TRANSITIVITY
PRESENTATION BASED ON GEROT & WIGNELL; BLOOR & BLOOR; MARTIN, MATTHIESSEN & PAINTER
�TRANSITIVITY
The system or resource for construing experiential meaning, i. e. meaning about the world outside and inside the speaker. It is the resource for construing (= interpreting
and expressing) events, happenings, goingson, mental states, sayings, behaviours and
relations of different kinds.
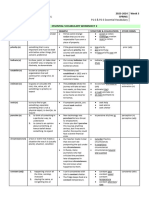
�Process type
Meanings
Examples
Material
actions and He ran. The window broke. He happenings (outside climbed the tree. She made a cake. world; observable) She broke the window. She gave him a present.
perception, cognition and
Mental affective processes (inner world; not directly observable)
I saw a bird, I heard a sound. I saw him cross the street. I knew the answers. I believe/think he is wrong. I fear the outcome. I like the smell. The woman scares me. The decision pleased me.
Behaviou r-al
human and animal physiological behaviour; human verbal and mental behaviour
He snored/coughed. He slept soundly. He breathed heavily. They shouted/cried/growled. He pondered/reflected over the
�Process type
Meanings
Examples He told a lie. He told a story. He said Hello. Im tired! he exclaimed. He answered that he was unaware of the decision. There is a bird on the tree. Ghosts exist. He is a (famous) scientist. He is the head of the department. He has blue eyes/a car.
Verbal
saying (mental process that becomes observable) existence being and having
Existential Relational
Meteorological
weather or time processes
Its 8 oclock. Its noon. Its windy. Its raining/snowing.
�Process type
Participants
Subtypes
Examples
Distinctive features/ Reactances
RELATIONAL
(being and having)
CARRIER & ATTRIBUTE
ATTRIBUTIVE
She is famous. She is a scientist. She has blue eyes.
Presence of be or verbs comparable in meaning.
-
TOKEN & VALUE
She is the leader. The IDENTIFYAconca-gua ING -S Present as is the unmarked tense highest in Present. beak in America.
-No substitution by any verb
-
�Process type
RELATIONAL
Participants
Subtypes
Examples
America is the beacon of democracy. The Aconcagua is the highest peak in America
Distinctive features/ Reactances
(being and having) Identify-ing an entity by reference to some other entity. Mean-ings of symbolizat ion.
TOKEN
INTENSIVE
Presence of definite NGp.
-
&
VALUE
POSSESSIVE
This is Neils. This belongs to Neil.
- substitution by represent
-
The time of the meeting is CIRCUMS- Friday. TANTIAL The cause for his illness is stress.
-Reversibility
-
�PARTICIPANTS IN RELATIONAL PROCESSES
Token: The concrete entity that embodies/ represents/ symbolizes a value (Susan is the kindest salesperson in the shop; He is the leader).
Value: A more abstract entity that can be perceived only if represented by a more concrete entity (Susan is the kindest salesperson in the shop; He is the leader).
�AMERICA
IS
THE BEACON OF DEMOCRACY
VALUE SUBJECT COMPLEMENT
TOKEN RELATIONAL: IDENTIFYING: INTENSIVE SUBJECT
THE BEACON OF DEMOCRACY
VALUE
IS
AMERICA
RELATIONAL: TOKEN IDENTIFYING: INTENSIVE
SUBJECT
SUBJECT COMPLEMENT
THE ACONCAGUA
TOKEN
IS
THE HIGHEST MOUNTAIN IN AMERICA
VALUE
RELATIONAL: IDENTIFYING: INTENSIVE
THE HIGHEST MOUNTAIN IN AMERICA
VALUE
IS
THE ACONCAGUA
RELATIONAL: TOKEN IDENTIFYING: INTENSIVE
�THI S BOOK
IS
M ARYS
VALUE
TOKEN RELATIONAL: IDENTIFYING: POSSESSIVE
THI S BOOK
BELONGS TO M ARY.
TOKEN RELATIONAL: VALUE IDENTIFYING: POSSESSIVE
THE TIME OF THE MEETING
VALUE
IS
FRIDAY
RELATIONAL: TOKEN IDENTIFYING: CIRCUMSTANTIAL
THE CAUSE FOR HIS ILLNESS
VALUE
IS
STRESS
RELATIONAL: TOKEN IDENTIFYING: CIRCUMSTANTIAL
�CRITERIA FOR IDENTIFYING VALUE AND TOKEN
TOKEN
More concrete entity America in America is the beacon of democracy
Subject in a clause with the verb represent America represents the beacon of democracy
VALUE
Abstract notion, value the beacon of democracy in same clause
Complement in clause with represent See the beacon of democracy in other box
�Process type
Participants
Senser Phenomenon Macrophenomenon (actPerception) Metaphenomenon (factemotion)
Subtypes
Examples
Distinctive features/ Reactances
MENTAL
(perceptions, cognitions, affection inner world Meta nonobserv-phenomenon able) Cognition (idea cognition)
He saw a -No substitution by bird. I saw any verb Perception him cross/crossing the street. -S Present as unmarked tense in I like/fear him. Present He pleases/ Affection scares me.
He knows all the answers. He believes that you are to blame. -Bidirectionality
-Capacity to project
�PARTICIPANTS IN MENTAL PROCESSES
Senser: an entity endowed with higher or lower consciousness, like a human being and, for some processes, an animal. It can be Subject (I like fruit) or Complement (Fruit appeals to/pleases me); Phenomenon: a thing (person, object, place, etc.) that can be perceived, known or that can be the object of an emotion of some kind. It is a participant in the mental clause and it is always a Ngp (He saw the animal; he knew the animal; He loves animals); Macro-phenomenon: Act: an event or happening or doing in the material world that can be perceived; only used with processes of perception. It is an embedded clause that is a participant in the mental clause (he saw [[him help the old lady/him helping the old lady]]; he heard [[him shout his name/him shouting his name]]).
�PARTICIPANTS IN MENTAL PROCESSES
Meta-phenomenon: fact: an abstract, non-material, semiotic entity that pre-exists the emotions it triggers; only used with processes of emotion/affection and an embedded participant element in the clause. I regretted (the fact) [[that I had not had the courage to speak to her]]. I liked (the fact) [[that she was black]]. [[That she was so young]] surprised me. Meta-phenomenon: idea: abstract but not pre-existing the process; rather brought into existence by it. Not really a participant in the clause but a separate clause: I understood // that it was futile. I knew // that it was of no use.
�HE
SENSER
SAW
A BIRD
MENTAL: PHENOMENON PERCEPTION
HEARD TIM THREATENING BOB
HE
SENSER
MENTAL: MACRO-PHENOMENON: PERCEPTION act (embedded cl.)
HE
SENSER
KNOWS
MENTAL: COGNITION
ALL THE ANSWERS
PHENOMENON
HE
SENSER
BELIEVES THAT YOURE TO BLAME
MENTAL: COGNITION METAPHENOMENON: idea (hypotactic cl.)
�HE
SENSER
REGRETS
MENTAL: AFFECTION
(THE FACT ) [[THAT HE WAS UNABLE TO HELP]].
META-PHENOMENON :FACT (embedded clause)
(THE FACT ) [[THAT HE WAS UNABLE TO HELP]] SURPRISES
META-PHENOMENON :FACT (embedded clause) MENTAL: AFFECTION
ME.
SENSER
SHE
PHENOMENON
PLEASES
MENTAL: AFFECTION
ME
SENSER
HE
SENSER
LOVES
MENTAL: AFFECTION
YOU
PHENOMENON
�MENTAL PROCESSES: BIDIRECTIONALITY
I
SENSER
FEAR
THE OUTCOME
MENTAL: PHENOMENON AFFECTION
THE OUTCOME
PHENOMENON
SCARES
MENTAL: AFFECTION
ME
SENSER
I
SENSER
DONT UNDERSTAND
MENTAL: COGNITION
THIS STUFF
PHENOMENON
THIS STUFF
BAFFLES
ME
SENSER
PHENOMENON MENTAL: COGNITION
�Process type
Participants
Subtypes
Examples
He told (us) a lie/a story.
Distinctive features/ Reactances
-Presence of
VERBA L (SAYING)
Sayer Verbiage Receiver
receiver -No substitution by do S. Present as unmarked tense in Pr.
-
Locution: Quoting
Im tired he
said
Locution: Reporting
He said (to me) he was tired.
Locution
-projection
�PARTICIPANTS IN VERBAL PROCESSES
Sayer: The person or thing (dictionary, sign, article, newspaper, etc.) that says sth. Receiver: the addressee; the person to whom sth is said Verbiage: the content of what is said, always expressed by a Ngp
Processes of saying or verbal processes can project another clause that expresses the content of what was said (locution). It can project it verbatim (quotation) or paraphrase it in line with the here and now of the speaker (report). The locution IS NOT a Participant in the verbal clause but a separate clause projected by it
�HE
SAYER
SAID
HE WAS TIRED
VERBAL LOCUTION REPORTING (Hypotactic cl.)
I AM TIRED
LOCUTION (Paratactic cl.)
HE
SAYER
SAID
VERBAL QUOTING
HE
SAYER
TOLD
US
A LIE
VERBIAGE (NG)
VERBAL RECEIVER
SHE
SAYER
ASKED
VERBAL
TOO MANY QUESTIONS
VERBIAGE (NG)
�Process type
Participant Subtypes
Examples
There are different species of whales. On the sofa was a cat
Distinctive features/ Reactances
-No substitution by do S. Present as unmarked tense in Pr.
-
EXISTEN TIAL
(EXISTENCE)
Existential
Existent
Existential (+ some other meaning)
Through the window, there -presence of the came the unstressed There in sounds of S position. Sydney.
�PARTICIPANTS IN VERBAL PROCESSES
Existent: it is the participant that the process introduces as existing, as having existence.
For some, the non-stressed there has no experiential role in the clause. It is just a dummy Subject, a place-holder for Subject. For others, it encodes the process together with be. When the clause starts with a Circumstance THERE can be omitted. It can be marked together with the verb be
�THERE
ARE
DIFFERENT SPECIES OF WHALES
EXISTENT
THE SOUNDS OF SYDNEY
EXISTENT
EXISTENTIAL
TRHOUGH THE WINDOW, THERE CAME
CIR: SPATIAL LOCATION
EXISTENTIAL
THERE
IS
A UNICORN
EXISTENT
IN THE GARDEN.
CIR: SPATIAL LOCATION
EXISTENTIAL
ON THE MATINEE JACKET
CIR: SPATIAL LOCATION
WAS
EXISTENTIAL
A BLOOD STAIN.
EXISTENT
GHOSTS
EXISTENT
EXIST.
EXISTENTIAL
�Process type
Participants
Subtypes
Examples
he slept soundly. He snored. He breathed. He babbled/ granted/ sang a song. He cried/laughed/gi ggled. They talked .
He pondered /meditated over the matter. He watched TV. He listened to the news
Distinctive features/ Reactances
-No substitution by do
BEHAVIOURAL
(physiologi cal, mental and paraverbal behaviour)
BEHAVER (behaviour) Range,
Physiological
(para) Verbal
S. Present as unmarked tense in Pr.
-
Matter,
Target
Mental Behaviour Perception, affection, cognition
-no projection
�BEHAVIOURAL PROCESSES They are half way between material processes, on the one hand, and mental and verbal processes on the other. They include: processes which are physiological in nature, with human or animal participants, like the expressed by the verbs sleep, snore, cough, breathe, sneeze, that is, where there is not properly an action being carried out,
�BEHAVIOURAL PROCESSES They include:
processes which have a mental quality to them but which involve volition and cannot project, particularly: processes of perception which are voluntary observe, watch, stare, listen to, look, feel (Feel the fabric, Feel the texture), processes of affection, where affection is expressed by Behaviour (chuckle, cry, frown, giggle, grin, laugh, moan, weep, embrace, kiss, frown, etc.); and processes of cognition, which are also voluntary and cannot project an idea (reflect,ponder, puzzle over a problem);
�BEHAVIOURAL PROCESSES They include:
finally, paraverbal or verbal processes which cannot project (shout, mutter, mumble, babble, grunt, talk, gossip, chat, converse, discuss, describe, etc.), but which present verbal activity as behaviour, not as saying proper. If the paraverbal processes project a locution, as it often happens in narrative, then they are to be analysed as verbal
He shouted like a monkey. He babbled and cried. I could not understand him because he mumbled. Ill kill you he shouted. = Verbal process
�PARTICIPANTS IN BEHAVIOURAL PROCESSES
Behaver: person or animal having the behaviour, usually endowed with consciousness. Most behavioural processes ONLY have a single participant, and thats the Behaver. Behaviour: found in very few cases in which the behaviour usually repeats the behavioural process with some added attribute (he breathed a deep breath; he dreamt a strange dream) Range: in very few cases in which the process takes a second participant that is not a behaviour and that is different in nature from the process itself: he watched a movie; they observed the stranger; they discussed/debated the problem.
�PARTICIPANTS IN BEHAVIOURAL PROCESSES
Matter: used with verbal behavioural and mental behavioural processes (They talked about the problem; They reflected/pondered over the problem). Target: used with verbal behavioural processes expressing insult, offence, criticism (They criticized his manners. He insulted him.) Both his manners and him in these sentences are the Target of the insult or the criticism.
�THE Y
BEHAVER
TALKED
BEHAVIOURAL: VERBAL
ABOUT THE PROBLEM
MATTER
SHE
CRITICIZED
HIS MANNERS
TARGET
BEHAVER BEHAVIOURAL: VERBAL
WE
BEHAVER
WATCHED
BEHAVIOURAL: MENTAL
A MOVIE
RANGE
HE
BEHAVER
REFLECTED
BEHAVIOURAL MENTAL:
OVER THE PROBLEM
MATTER
HE
SLEPT
SOUNDLY
A:cir
HE
SNEEZED
BEHAVER BEHAVIOURAL: PHYSIOLOGICAL
BEHAVER BEHAVIOURAL: PHYSIOLOGICAL