Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Determines The Shape of A Molecule?
What Determines The Shape of A Molecule?
Uploaded by
Arthur WongOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Determines The Shape of A Molecule?
What Determines The Shape of A Molecule?
Uploaded by
Arthur WongCopyright:
Available Formats
What determines the shape of a molecule?
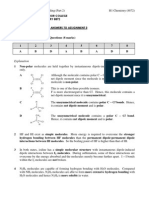
Draw and name the bonding in the following four molecules. Label the bond angles. a) b) c) d) AlCl3 SiF4 SF6 CO2
Put the strengths of repulsion in order. lone-lone bonded-bonded bonded-lone
Now draw the following molecules explaining the bond angles in each. CH4 NH3 H2O
Why is the hydrogen-hydrogen bond NON-POLAR in H2?
What happens to the bond if we have HCl?
Define: -electro negativity -Permanent dipole
Why is CH4 a non-polar molecule despite having permanent dipoles? Why is H2O polar and CO2 non-polar?
In terms of electronegativity which types of elements are most likely to form - A non polar covalent bond - An ionic bond - Polar covalent bonding?
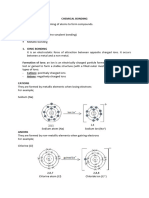
What causes intermolecular forces? What are the 3 types? Can you put them in order of relative strength?
Where do permenant dipole-dipole interactions come from?
Can you give an example?
Explain how van der waals forces occur.
What increases the strength of van der waals forces?
Explain why boiling point increases down a group.
What is a hydrogen bond? Give an example in your answer.
Explain these properties of H2O in terms hydrogen bonds. 1. Ice is less dense than water 2. Water has relatively high melting and boiling points
Draw a picture and explain it to describe metallic bonding.
Why do metals have high melting and boiling points? Why can they conduct electricity? Why are the malleable/ductile?
How does metallic bonding differ from covalent bonding?
Draw and explain the giant ionic lattice structure between sodium and chlorine.
Why does the MgO lattice have higher melting and boiling points than NaCl lattice?
Explain the difference in electric conductance of an ionic compound when solid, molten or aqueous.
Why do ionic compounds dissolve in polar solutions but not non-polar?
Draw a simple molecular lattice of I2 molecules naming and labelling any BONDS and any FORCES.
When I2 melts or boils what is happening? Describe the a) melting/boiling point b) Electrical conducance c) Solubility Of simple molecular lattices
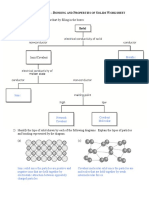
What is the difference between simple molecular structures and giant covalent structures?
What properties do giant covalent structures GENERALLY have?
Diamond
Graphite
Drawing
Electrical Conductivity Hardness
You might also like
- Unit 3 - Chemical BondingDocument58 pagesUnit 3 - Chemical BondingTrang Vũ Thị BằngNo ratings yet
- F321 Bonding and StructureDocument10 pagesF321 Bonding and StructureDoc_Croc100% (1)
- Chemical BondsDocument10 pagesChemical BondsGAMING WITH SPELLNo ratings yet
- Answers To Assignment 3Document4 pagesAnswers To Assignment 3Zul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding MCQDocument15 pagesChemical Bonding MCQVinay Krishna Kodali50% (4)
- Chemical Bonding 1Document101 pagesChemical Bonding 1Aarav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Y 12 PeriodicityDocument28 pagesY 12 Periodicityنور هدايو احمدNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6Muhammad Qadir RafiqueNo ratings yet
- LBC Alchemy SE Lesson26Document5 pagesLBC Alchemy SE Lesson26Sean MartinsonNo ratings yet
- Structure of MoleculesDocument6 pagesStructure of MoleculesZeeshan MahdiNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesChemical BondingdiegocmakoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document6 pagesLesson 2sathmi gurusingheNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Elements and CompoundsDocument9 pagesBonding in Elements and CompoundsSolita SinghNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties of Solids Worksheet Solutions 1kadax6Document4 pagesBonding and Properties of Solids Worksheet Solutions 1kadax6Mel Patricia M. CabreraNo ratings yet
- Bonding BookletDocument11 pagesBonding BookletAfridxDominatorNo ratings yet
- IB Bonding Note Cards SL HLDocument59 pagesIB Bonding Note Cards SL HL陳定均No ratings yet
- Reveiw - CH06 Bonding KEYDocument5 pagesReveiw - CH06 Bonding KEYMae Seihdrean Bautistä - MAEd Sci 1No ratings yet
- 1 NotesDocument8 pages1 NotesillegiblecaptchaNo ratings yet
- 2021 IMF Packet WelchDocument9 pages2021 IMF Packet WelchbobNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Class IXDocument2 pagesPaper 1 Class IXsuccessacademy215No ratings yet
- Bonding PacketDocument24 pagesBonding PacketIra Munirah100% (2)
- Chemical Bonding-Wps OfficeDocument16 pagesChemical Bonding-Wps OfficeJoel TitusNo ratings yet
- Number of Valence Electrons Group NumberDocument20 pagesNumber of Valence Electrons Group NumberManonmani PalaniswamyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Level M Chapter 9 BQ-AK 2223ISCERBILDocument3 pagesChemistry Level M Chapter 9 BQ-AK 2223ISCERBILProdread LordNo ratings yet
- L0 - Bonding NotesDocument23 pagesL0 - Bonding NotesRuha VNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument27 pagesChemical BondingSachin Kumar50% (2)
- Chemical Bonding MCQDocument15 pagesChemical Bonding MCQHaider JalalNo ratings yet
- Higher Thinking QuestionsDocument4 pagesHigher Thinking QuestionsCaron AsgaraliNo ratings yet
- ClassquestionbondingDocument2 pagesClassquestionbondingJesus Monje VenturaNo ratings yet
- A2AS CHEM REVISED Support 20837Document6 pagesA2AS CHEM REVISED Support 20837Tianming KingsleyNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument51 pagesChemical BondingBehzod ShoraimovNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chemical BondingDocument14 pagesNotes - Chemical Bonding黄心盈No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Practice Test 4u1Document4 pagesChapter 4 Practice Test 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- C.7A IUPAC Nomenclature Rules, C.7B Write Chemical Formulas and C.7D Metallic Bonding and Properties - Made With ConkerDocument6 pagesC.7A IUPAC Nomenclature Rules, C.7B Write Chemical Formulas and C.7D Metallic Bonding and Properties - Made With Conkerdileepsiva143No ratings yet
- Lesson 10.2 The Solid StateDocument14 pagesLesson 10.2 The Solid StatefitriNo ratings yet
- S2 - 4 (By: Feroz Akhtar)Document5 pagesS2 - 4 (By: Feroz Akhtar)Feroz AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 8 Thhourlab 9 BakerbrunatikallalkaneoberlanderDocument5 pages8 Thhourlab 9 Bakerbrunatikallalkaneoberlanderapi-297169088No ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 4.2Document4 pagesChemistry Unit 4.2Sonal Perera100% (1)
- Compounds - Bonding U1 N U2Document19 pagesCompounds - Bonding U1 N U2muhajireenNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE - 033838Document26 pagesUnit 4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE - 033838Gautam SinghNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledtaysonNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesChemical Bondingparth ladaniNo ratings yet
- A Getting-It-On Review and Self-Test Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesA Getting-It-On Review and Self-Test Chemical BondingAnonymous RD1CrAINo ratings yet
- Unit1 Mod 3 Group IV ElementsDocument9 pagesUnit1 Mod 3 Group IV ElementsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- RW-1 2 3 4 5 6 7Document7 pagesRW-1 2 3 4 5 6 7Smahs ZabirNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Igcse ElectrolysisDocument86 pagesEdexcel Igcse ElectrolysisshoshoNo ratings yet
- Xi Chem October Worksheet-1 22-23Document3 pagesXi Chem October Worksheet-1 22-23Panav KhungarNo ratings yet
- Revision Chem Bonding NotesDocument9 pagesRevision Chem Bonding Notesrania samirNo ratings yet
- ELECTRO CHEMISTRY QDocument3 pagesELECTRO CHEMISTRY Qashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Metals and Nonetals - 3 Ionic CompoundDocument1 pageMetals and Nonetals - 3 Ionic Compoundbhumika motiyaniNo ratings yet
- QB 10 Chapter 1&2Document5 pagesQB 10 Chapter 1&2Nitin SNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - CH 11 NotesDocument3 pagesPhysical Science - CH 11 NotessuhughesNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Chemistry-Xii The Solid State CHAPTER - 1 (Weightage 4 Marks) Very Short Answer Type Questions (Of 1 Mark Each)Document63 pagesQuestion Bank Chemistry-Xii The Solid State CHAPTER - 1 (Weightage 4 Marks) Very Short Answer Type Questions (Of 1 Mark Each)Shiv GuptaNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Chemistry Guess Paper 2020Document1 page9th Class Chemistry Guess Paper 2020Afreen hashim100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)