Mr.
Haroon Rahim
(Pharm-D, M.Phil, R-Ph & PhD Scholar)
Lecturer Department of Pharmacy Sarhad University of Science & Information Technology Peshawar
�Dispensing
Dispensing is an important part of the practice of pharmacy,
in which the pharmacist or the pharmacy technician (under
the direct supervision of the pharmacist) interprets the physician's requirements on the prescription and accordingly supplies medicines for the treatment of his patient (s).
This usually involves interpreting a written prescription but
may, on occasions, also include taking instructions given by word of mouth or by telephone from the physician.
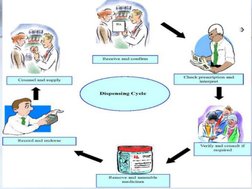
�The various activities involved in Dispensing are
Receiving and confirming orders Checking prescription and interpretation
Verifying and consulting if required
Removing medicines for issue and assembling Billing and counterchecking
Issuing medicines to the client with clear instructions and counseling
�Dispensing modules for good pharmacy practice
1.
Dispensing environment
a) b) c) d)
Prescription Counter Waiting Area Requirements of a good dispensing environment Barriers, noise and distractions that can affect dispensing Receiving the prescription Reading the prescription and checking for A. Legality B. Legibility C. Completeness and correctness Filling a prescription Removal of medicines from shelves. Assembling of medicines. Billing. Packing. Refilling a prescription Dispensing errors Role of pharmacists in promoting correct dispensing Refusal to dispense prescriptions Alternatives to conventional prescriptions.
2.
Handling of Prescriptions
a) b)
3.
Processing a prescription
a) b) c) d) e) f)
4.
Other aspects of dispensing
a) b) c) d)
�DISPENSING ENVIRONMENT 1.1 Prescription counter
Ideally the prescription counter should:
Be accessible to the client
Preferably be separate and in a quite location. If there are other separate sections (e.g
cosmetics, general items, OTC section), it should be slightly away from them
Be calm. Orderly, attractive and marked with an identifying sign or symbol which can
be easily identified and seen from other parts of the pharmacy.
A different color, appearance, demarcation etc may be given to the prescription
section, to provide added emphasis.
Have a waiting area for clients who wait for their prescriptions to be dispensed or
filled
�1.2 Waiting area
What should and ideal waiting area provide?
Comfortable chairs/place to sit (especially for
elderly/disabled/sick patients to rest).
Current
popular
health
magazines
and
carefully selected material to good health, to
keep the client busy/occupied and prevent
boredom while waiting to receive medicines.
Pamphlets and posters related to public,
family and other individual health problems prominently displayed (as the waiting area could be used as a health education center)
�1.3 Requirements of a Good Dispensing Environment
1. 2.
Be clean: To give a professional impression and outlook to the pharmacy. Be organized: To provide for a safe and efficient working area. (Such that things are found in the right place at the right times and there are minimum obstructions and hurdles).
3.
Have sufficient space For easy movement of personnel in the pharmacy, and to prevent
congestion and physical contact among staff while working.
4.
Temperature and humidity controlled As appropriate temperature and humidity are necessary for stability of medicines till the expiry date.
5.
No loud music playing, gossiping, talking, or television (e.g. a cricket match or a movie) : To avoid distractions during dispensing.
6.
Have medicines stored in an organized way on shelves in alphabetical order or using
the method normally employed in that particular pharmacy: To ensure quick, but safe
selection of the correct medicines from the shelves to minimize dispensing errors.
BE CLEAN, GET ORGANISED!! GIVE THE PHARMACY A PROFESSIONAL
LOOK
�Maintaining a clean environment requires
A regular routine of cleaning shelves, medicines/products, and a daily
cleaning of floors. A regular schedule for checking, cleaning and defrosting the refrigerator. Immediate wiping of accidental spills due to breakage, etc, during dispensing.
Activity 1: Prepare separate SOPs for cleaning the floor, shelves,
refrigerator, drawers etc. Each SOP should define responsibilities to the pharmacy staff.
the periodicity with the
which cleaning (of each) should be carried out and also assign
Activity 2: Prepare a work chart to be signed by the person doing the
cleaning and the person supervising, on the completion of work
�Advantages of a good dispensing enviroment I. Reduces dispensing errors. II. Reduces fatigue among pharmacy staff. III. Enhances services. IV. Improves the image of pharmacy V. Increases clients VI. Increases speed. VII.Creates a professional image
Working in a clean and an organized environment in a pharmacy, aids
in accuracy while dispensing, and also gives a professional look to the pharmacy. Presence of a separate prescription counter and waiting area can further Highlight professionalism and competence of the
pharmacist. Pharmacists handle medicines, and a slight dispensing
error could result in serious consequences i.e. health -wise for the patient, and for the pharmacy a loss of reputation. Thus a good dispensing environment is recommended for every pharmacy.
��2) HANDLING PRESCRIPTIONS
2.1 Receiving the Prescription
As clients come into the pharmacy, they must be made to feel
attended to and comfortable by : Friendly gestures. A smile. Eye-to-eye contact. A friendly welcome. Courtesy. Feeling of caring .
2.2 Communication should be initiated in such a manner that it encourages the client to convey his/her needs by producing a prescription or by asking for other products or advice
�Upon receiving the prescription, the pharmacist should confirm
Whether the client is the patient
himself or has come on the patient's behalf. The relation of the client with the patient. The client may politely be requested to wait, while the pharmacist reviews the prescription for:
Legality
Excuse me sir! Is this your medicine
No
and completeness of prescription. Therapeutic aspects Appropriateness for the individual
For whom medication is prescribed
It is prescribed for me
�2.2 Reading the Prescription and Checking for Completeness and Correctness
While reading and checking the
prescription, the pharmacist Should
Be alert, and concentrate on the
prescription.
Not be distracted.
Not engage in talking or chatting. Engage/
use in
his
professional/ the
experience prescription.
assessing
� After receiving the prescription, it is important for the
pharmacist to read the prescription to verify whether
It is legal and complete with respect to the various parts of the
prescription, and therefore
It can be dispensed as such, or not.
Legality
A prescription is legal when :
It is written (can also be typed) by a R.M.P. Signed by the R.M.P. Has all the information required to be contained with respect to parts
of prescription
�Legibility
Handwritten names of patients and medicines are often
difficult to read. In case of illegibility of name, age, etc, ask the patient for the correct spelling tactfully. For example the pharmacist may ask
Excuse me the first name is Jame or Jane
Always use excuse me or please etc and be polite
�Never dispense Guess work
Legibility is a problem requiring alertness and critical judgment on the part of the
pharmacist. Careless handwriting and similarity in spelling of names of different
drugs add to the difficulty.
Example of a Reading error:
Arlidin and Artidin - Due to illegible handwriting of doctors, Artidin could be
read as Arlidin. Artidin is a brand containing Diclofenac whereas Arlidin contains Nylidrin two different drugs used for two different conditions. When handwriting is illegible, the best thing to do is to contact the physician over the phone and
confirm.
Remember, you are dealing with medicines and thus, the lives of patients so be sure
of what you are dispensing. Imagine the disastrous consequences of dispensing the wrong medicine NEVER DISPENSE GUESS WORK
� b) The dosage form, the dosage and the quantity to be
dispensed have to be legible so that dispensing becomes easier for the pharmacist.
The instructions written for administration should state
clearly what the physician expects from the patient so that the pharmacist can counsel the patients efficiently.
All terminology, including units of measures (metric,
apothecary or English) and Latin abbreviations should be
properly interpreted
�Completeness and correctness
The prescription serves as a vehicle for communication from the licensed
practitioner to the pharmacist about the pharmaceutical care of the patient.
Details to be checked for
i) Physician's details.
ii) Patient's details. iii) Check the product details
Checking the product details will include checking :
Name of the product. Dosage form. Strength/ potency of the medicine. Total amount to be dispensed and its availability Dosage and directions for use. Frequency of administration
�General dispensing procedure
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Work on your own place. Wear freshly laundered overall coat. Provide yourself with a clean glass-cloth, a duster and either sponge. Work in a clean and tidy manner. Read the prescription carefully, make sure you understand it and that it is legally correct. If necessary, find out the formula of the prescription in an appropriate source of information.
�7. Check the doses of internal preparations. 8. Find, from an appropriate source, if any ingredient is 9. 10. 11. 12.
13.
a poison. Conform that there are no pharmaceutical or therapeutic incompatibility in the preparation. if you are unsure of correct method of preparation refer to your practical notebook. Look up the storage conditions for the preparations. Work out the calculations. Check the calculations.
�14. Collect the correct container and closure. 15. If necessary, trim the label to fit the container but do not 16. 17. 18. 19.
20.
21.
remove the name of suppliers. Write the main label and collect any special labels that are required. Make the preparation, pack it in the containers and polish the label. Check the label and fix them to the container. Check the finished preparation. Wrap the container and write the patients name and address on the wrapper. Make the appropriate records.