke Petrol Engine: Hemanth Kumar R 07ME034Document6 pagesCommunication Lab 4-Stroke Petrol Engine: Hemanth Kumar R 07ME034Hemu723No ratings yet
- Bahirdar University Bahirdar Institute of ThecnologyDocument6 pagesBahirdar University Bahirdar Institute of ThecnologyKaleab EndaleNo ratings yet
- Green EngneDocument14 pagesGreen EngneRishav Thakur100% (1)
- Multi Point Fuel Injection SystemDocument23 pagesMulti Point Fuel Injection SystemVenkatesan SwamyNo ratings yet
- Report On Sae SupraDocument21 pagesReport On Sae SupraSanchit Agarwal0% (1)
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Tum Hi Ho Guitar ChordsDocument2 pagesTum Hi Ho Guitar ChordsHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- PDR Final ProjectDocument14 pagesPDR Final ProjectHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Tere Bin Ho Na Sakega GujaraDocument3 pagesTere Bin Ho Na Sakega GujaraHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Subhanalla: (D Udud Udud) (A) (A)Document2 pagesSubhanalla: (D Udud Udud) (A) (A)Harshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Madari Guitar ChordsDocument2 pagesMadari Guitar ChordsHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Madari Guitar ChordsDocument2 pagesMadari Guitar ChordsHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Soniye ChordsDocument1 pageSoniye ChordsHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Jane Kyon Shafkat BhaiDocument1 pageJane Kyon Shafkat BhaiHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Paani Da RangDocument2 pagesPaani Da RangMohite Rao GokhaleNo ratings yet
- Asus2 D BM E Asus2 Asus2 D BM E F#MDocument2 pagesAsus2 D BM E Asus2 Asus2 D BM E F#MHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Hum Jee Lenge LyricsDocument1 pageHum Jee Lenge LyricsHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Interview Qusetions For FreshersDocument2 pagesMechanical Engineering Interview Qusetions For Freshersprasaad08No ratings yet
- PDP Final Year ProjectDocument32 pagesPDP Final Year ProjectHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument27 pagesVector CalculusHarpreetSinghNo ratings yet
- Me 1997Document13 pagesMe 1997Harshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Hum Jee Lenge LyricsDocument1 pageHum Jee Lenge LyricsHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Fee Notice Dec 13Document2 pagesFee Notice Dec 13Harshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Robotics PPT DownloadedDocument92 pagesRobotics PPT DownloadedHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- B.techMAE 8 SemDocument173 pagesB.techMAE 8 SemHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Six-Stroke EnginesDocument17 pagesA Presentation On Six-Stroke EnginesHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesMechanical EngineeringmannamalairajaNo ratings yet
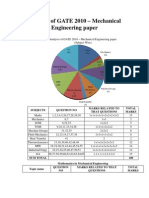
- Analysis of GATE 2010 PDFDocument5 pagesAnalysis of GATE 2010 PDFHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Me 2006Document25 pagesMe 2006Harshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Song: Challa Singer: Rabbi Music: A R Rahman Lyrics: Gulzar Movie: Jab Tak Hai Jaan Release Date: November 13th 2012 Language: Punjabi Country: IndiaDocument2 pagesSong: Challa Singer: Rabbi Music: A R Rahman Lyrics: Gulzar Movie: Jab Tak Hai Jaan Release Date: November 13th 2012 Language: Punjabi Country: IndiaHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Placement QuestionsDocument2 pagesMechanical Placement QuestionsHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Job Interview QuestionDocument3 pagesMechanical Job Interview QuestionGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- EX - NO:6 Dismantling of Jet Engine AimDocument4 pagesEX - NO:6 Dismantling of Jet Engine AimesakkimuthuNo ratings yet
- Het 1 JuliDocument44 pagesHet 1 Juliade m hermawanNo ratings yet
- G.S.S.S. Banur Distt. PATIALA State PUNJABDocument7 pagesG.S.S.S. Banur Distt. PATIALA State PUNJABapi-3731257No ratings yet
- UMLeonMK2 PDFDocument94 pagesUMLeonMK2 PDFturbitolocoNo ratings yet
- 0.5% O Rating CAT Engine Specifications: G3306 Gas Petroleum EngineDocument8 pages0.5% O Rating CAT Engine Specifications: G3306 Gas Petroleum EngineJeff LNo ratings yet
- PERKINS 825-1250 kVA: Technical SpecificationsDocument2 pagesPERKINS 825-1250 kVA: Technical SpecificationsJack ElhaqNo ratings yet
- Steering Control System: SectionDocument50 pagesSteering Control System: SectionАндрей НадточийNo ratings yet
- Engine AssamblyDocument232 pagesEngine AssamblySergey Sergeev100% (1)
- Piaggio X9 125 180 Servis ManualDocument268 pagesPiaggio X9 125 180 Servis Manualakula444450% (4)
- Technical Specifications - Autodata 01Document6 pagesTechnical Specifications - Autodata 01Emil IacobNo ratings yet
- Project On The Fabrication of Intelligent Reverse Braking System..... Chapter 1-3Document27 pagesProject On The Fabrication of Intelligent Reverse Braking System..... Chapter 1-3ovieNo ratings yet
- Parts Catalog: 0CW10-M00800ENDocument24 pagesParts Catalog: 0CW10-M00800ENSeibNo ratings yet
- 03 Apd SepatuDocument26 pages03 Apd SepatuInspector CilegonNo ratings yet
- Touareg 4.2Document36 pagesTouareg 4.2zozo0424No ratings yet
- Task 4 Primary and Secondary Flight ControlsDocument9 pagesTask 4 Primary and Secondary Flight ControlsSebastian KubiakNo ratings yet
- FT 200Document36 pagesFT 200api-242597694No ratings yet
- (TM) Honda Catalogo de Piezas Honda Gl1100 1980 Al 1982 en InglesDocument195 pages(TM) Honda Catalogo de Piezas Honda Gl1100 1980 Al 1982 en Inglesgustavo renzoNo ratings yet
- Himsen Cat h1728Document12 pagesHimsen Cat h1728Mohsen100% (1)
- Afterburner - Gas Turbine, Turbojet, Turbofan) Rolls Royce - T PDFDocument11 pagesAfterburner - Gas Turbine, Turbojet, Turbofan) Rolls Royce - T PDFEstevam Gomes de Azevedo100% (1)
- Price ListDocument519 pagesPrice Listabrar nurtata100% (1)
- Tad734Ge: 50 Hz/1500 RPM 60 Hz/1800 RPMDocument2 pagesTad734Ge: 50 Hz/1500 RPM 60 Hz/1800 RPMYasser JaviNo ratings yet
- JMG - R230 Panel-IndicatorsDocument3 pagesJMG - R230 Panel-IndicatorsMiguel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Null 4Document8 pagesNull 4Roberto AgandaNo ratings yet
- BOEINIG B787-9 Normal Procedures V2.4Document2 pagesBOEINIG B787-9 Normal Procedures V2.4IF GlobalNo ratings yet
- Alu Coated Piston Rings PDFDocument2 pagesAlu Coated Piston Rings PDFAlexandru AlexNo ratings yet
- LuscombeDocument7 pagesLuscombeAlejandro FerrariNo ratings yet