Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Juvenile Hormone
Uploaded by
jugesmangangOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Juvenile Hormone
Uploaded by
jugesmangangCopyright:
Available Formats
By: JUGES RAJ
INTRODUCTION
ROLE
OF JUVENILE HORMONE (JH) FORMS OF JH SYNTHETIC FORMS OF JH APPLICATIONS OF JH EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH RELATED TO JH CONCLUSION REFERENCES
In
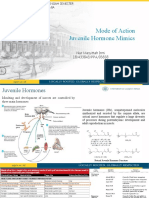
insects Juvenile Hormone (JH) refers to a group of hormones, which ensure growth of the larva, while preventing metamorphosis. Juvenile hormone is secreted by corpus allata. Chemically, they are a group of acyclic sesquiterpenoids that regulate many aspects of insect physiology i.e., development, reproduction etc
Juvenile
hormone (JH), produced by the corpora allata, regulates two important processes in insects. The first is development; as an insect develops, the degree juvenility of the next stage is determined by the amount of JH in the blood; the lower the JH, the more adult the next stage. Experimental removal of the corpora allata results in premature development of adult characteristics.
The
other function of JH is, in many insects, to regulate the production of eggs in the female's ovaries. Because mating behavior is often synchronized with the ovarian cycle, it makes sense for mating behavior and pheromone production to be linked with JH.
Methyl
farnesoate CAS methyl (2E,6E)-3,7,11-trimethyl-2,6,10-dodecatrienoate Formula: C16H26O2 Juvenile hormone 0 (found in Lepidoptera) CAS methyl (2E,6E)-10R,11S-(oxiranyl)-3,7-diethyl-11-methyl-2,6tridecadienoate Formula: C19H32O3
Juvenile
hormone I (found in Lepidoptera) CAS methyl (2E,6E)-10R,11S-(oxiranyl)-7-ethyl-3,11-dimethyl-2,6tridecadienoate Formula: C18H30O3 Juvenile hormone II (found in Lepidoptera) CAS methyl (2E,6E)-10R,11S-(oxiranyl)-3,7,11-trimethyl-2,6tridecadienoate Formula: C17H28O3
Juvenile
hormone III [17] CAS methyl (2E,6E)-10R-(oxiranyl)-3,7,11-trimethyl-2,6dodecadienoate Formula: C16H26O3 Juvenile hormone JHB3 [18] (found in diptera) CAS methyl (2E,6E)-6S,7S,10R-(dioxiranyl)-3,7,11-trimethyl-2dodecaenoate Formula: C16H26O4
The
most common form is JH III , which is structurally-
Since
juvenile hormone plays a very important role in the life cycle of insects, it can be used in various ways 1) In pest control,usually incorporated as a part of IPM programs. 2) For control of insect-spread diseases like malaria (via production of sterile mosquitoes).
Juvenile
Hormone plays a significant role in the life cycle of an insect. Economic losses incurred due to pest attack can be successfully avoided with the use of JH. Several human diseases spread through insects can also be effectively controlled using JH.
Journal
Of Insect Science (Vol: 8)
www.plosone.org www.wikipedia.org
You might also like
- Sex HormonesDocument58 pagesSex Hormonesbug4444not100% (1)
- SteroidsFromPhysiology2ClinicalMedicineITO12 PDFDocument220 pagesSteroidsFromPhysiology2ClinicalMedicineITO12 PDFJasonNo ratings yet
- CRANE SIGNAL PERSON TRAINING SlidesDocument73 pagesCRANE SIGNAL PERSON TRAINING SlidesAayush Agrawal100% (1)
- A&P Coloring Workbook - The Endocrine System PDFDocument12 pagesA&P Coloring Workbook - The Endocrine System PDFAnonymous WwJAxdz100% (4)
- CSEC Biology June 2012 P2Document17 pagesCSEC Biology June 2012 P2Joy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Gonadal Hormones 1-13Document66 pagesGonadal Hormones 1-13abstabsNo ratings yet
- Architecture For AutismDocument16 pagesArchitecture For AutismSivaRamanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Endocrine SystemDocument53 pagesLecture 2 Endocrine SystemLouella ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1, Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument86 pagesLecture 1, Introduction To EndocrinologyAlexandru Ionut Popistaș100% (1)
- Coma ManagementDocument5 pagesComa ManagementElena DocNo ratings yet
- Planning PlaygroundDocument16 pagesPlanning PlaygroundAdnan AliNo ratings yet
- Nfpa 791-R2024Document20 pagesNfpa 791-R2024Ivan MarquezNo ratings yet
- Homeopathic Remedy Pictures Alexander Gothe Julia Drinnenberg.04000 1Document6 pagesHomeopathic Remedy Pictures Alexander Gothe Julia Drinnenberg.04000 1BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Health Clinic InitiativeDocument47 pagesMobile Health Clinic InitiativededdyNo ratings yet
- Repro 3Document51 pagesRepro 3Hachi Nini Shop IINo ratings yet
- V.G. Vaze College of Arts, Science and Commerce Steroids: MSC Part-2, InternalsDocument19 pagesV.G. Vaze College of Arts, Science and Commerce Steroids: MSC Part-2, InternalsPranav PatilNo ratings yet
- Hormone Replacement in Men PDFDocument1 pageHormone Replacement in Men PDFPanser CueNo ratings yet
- SteroidsDocument22 pagesSteroidsrashid_ahmed_rajputNo ratings yet
- Sex Hormone Synthesis, Regulation, and Function - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewDocument7 pagesSex Hormone Synthesis, Regulation, and Function - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewWahyu W'cas PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Male Sex Hormone: Ricardo R. Santos, MDDocument15 pagesMale Sex Hormone: Ricardo R. Santos, MDim. EliasNo ratings yet
- Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone:Gonadotropin:Sex Steroid Signaling PathwayDocument26 pagesGonadotropin Releasing Hormone:Gonadotropin:Sex Steroid Signaling PathwayPlzstudylav SyedNo ratings yet
- Development Team: Zoology Animal Physiology Reproductive HormoneDocument26 pagesDevelopment Team: Zoology Animal Physiology Reproductive HormoneIrfan Pathan KakarNo ratings yet
- Antispermatogenic Effect of Carica Papaya Seed Extract On Steroidogenesis PDFDocument3 pagesAntispermatogenic Effect of Carica Papaya Seed Extract On Steroidogenesis PDFAlwin Ardiansyah PulunganNo ratings yet
- The Plant Hormones Peter DaviesDocument12 pagesThe Plant Hormones Peter Davieslaura natalia castellanos ardilaNo ratings yet
- Artigo IDocument7 pagesArtigo Iestudos.eaoapNo ratings yet
- Tura KuDocument104 pagesTura KuFitzgerald BillyNo ratings yet
- Butea Superba Sci - Erectogenic and Aphrodisiac Effects of Butea Frondosa Koenig in Rats - Involvement of Enzyme InhibitionDocument11 pagesButea Superba Sci - Erectogenic and Aphrodisiac Effects of Butea Frondosa Koenig in Rats - Involvement of Enzyme InhibitionyunusNo ratings yet
- La Ciencia de Los EsteroidesDocument6 pagesLa Ciencia de Los EsteroidesTATIANA BARRIOS ESCORCIANo ratings yet
- Enzima Aromataza Din Creier Barbati Are Rol in Intensitatea Driveului SexualDocument15 pagesEnzima Aromataza Din Creier Barbati Are Rol in Intensitatea Driveului SexualAbelard BonaventuraNo ratings yet
- Effect of Nonylphenol On Male Reproduction Analysis of Rat Epididymal Biochemical Markers and Antioxidant Defense EnzymesDocument8 pagesEffect of Nonylphenol On Male Reproduction Analysis of Rat Epididymal Biochemical Markers and Antioxidant Defense EnzymesOrlando Karim Shiro Jr.No ratings yet
- Hormonal Management of Male InfertilityDocument22 pagesHormonal Management of Male Infertilitydranibalurologoencancun.mxNo ratings yet
- Anna Belen Ignacio-Alensuela, MD Fpogs, FpsreiDocument45 pagesAnna Belen Ignacio-Alensuela, MD Fpogs, FpsreiBadini ChanalNo ratings yet
- LemakDocument4 pagesLemakdtr.fam21No ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Steroid Hormones / Steriodgenesis Steroid HormoneDocument10 pagesBiosynthesis of Steroid Hormones / Steriodgenesis Steroid Hormoneajay004004No ratings yet
- Develop. Growth and Differ., 29 (L), 1-12Document12 pagesDevelop. Growth and Differ., 29 (L), 1-12Perpustakaan UPI FABIO UNSOEDNo ratings yet
- InTech-From Soybean Phytosterols To Steroid HormonesDocument23 pagesInTech-From Soybean Phytosterols To Steroid HormonesNikhil GandhiNo ratings yet
- Bourgaud 2006Document16 pagesBourgaud 2006Patrisia HallaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Notes: Veterinary PhysiologyDocument16 pagesEndocrinology Notes: Veterinary PhysiologyBrian AllanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Reproductive SystemDocument25 pagesPhysiology of Reproductive SystemEstherNo ratings yet
- Assignment Topic: Hormones Submitted To: Mam. Anum Shehzadi SUBMITTED BY: Ahsan Zafar Roll No. Bpd02181275 Section & Semester: 9 (B)Document21 pagesAssignment Topic: Hormones Submitted To: Mam. Anum Shehzadi SUBMITTED BY: Ahsan Zafar Roll No. Bpd02181275 Section & Semester: 9 (B)Ghilman HabibNo ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Reproductive PharmacologyDocument11 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Reproductive PharmacologyNurhidayantiAyaMSNo ratings yet
- General and Comparative Endocrinology: Teresa Modesto, Ana M.M.S. Freitas, Adelino V.M. CanarioDocument9 pagesGeneral and Comparative Endocrinology: Teresa Modesto, Ana M.M.S. Freitas, Adelino V.M. CanarioharisankarhsNo ratings yet
- BJP 2008165 ADocument20 pagesBJP 2008165 ARobert FluoroCarbonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ResonanceDocument51 pagesEndocrine ResonanceEkta ManglaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Reproductive Endocrinology in Males (15pages)Document15 pagesLecture 1 - Reproductive Endocrinology in Males (15pages)GiselleCamilliaNo ratings yet
- Trabajo DianaDocument7 pagesTrabajo DianaAlejandra Paez NúñezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesChapter 13: Endocrine SystemKarren Taquiqui PleteNo ratings yet
- Vingren 2008Document8 pagesVingren 2008Vukašin Schooly StojanovićNo ratings yet
- Lecture Reproductive - Glands FinalDocument32 pagesLecture Reproductive - Glands FinalerikaquitaraaaNo ratings yet
- Management of Anabolic Steroid Induced Infertility.Document10 pagesManagement of Anabolic Steroid Induced Infertility.kevinNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Endocrine 1Document17 pagesMale Reproductive Endocrine 1Agustinus SuryaNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Pheromone Biosynthesis by A Brain Hormone in Two Moth SpeciesDocument5 pagesRegulation of Pheromone Biosynthesis by A Brain Hormone in Two Moth SpeciesRamona MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Nur Masyittah Irmi - AgrokimiaDocument6 pagesNur Masyittah Irmi - AgrokimiaNur Masyittah IrmiNo ratings yet
- 17.2 Hormones Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pages17.2 Hormones Anatomy and PhysiologyPrincess RuthNo ratings yet
- INFERTILITAS HormonDocument64 pagesINFERTILITAS HormonJulie Carnetion DNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction EndocrinologyDocument40 pages1 - Introduction EndocrinologyBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- The Biology and Biochemistry of Steroid Hormones: Advanced ArticleDocument16 pagesThe Biology and Biochemistry of Steroid Hormones: Advanced ArticleqhqhqNo ratings yet
- General Principles of EndocrineDocument30 pagesGeneral Principles of EndocrineSalah Salah 201-901-341No ratings yet
- Plant Hormone ReceptorsDocument12 pagesPlant Hormone ReceptorsJitendra MishraNo ratings yet
- Return To The Medical Biochemistry PageDocument8 pagesReturn To The Medical Biochemistry Pagevibhav82No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0065128116303695 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0065128116303695 MainIlenia AlfieriNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Physiology PDFDocument70 pagesReproductive Physiology PDFDrbee10No ratings yet
- Steroid GlossaryDocument2 pagesSteroid GlossaryNikita SHARMANo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: The Endocrine SystemDocument15 pagesChapter 18: The Endocrine SystemAbdulla Hil KafiNo ratings yet
- Sesquiterpene Lactones - Structural Diversity and Their Biological ActivitiesDocument22 pagesSesquiterpene Lactones - Structural Diversity and Their Biological ActivitiesAri Puji AstutiNo ratings yet
- Effects of Gonadotrophin in Vivo and 2-Hydroxyoestradiol-17Document13 pagesEffects of Gonadotrophin in Vivo and 2-Hydroxyoestradiol-17Perpustakaan UPI FABIO UNSOEDNo ratings yet
- Fish Pheromones and Related CuesFrom EverandFish Pheromones and Related CuesP. W. SorensenNo ratings yet
- Xenobiotic Regulation of Estrogen and Progesterone Receptor - Mediated Gene ExpressionFrom EverandXenobiotic Regulation of Estrogen and Progesterone Receptor - Mediated Gene ExpressionNo ratings yet
- SD BIOLINE HIV 12 3.0 BrochureDocument2 pagesSD BIOLINE HIV 12 3.0 BrochureDina Friance ManihurukNo ratings yet
- Effect of A Physiotherapy Program in Women With Primary DysmenorrheaDocument6 pagesEffect of A Physiotherapy Program in Women With Primary DysmenorrheaPaula RangelNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Science Y5 SECTION ADocument10 pagesSummative Test Science Y5 SECTION AEiLeen TayNo ratings yet
- 7 Contoh Analytical Exposition Pendek Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pages7 Contoh Analytical Exposition Pendek Bahasa InggrisDarsi YujiwatiNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 1Document36 pagesSample Paper 1Annshai Jam MetanteNo ratings yet
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: The History, Current View and New PerspectivesDocument14 pagesDiffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: The History, Current View and New PerspectivesPepe PintoNo ratings yet
- Dental Trauma - An Overview of Its Influence On The Management of Orthodontic Treatment - Part 1.Document11 pagesDental Trauma - An Overview of Its Influence On The Management of Orthodontic Treatment - Part 1.Djoka DjordjevicNo ratings yet
- Medicine Supplies & First Aid Treatment LogsheetDocument4 pagesMedicine Supplies & First Aid Treatment LogsheetMark BuendiaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal ParuDocument31 pagesJurnal Parudr. syah sembung wasisoNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Job and OccupationDocument3 pagesUnit 5 Job and OccupationAstriPrayitnoNo ratings yet
- Cebu Normal University: Submitted By: DIANA ROSE B. ZAMORASDocument3 pagesCebu Normal University: Submitted By: DIANA ROSE B. ZAMORASDiana ZamorasNo ratings yet
- PN 1Document1 pagePN 1Florin Eugen ConstantinescuNo ratings yet
- (Norma) Guia Fda CovidDocument14 pages(Norma) Guia Fda CovidJhovanaNo ratings yet
- Psych 7A FinalDocument16 pagesPsych 7A FinalMatthew Kim100% (1)
- Statement of PurposeDocument5 pagesStatement of PurposesagvekarpoojaNo ratings yet
- Adoption LawsDocument10 pagesAdoption LawsAneesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Anita Wagh-8-3-99-944 PDFDocument5 pagesAnita Wagh-8-3-99-944 PDFbutlesrNo ratings yet
- Course Profile - HIRARC - 1 DAYDocument4 pagesCourse Profile - HIRARC - 1 DAYRizal de silvaNo ratings yet
- MDSAP QMS ManualDocument43 pagesMDSAP QMS ManualmamjaguarNo ratings yet
- Cancer Genetics-Genetic InstabilityDocument60 pagesCancer Genetics-Genetic InstabilityMadhu MithaNo ratings yet
- Objective: Curriculum Vitae Md. Motaher Hossain Contact & DetailsDocument2 pagesObjective: Curriculum Vitae Md. Motaher Hossain Contact & DetailsNiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Management of Major Haemorrhage in Critical CareDocument13 pagesContemporary Management of Major Haemorrhage in Critical CareYo MeNo ratings yet