Professional Documents
Culture Documents
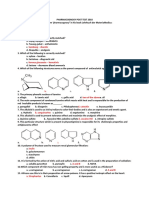
Mod 2 Pharmacognosy PDF
Uploaded by
Joelly C. ValendezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mod 2 Pharmacognosy PDF
Uploaded by
Joelly C. ValendezCopyright:
Available Formats
PHARMACOGNOSY
------------------------------------------------------------------------
PHARMACOGNOSY CRUDE DRUGS
Applied science -> biological, biochemical and economic – vegetable or animal drugs consists of natural substances that
features of drugs of biological origin and their constituents had undergone only the processes of collection and drying; plant
Medicinal products in their crude or unprepared form exudates
HISTORY OF PHARMACOGNOSY Natural Substances – formed in nature; whole plants or parts;
animals or organs; no molecular modifications had been made
Bablylonians
Derivatives of Extractives – chief principle or constituents of
Laws of Hammurabi (172 BC); clay models of human body;
crude drugs that are separated and used in a specific manner
medicinal effects of 250 plants; mages and physician; wheat
Menstruum – solvent; liquid/liquid mixture used to extract
and barley
active principle
Marc – undissolved portion of the drug that remarks after
Ayurveta (2500 BC)
extraction process is completed
Traditional medicine; “Science of life”; Mother of all healing
arts
Methods of Extraction
Charaka – text on internal medicine
Infusion – hot water (ex. tea); short contact of action
Sushruta – 184 chapters; 1120 illness
Maceration – soaked in solvent for long period of time
Percolation – passage through percolate (ex. Simple Syrup
Egyptians (Ebers papyrus – 1150 BC)
USP)
Embalming; George Ebers; priest and doctors; human anatomy
Digestion - <35-40oC
and use of plants
Decoction – boiling water
Greeks Liquid-Liquid Extraction Partitioning Distillation
Dioscorides – wrote “De Materia Medica” or The Medicinal
Indigenous Plants – plants growing in their native countries (ex.
material; aloe, belladonna, colchicum, ergot, opium; 600
Rinorea niccolifera – metal eating plant; more on nickel)
plants
Naturalized Plants – plants that grow in foreign land other than
Claudius Galen – described methods and processes of
their native homes
preparing formulas containing plant and animal drug; FATHER
OF PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOUNDING
Preparation of Crude Drugs
1. Collection – ensuring the true natural source of the drug:
Germans
improper collection, collection time, highest content
CA Seydler (1815) – coined the term, “pharmacognosy” from
Harvesting – specific or proper season; manual labor vs
“pharmakon” and “gnosis” in Analecta Pharmacognistica
mechanical devices
JA Schidt (1811) – used the word, “pharmacognosy”; Lehrbuck
2. Drying – remove moisture to prevent bacterial and fungal
de Materia Medica; described study of medicinal plants and
growth with enzymatic degradation; fixed constituents,
their properties
facilitates grinding and milling; converts plants to convenient
Fluckiger – simultaneous application of various scientific
form
disciplines with the object of acquiring drugs from every point
3. Curing – special drying process that enhances properties of
of view
plants’ active ingredients
Pellitier and Caventou – Quinine 4. Garbling – final step in preparation of crude drugs; removal of
Freidrich Serturner - Morphine extraneous matter
*Last Packaging, Storage, Preservation – protection and
marketability; maintain high degree of quality of drug
PAGE 1 OF 11 © MANOR REVIEW CENTER NOTES (K.L)
Evaluation of Crude Drugs – determine quality and purity; A. CLASSIFICATION OF CARBOHYDRATES
qualitative (intrinsic value of drug; type of medicinal prinnciples)
I. MONOSACCHARIDES – simplest carbohydrate unit; cannot be
and quantitative (amount)
hydrolyzed; identification test: Benedicts and Barfoed’s =
Organoleptic Evaluation – organs of senses; evaluates brick red ppt.; *neuramonic – aka sialic
macroscopic appearance of drug PENTOSES
Microscopic – evaluate in a cellular level Xylose – “wood sugar”; obtained from boiling corn cobs, straw;
Pharmacologic Evaluation diagnostic aid for intestinal malabsorption; absorbed but not
o Bioassays – assays using living animals or excised organs to metabolized
evaluate effects of drugs o Xylan -> Xylose (aldehyde) -> xylulose (ketoses)
Chemical Evaluation – assay of active constituents using HEXOSES – most important monosaccharide
chemicals (titration); best determination of official potency Glucose – aldohexose; aldehyde group is present in C1;
reducing sugar as determined by Benedict’s Test; occurs as
CLASSIFICATION OF DRUGS linear and cylic;
1. Morphology – forms; plant part used; convenient but no o β-D-Glucose – most abundant
chemical correlation o D-Glucose – aka Dextrose, Blood Sugar, Grape Sugar,
2. Taxonomic (Lireus) – evolutionary development; no Physiologic Sugar
correlation on chemical and biological activity o Uses:
Phylogeny – natural relationship that occurs among plants Parenteral – rigorously purified; as nutrient
and animals Pharmaceutic necessity – less rigorous purification; Liquid
3. Pharmacologic – based on therapeutic effect on body Glucose – syrupy liquid; incomplete acid hydrolysis of
4. Chemical – preferred method of classification – based-active starch; almost colorless and taste sweet; Dextrose
constituents that are present; phytochemical studies but excipient – crystalline sweetening agent (Oral Glucose
ambiguous at times Tolerance Test – 75g)
Fructose – ketohexose = (+)Seliwanoff’s Test: pink/red; ketone
Active Constituents – considered secondary metabolites; group is present in C2; reducing sugar; fruit sugar; sweet fruits
through drug biosynthesis or biogenesis and honey; aka Levulose (sweetest monosaccharide); obtained
from inversion of aq. sucrose solution; honey (mostly sucrose)
BIOGENESIS o High Fructose Sweeteners – isomerization of glucose
isomers from Streptomyces sp.
Ontogemy or Stage of Development
o Uses:
Ex. Cannabis sativa (cannabidiol – plant is young; cannabinol
Food for diabetic
– mature plant)
Ingredient in infant feeding formula
Heredity – same but not the same
Ingredient in Fructose injection nutruient
Environment
Galactose – aldohexose; “Brain Sugar”; C4 epimer of glucose
(C2 – mannose); milk:lactose::neuronal fibers:galactosides;
I. CARBOHYDRATES Gaucher’s Disease; (+) Mucic acid and Phenylhydralazine =
Polyhydric aldehyde or ketone alcohols that contain C, H, and crystal formation (osazone crystals)
O
H and O has same ratio as that of water, thus named CARBO + II. DISACCHARIDES – composed of two monosaccharide units;
HYDRATES Photo formed via dehydration synthesis; glycosidic bond
First product of synthesis [C•H2O]n Sucrose – “table sugar”; obtained from:
Xylem – H2O o Saccharum officianarum (sugar cane) – (+) lime = decreased
Phloem – nutrients – food (∆ source; ∆ storage; structure) albumin; use SO2 clear = clarification
Most abundant organic molecule in nature o Beta vulgaris (sugar beets) – cossettes (“cut limps livers” –
chop finely)
o Acer saccharum (sugar maple)
- non-reducing sugar: (-)Benedict’s Test
- glucose + fructose, α-1,2 bond
- uses: demulcent, sweetening agent to mask taste, coating
agent, preservative (85%), production of syrups, retards
oxidations
PAGE 2 OF 11 © MANOR REVIEW CENTER NOTES (K.L)
- Molasses – residual dark colored syrup after complete III. POLYSACCHARIDES
crystallization of sucrose; only disaccharide in free state; Homoglycans – polysaccharides that yield one type of
food and ethanol industry monosaccharide unit upon hydrolysis
Maltose – malt sugar; produced-germination of barley; o Starch – temporary storage form of photosynthetic products
glucose + glucose, α-1,4 bond; major degradation product of from:
starch; reducing sugar (beer, ovaltine, cereal drinks); glu + glu Zea mays – corn
+ glu = maltotriose (oligosaccharide – 3-10C) Triticum aestivum – wheat
Lactose – milk sugar (cow’s milk); glucose + galactose, β-1,4 Solanum tuberosum – potato
bond; reducing sugar; milk products: Oryza sativa – rice
1. Whole milk –(sit)-> butter Maranta arundinacea – arrowroot
2. Butter milk –(churn)-> cream Constituents:
3. Skimmed milk -> whey Bases of Amylose Amylopectin
(rennin – young calf) coagulum –(tx)-> cheese Differences
Structure Linear/Helical Branched
* Kamyss – fermented spoiled milk
250-300 units (every 25-30 mins)
* Condensed Milk – partial condense autoclave, evapo α-1,4 1000 or more
Lactulose – fructose + galactose, β-1,4 bond; alkaline α-1,4 and α-1,6
rearrangement of lactose; converted by lactose to lactic and Solubility Insoluble Soluble
acetic acid, which causes irritation of the intestines and in water
subsequent cathartics – ideally used with MI and stroke Iodine test Deep/Dark blue Blue violet/purple
Enzymes that breaks down starches:
1. Alpha amylase – present in pancreatic juice and saliva;
PRODUCTS OF OXIDATIVE METABOLISM
*metabolism/breakdown of carbohydrates starts in
Cherry Juice – ripe fruit of Prunus cerasus (Rosaceae); contains
mouth
pectin and 1% malic acid; cherry syrup
2. Beta amylase – hydrolyses starch to nearly pure
Plant Acids – uses: acidulants in effervescent formulations;
maltose
component of buffer systems
Uses: tablet filler, binder and disintegrant; antidote for
o Citric Acid – Scheele – lemon juice (1784); citric –
iodine poisoning
Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) –(Deniges Test)-> tartaric (by
Starch Preparations:
product, dicarboxylic) = wine
1. Pregelatinized starch – chemically or mechanically
o Lactic Acid – acidulant – infant feeding formula, feminine
processed to rupture all or part of granules; tablet
wash (0.2% chlohexidine – vaginal; 0.6% - mouth) – (INSERT)
binder
Alcohol/Ethanol – 95% ethanol by volume 15.56oC; product of
2. Sodium starch glycollate – disintegrating agent
fermentation; undergo process of distillation to concentration
3. Hetastarch - >90-99% amylopectin; plasma expander;
the alcohol content to 40-55%; low conc. – CNS stimulant; high
hydroxyethylstarch; Voluben®
conc. – CNS depressant
4. Glutens – tacky proteins that impedes flow of starch
o Brandy - wine
o Glycogen – storage polysaccharide in animals; more
o Whiskey – malted grain
branched than starch (every 10); red color with iodine
o Rhum - molasses
o Inulin – polyfructan of fructofuranose; Chicorium intybus
o Diluted Alcohol – 48.4-49.5% ethanol at 15.56% oC
(Asteraceae) – chicory root; improve digestion; Uses:
ingredient in culture media; evaluation of renal function
PRODUCTS OF REDUCTIVE METABOLISM
o Dextran – glucosan; Leuconostoc mesenteroides; plasma
Mannitol – from manna, dried exudate of Franxinus ornus;
expander
osmotic diuretic and osmotic laxative, GFR; used in people
o Cellulose – structural polysaccharide in plants (from the hair
with neurological trauma
of seeds of Gossypium hirsutum)
Sorbitol – from berries of mountain ash, Sorbus aucuparia; aka
Purified/Absorbent Cotton – surgical dressing
D-glucitol; tastes ½ sweet as sugar; used in manufacture of
Soluble Guncotton/Pyroxylin – formed by action of nitric
toothpaste and chewing gum xylitol as alternative
and sulfuric acid on cotton; Other ingredients: castor oil
(flexibility); camphor (water-proof); Use: topical
protectant
Other Cellulose Derivatives – cellulose acetatephthalate
(CAP) – coating agent; methylcellulose and ethycellulose –
artificial tears
PAGE 3 OF 11 © MANOR REVIEW CENTER NOTES (K.L)
o Chitin – structural polysaccharides in animals; exoskeleton: SEED GUMS
mollusks and arthropods; homoglycan of N- GUM SOURCE
acetylglucosamine Psyllium Seed coat of:
Chitosan – deacetylation of chitin; water purification Plantago psyllium – Spanish
Plantago ovata – Blonde
Glucosamine – acid deacetylation and hydrolysis of chitin
Cydonium/Quince Seed Ripe seed of Cydonia vulgaris
Heteroglycans – polysaccharides that yield more than one Guar Gum or Guaran Endosperm of Cyamopsis
types of monosaccharide units upon hydrolysis tetragonolobus
Locust Bean Gum/Carob Pulp Endosperm of the seed of
or St. John’s Bread Ceratonia siliqua Chocolate substitute
B. GUMS AND MUCILAGES MICROBIAL GUM
natural plant hydrocolloids that may be classified as anionic or GUM SOURCE NOTES
non-ionic polysaccharides Xanthan Action of Has a pseudoplastic activity
produced by plants as a protective after injury; upon Gum Xanthomonas enable toothpastes and
hydrolysis, they yield arabinose, galactose, glucose, mannose, campestris on ointments to spread easily
carbohydrates
xylose and other uronic acid derivatives
Pb acetate and alcohol
LINEAR BRANCHED C. PLANT EXTRACTIVES
Solubility Less More Pectin – intracellular cementing materials; partially
Stability Less More methoxylated galacturonic acid (swelling); extract of inner
Use Viscosity enhancers Gelating agents
portion of rind of citrus fruits (pomelo, grapefruit, orange,
ponkan, lemon, calamansi, dalanghita, apple) and apple
GUMS MUCILAGES
Production Pathologic (injury) Physiologic pomace; antidiarrheal agent;
(natural) o Kaopectate – Kaolin + Pectin -> antidiarrheal preparation
Solubility in water Readily soluble Slimy mass o Protopectin – unripe
o Pectin (sol) – just ripe
PLANT EXUDATES BOTANICAL SOURCE o Pectic acid – overripe
Acacia - Gum Arabic -> arabin -> K, Ca, Acacia Senegal
Mg, Arabic acid; mucilage; emulsifier;
suspending agent (33-35%); 12% H2O D. GLYCOSIDES
content; <60% alcohol Heteroglycans; “sugar ethers”; BETA form occur in plants; N-,
S-, C-, O, alpha or beta; regulatory, protective and sanitary
Tragacanth Astragalus gummifer
Types: vermiform (worm); taragacanth
compounds
sorts (tear) Components: glycone (acts as vehicle; inactive) and aglycone
Constituents: Bassorin (swells: 2/3); (genin; basis for classification; active)
traganthin (dissolves: 1/3) CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES
SA: 5-6%
o Unsaturated steroidal aglycone tests
K: galactomannan -> bulk laxative
Karaya – most fetid gum Sterculia gum Sterculia urens Libermann-Burchard = blue/green; yellow for saturated
Indian – Ghatti; alternative fro acacia Anogeissus latifolia Salkowski = red/violet
MARINE GUMS o 2-deoxy sugar glycone test
GUM SOURCE CONSTITUENTS Keller-Killanii test = reddish brown)
Agar or Algae o CARDENOLIDES vs BUFADIENOLIDES (C235-B246)
Japanese Gelidium cartilagineum Agarose CARDENOLIDES BUFADIENOLIDES
Isinglas Gracilaria confervoides Agaropectin - Common (active) - Rare (Bufo sp); (inactive)
Algin Brown Seaweeds Mannuronic acid - C-23 α and β unsaturated 5- - C-24 doubly unsaturated 6-
Macrocystis pyrifera membered lactone ring membered lactone ring
Carageenan Red Algae Kappa-gelling o Digoxin – H2O; Digitoxin – lipid; Desllanatoside –
or Irish Moss Chondrus crispus component
digitalization = rapid
Gigartina mamillosa Iota-gelling
component o Convallaria – Convallatoxin – Lily of the Valley
Lambda – non-gelling o Apocynum – Dogbane – cymarine
component o Adonis – Pheasant’s Eye – adonitoxin
Danish Agar Furcellaria fastigiata Kappa o Black Hellebore – Xmas Rose – hellebrin
o Strophantus – K strophantin (good) G strophantin (bad) –
(toxic)- Oubain
o Sqiuill – Scillarenin -> expectorant (bufadienolides)
PAGE 4 OF 11 © MANOR REVIEW CENTER NOTES (K.L)
ANTHRAQUINONE GLYCOSIDES o Emulsin – amygdalase and prunase (collectively)
o Aglycone: Anthracene o APE = A+P+E
o Use: cathartic <drastic> o Guingard’s Test = brick red/red coloration
o Derivative color: orange Bitter almond – Prunus amygdalus; source of Laetrile (Vit
o Identification Test: Borntranger’s Test B17) – controversial treatment for sickle cell anemia
o Cascara Sagrada – Rhamnus purshianus Wild cherry – Prunus serotina; flavored vehicle,
i. Constituents: expectorant and sedative
Cascarosides A and B – optical isomers of barbaloin Apricots – Prunus armeniaca
Cascarosides C and D – optical isomers of chrysaloin
ii. LANE’s Pill – casanthol, purifiesd mix of anthranol ISOTHIOCYANATE GLYCOSIDES
glycosides o Rapeseed – Brassicca napus; gluconapin
iii. Cured in MgO for 1 year o Watercress – Nastutium officinale; gluconasturtiin
o Frangula or Buckthorn Bark – Rhamnus frangula o Odor test mustard smell (volatile); garlic (allicin)
i. Present in Movicol® – Karaya (laxative) + Frangula o Ferric chloride test blood red (non-volatile)
(cathartics); for constipation o Black Mustart or Sinapis Nigra – Brassica nigra – sinigrin
o Aloe – dried latex or juice of Aloe barbadensis or Aloe vera Sinigrin/sinalbin –(myrosinase)-> allyl/acrinyl
<Curacao aloe>; hybrids of Aloe ferox with Aloe Africana and o White Mustard – Brassica alba – sinalbin
Aloe spicata <Cape aloe>; (cathartics and BURNS) FLAVONOL GLYCOSIDES – flavonoids or bioflavonoids from
i. Constituents: barbaloins and aloe emodin citrus fruits and soya
o Rhubarb – glucohein o Rutin and Hesperidin – vitamin P or permeability factors;
Rheum or Chinese Rhubarb Indian Rhubarb or Himalayan treatment of capillary bleeding secondary to capillary
(Therapeutic) Rhubarb (Ornamental) fragility
Rheum officinale Rheum emodi
o Hesperitin, Diosmin, and Naringen – treatment of
Rheum palmatum Rheum webbianum
symptoms of common colds
o Senna – dried leaflet of Cassia acutifolia <Alexandria>;
o Yellow Pigment – rutin and quercetin
Cassia angustifolia <Tinnevelly>; cultivated in wat lands
o Milk Thistle – Silybum marianum; silibinin, silymarin,
resembling rice paddies; derivative color: blue green
hepatoprotective
Constituents: Sennosides A, B, C, and D
o Gingko – Ginggko biloba; gingkolides, bilolabides; memory
o Chrysarobin – from Goa powder, Andira araroba; only
enhancement
anthraquinone glycoside that is NOT used as cathartic
ALCOHOL GLYCOSIDES – Salicin – salix and populous
because it is very irritating; used as keratolytic; hot benzene
o Salix purpurea and Salix fragilis
is used to extract this substance
o Aglycone: saligenin
SAPONINS – foam upon shakin (froth test); bitter, acrid taste;
o Anti-inflammatory; anti-rheumatic
sternutatory (may irritate mucous membrane = sneezing);
o Tests:
destroy RBCs of cold blooded animals -> fish poisons; froth,
Fehling’s – brick red
hemolysis, capillary
Nessler’s – gray
o Glycyrrhiza or Licorice – dried roots of Glycyrrhiza glabra;
Tollen’s – silver mirror
increase foaminess of beer
Schiff’s – recolorization
Constituents: glycrrrhizia, glycyrrhziac acid
ALDEHYDE GLYCOSIDES
o Dioscorea or Yam
o Vanilla – cured fruit of Vanilla planifolia (orchidaceae) –
Dioscorea spiculiflora – contains diosgenin which is a
Mexican, Vera Cruz, Bourbon
glucocorticoid precursor;
Constituent: vanillin
Dioscorea floribunda – best source of steroids;
Use: flavoring agents
Diosgenin – anti-inflammatory
o Ginseng – Panax ginseng (Asia); Panax quinquefolius PHENOL GLYCOSIDES
(American); aphrodisiac and an adaptogen o Urva ursi – dried leaf of Arctostaphylos urva ursi
Constituents: panaxosides, ginsenosides, Constituents: arbutin (hydroquinone + sugar)
chikusetsusaponins Use: astringent and diuretic
o Poison Ivy (Rhus radicans) and Poison Oak (Rhus
CYANOPHOIC OR CYANOGENIC GLYCOSIDES
toxicondendron); uroshiol – delayed contact dermatitis (type
o Amygdalin (H2O and amygdalase) mandelonitrile glucose
IV)
(H2O and prunase) mandelonitrile + glucose
benzaldehyde +HCN
o Rosaceae
PAGE 5 OF 11 © MANOR REVIEW CENTER NOTES (K.L)
LACTONE GLYCOSIDES deposit ova); constituent: tannic acid (Gallic + Ellagic = Tannic
o Coumarin – from Tonka beans, Dipteryx odorata; [GET]) astringent
constitutents: dicoumarol bishydroxycoumarin Chinese/Japanese Gall – Rhus chinensis; Aphis sp. – gallic acid
anticoagulant, Warfarin; Test for unsaturated lactone: (Bismuth subgallate – protectant; deodorizer for flatulence)
Kedde’s = blue-violet
o Cantharides – from dried insect, Cantharis vesicatoria; III. LIPIDS
Russian/Spanish fly; Blistering fly FIXED OILS FATS WAXES
Constituents: cantharidin-irritant, vesicant and Long chain fatty Long chain fatty Long chain fatty
rubefacient acids + glycerol acids + glycerol acids + high
Causes priaprism – sustained erection From vegetables From animals molecular weight
o Psoralens – photosensitizing furocoumarins; from Bishop’s Liquid at room Sold at room temp alcohol (cetyl
flower, Ammi majus temp EXCEPTIONS: alcohol, stearyl
EXCEPTIONS: Liquid F: Cod liver alcohol)
Methoxsalen – repigmentation in vitiligo Solid FO – oil EXCEPTIONS:
Trioxsalen Theobroma, Liquid W: Jojoba
Myristica oil
USE: storage USE: storage USE: protectant
II. TANNINS
Complex substances or polypeptides that are difficult to
Fatty Acids
separate because they do not crystallize
o Saturated – capric, lauric, myristic, palmitic, stearic,
Phenolic in nature; non-crystallizable polyphenols; protein
arachidic
precipitant (astringent); found in barks and leaves
o Unsaturated (=) – palmitoleic, oleic, linoleic, linolenic,
Local sources: arachodonic
o Guava – Psidium guajava
Uses: emollients; vehicles for IM injection (COCOPESE);
o Kamachile – Pithecolobium dulce
cathartic (castor oil); soap production; increase caloric value
o Duhat – Syzigium cumini
(TPN)
Characteristics:
USP Tests:
o Acidic
o Acid value or Acid number – mg of KOH needed to neutralize
o Sharp puckering taste
free FAs
o Causes precipitation of alkaloids
o Saponification value – mg of KOH needed to saponify the
o Industrial – leather and ink
esters
o Clinical – astringents – GI or skin, treatment of burns
o Iodine value – g of iodine absorbed in 100g of sample
Chemical classes: (True tannins vs Pseudo tannins –
Expression – cold-pressed oil; hot-pressed oil; only from fixed
chlorogenic acid and catechins)
oils
A. True Tannins – animal skin leather; (+) Gold Beater’s Skin
Rendering – fats
Test
Solvent extraction – fats; hexane – best solvent for extracting
i. Hydrolyzable – readily hydrolyzed to yield phenolic acids
fats
and sugars
Types of oils – ability to absorb oxygen; oxygen saturates
Pyrogallol
double bonds forming oxides that polymerize to form films;
Leather: bloom
paint industry
FeCl3 = blue-black; Br2 test = (-)
IODINE VALUE RANGE EXAMPLES
ii. Non-hydrolyzable (aka Condensed Tannins/
Non-drying <100 Olive; Almond
Phlobatannins) – results from condensation of catechin Semi-drying 100-120 Cottonseed; Sesame
and leucocyanidin Drying >120 Linseed; Cod liver oil
tend to polymerize phlobaphenes (red colored Reactions of Lipids
product) o Hydrogenation – liquid oil to semi-solid fat; passing of H
Leather: tanners red with Pd/Ni in 160-200oC; shortening and cooking fat
FeCl3 = green-black; Br2 test = (+) o Sulfation – reaction with sulfuric acid; temp at chilling;
B. Pseudo Tannin sulfates adds to double bonds, surfactants
Hamamelis Leaf – Witch Hazel Leaf, dried leaf of Hamamelis
viriniana; constituent: hamamelitanin; used for hemorrhoids
Nutgall – excrescence obtained from young twigs of Quercus
infectoria, Fagacea (when Cynips tinctoria bores a hole to
PAGE 6 OF 11 © MANOR REVIEW CENTER NOTES (K.L)
IV. FIXED OILS Cod Liver Oil – from Gadus morrhua; sclerosing agent to
obliterate varicose veins; source of vitamin A and D (Scott’s
SEED OILS
FIXED OIL BOTANICAL SOURCE
emulsion)
Cottonseed Oil – IM injection; not Gossypium hirsutum Undecylenic Acid – pyrolysis of ricinoleic acid from castor oil;
edible; constituent: gossypol –x-> male has antifungal property
sterility; ID test: Halphen/Bevan Azelaic Acid – onolysis of Castor oil; anti-acne
Sesame Seed Oil – Benne/Teel Oil; Sesmum indicum
uses: IM injection, edible; constituent:
sesamol (phenol) – self-preserving + VI. WAXES
lignin sesamolin & pyrethrin Spremaceti – head of spermwhale, Physeter macrocephalus;
insecticides; ID test: Bauduoin
synthetic spermaceti – cetyl ester wax
Coconut Oil – constituents: lauric, Cocos nucifera
myristic, triclycerides Jojoba Oil – seeds of Simmondsia chinensis, Buxaceae;
Castor Oil – tangan-tangan; ricinoleic Ricinus communis hydrogenated form resembles spermaceti; eicosenoic acids:
(good) - cathartic eicosenol and docosenol
trcinoleic (good) Beeswas or Yellow Wax – honeycomb of bees, Apis mellifera;
ricin (toxic) = abrin (jequirity bean)
stiffening agent in plasters and cerates; White Wax – bleached
Peanut Oil – peanut oil cake; peanut Arachis hypogaea
butter; afflotoxin aspergillus (due to yellow wax; myricyl pamitate
improper storage and drying) Carnuba Wax – leaves of Copernicia prunifera; myricyl
Soybean Oil – stigmasterol - steroid; Glycine soja cerotate
lecithin – regulate cholesterol;
antilipemic agents
Corn Oil – germ oil cake – IM injection; Zea mays VII. VOLATILE OILS
antilipemic agents; Hydrogenated Odorous principle in carious plants
volatile oils = sergers Colorless and photosensitive; light resistant tight container in
Safflower Oil – antilipemic agents Carthamus tinctoria
a cool and dry place
Sunflower Oil – antilipemic agents Helianthus anuus
Ethiodized Oil Injection Iodine addition Undergoes auto-oxidation and resinification
product of ethyl ester Plant families:
of fatty acid of Poppy o Glandular hairs or trichomes (lamiaceae labiatae)
seed o Modified parenchymal cells piperaceae
PERICARP OILS o Oil tubes or vittae apiacea (umbelliferae)
FIXED OIL BOTANICAL NOTES o Lysigenous and schizogenous passages pinaceae and
SOURCE
rutaceae
Olive Oil – Olea Grades:
ID test: europaea 1. First Grade Virgin Olive Oil – Physical characteristics:
Milon’s extracted with less pressure o Possess characteristic odors, high refractive index, optically
2. Second Grade Virgin Olive Oil – active, immiscible in H2O but can be sufficiently be soluble
pulp in #1 is extracted with more to impart odor in water aromatic water
pressure
VOLATILE OILS FIXED OILS
3. Technical Oil – extracted with
hot water Distillation Saponification
4. Sulfur Grade – extracted with Resinification Rancidity
(-) Grease Spot (+) Grease Spot
Carbon disulfide; inferior quality
5. Tournant Oil – fallen and Methods of Obtaining Volatile Oils
decomposing fruits Distillation
o Water Distillation – dry sample; turpentine oil
V. FATS AND RELATED COMPOUNDS o Water and Steam Distillation – dry sample; clove and
cinnamon oil
Theobroma Oil – Theobroma cocao; food for the gods
o Steam Distillation - peppermint and spearmint
o Uses: cocoa syrup – beverage; cocoa butter – suppository
o Destructive Distillation – empyreumatic oils (heat without
base (melts at 30-35oC)
access of air); pinaceae and cuppressiaceae – only family to
o Nibs prepared cacao/breakfast cacao
use destructive distillation (“char”)
Lanolin – purified fatlike substance from wool of sheep Ovis
Enzymatic Actions – mustards
aries, Boviidae; contains 25% water; Uses: water absorbable
ointment base; emollient Expressions
o Anhydrous lanolin – woolfat (contains 0.25% water) o Ecuellle and Piquer – rolling a fruit in a trough line with
sharp tiny projections enough to puncture the rind – citrus
fruit
PAGE 7 OF 11 © MANOR REVIEW CENTER NOTES (K.L)
o Enfleurage – flower petals (or small plant part) on a fatty 1. Camphor – Cinnamomum camphora; natural
pomade followed by EtOH extraction camphor: (+); synthetic camphor: racemic (-); anti
Components of Volatile Oil pruritic, rubefacient, anti-infective
STEREOPTENE ELEOPLENESES 2. Spearmint – Mentha spicata; carvone (-); (+) carvone
- Solid oxidized hydrocarbon portion - Liquid hydrocarbon portion – same odor as caraway (Carum carvi)
- Menthol - Methysalicylate 3. Buchu Oil – Berosma betulina; diosphenol; menstrual
- Amenthol - Encalyptol
- Thymol - Eugenol problem, carminative, anti-rheumatic
4. Wormwood/Quinghaosu – Artemia annua; Artemisia
Medicinal and commercial use: fabrication of perfumes ketone and camphor; anti-malarial artemisinin,
o Top Notes – (smell – minute to hour); most volatile product; artenether, artesunate
leave skin readily – lemon (limonene – most used flavorant), Phenol Volatile Oil
lavender, anise oil 1. Clove Oil – Engenia caryophyllus; eugenol; toothache
o Middle Notes – (3-6 hours); intermediate tenacity and drops, dental analgesic
volatility – thyme, neroli and rose oil 2. Thyme – Thymus vulgaris; thymol antifungal and
o Base Notes – (long hours); low volatility and high tenacity; antibacterial
aka Fixatives = staying power 3. Creosole Oil – Fagus grandiflorus; creosole
Musk – dried secretion from the preputial follicles of the disinfectant, guiacol
male musk deer of Asia, Moschus spp – muskane 4. Jupiter Tar – Juniperus oxycedrus; cadinene; anti-
Civet – glandular secretion appearing in an outwardly exzema Polytar®
discharging pockets of civet cat, Paracloxutus hermaphrodites Phenolic Ether Volatile Oil
Amber gris – most valuable material; pathologic product 1. Nutmeg/Myristica Oil – Myristica fragrans;
formed in stomach of spermwhale when if feeds on squid or constitentuents: safrole and myristicin; halloahogen
cattlefish (ambrein) 2. Anise Pimpenella – Pimpenella anisum –
Constituents of Volatile Oils: anisaldehyde, transanethol
o Terpenes – natural products whose structure are made up 3. Fennel – Freniculum vulgare; fendiole, transanethole
of isoprene units:
Monoterpene – 2 Sesquiterpene - 3
Hydrocarbon Volatile Oils Diterpene - 4
1. Turpentine Oil – Pinus palustris; rectified tuperntine; Triterpene - 6
terpinhydrate/terpinol – expectorant; α and β Tetraterpene – 8
pinene o Acetate-Mevalonate Pathways
** turpentine oil + NaOH = rectified turpentine o Shikimic Pathway – aromatic compound
** RT + HNO3 = terpinhydrate/terpinol
2. Peppermint Oil – Mentha piperita; menthol VIII. RESIN AND RESIN COMBINATION
(antipruritic) (+) synthetic, (-) natural; Japanese RESINS – amorphous products with complex chemical nature;
Peppermint Oil – Mentha arvensis; increase menthol hard transparent or translucent and when heated they soften
concentration; flavorant, carminative, stimulant and melt; complex mixtures of:
counter – irritant *****INSERT HERE********* Resin acids
Aldehyde Volatile Oil Resin alcohols
1. Cinnamon Oil – Cinnamomum loureiril; Cinnamomum Resinotannols
zeylanicum; Cinnamomum cassia (aka cassia oil); Esters
constituent: cinnamaldehyde; uses: flavoring, Resenes – B-complex neutral substances devoid of
carminative, antiseptic characteristics
2. Lemon Peel Oil – rind of the fruit Citrus limon; lemon RESIN SOURCE CONSTITUENTS/NOTES
oil; citral and limonene Rosin/Colophony Pinus palustris
3. Citronella Oil – leaves of Cymbopogon winterianus – Podophyllum Podophyllum Podophyllin – caustic agent
tanglad; citronellal; insect repellant peltatum for warts
4. Hamamelis Oil – Hamamelis virginiana; 2-hexanal; Peltatin – purgative
Podophyllotoxin –
hemorrhodal preparation etoposide, tenoposide
Ketone Volatile Oil Eriodictyon/Yerba Eriodictyon
Santa californicum
PAGE 8 OF 11 © MANOR REVIEW CENTER NOTES (K.L)
Jalap Exogonium Jalapin and purganol – o Secondary – fermentation of primary bile acids by intestinal
purge drastic purgative flora; desoxycholic acid, litocholic acid
Mastic Pistacia Masticin and mastichic acid
Steroid Hormones
lentiscus
Kava/Kava-kava Piper Styrylpyrones – yangonin, o Glucocorticoids – carbohydrate metabolism; anti-
methysticum kawaiin, methysticin inflamatory; cortisone, cortisol
Cannabis/Indian Tops of Resin: Hashish o Mineralocorticoids – electrolyte and water balance;
Hemp/ Cannabis Constituets: THC, aldosterone
Marijuana/Pot sativa Cannabidiol, nabilone o Sex Hormones – Males: androgens, testosterone; Females:
Duquenois Test: violet on
chloroform layer
estrogen, progestin
RESIN COMBINATIONS:
Oleoresins – volatile oils + resin X. ALKALOIDS
OLEORESINS SOURCE CONSTITUENTS Bitter, basic nitrogenous compounds; physiologically active;
Turpentine/ Pinus palustris most of them ends in –ine;
Gum Turpentine
Nitrogen can be: Primary amine – RNH2; Secondary amine –
Capsicum/ Capsicum frutescence Capsaicin –
Cayenne Pepper C. annum var longum vesicant; irritant R2NH; Tertiary amine – R3N
– African chilles (Louisiana long pepper) All are solids except for: [CANS]
Ginger Zingiber officinale Zingebol and o Coniine – Coniium maculatum; poison hemlock (Socrates)
bisabolene – o Arecoline – scotchbroom (Cysticus coparius), lupin – Lupinus
stomachic;
mutabilis – anti-arrhythmic
antibacterial
White Pine Pinus strobus o Nicotine
Balsam of Copaifera spp. o Sparteine
Comaiba Alkaloidal Reagents – form double salts with compounds of
Oleo-Gum-Resin – volatile oil + gum + resin mercury, gold, platinum, and other heavy metals
o Myrrh/Gum Myrrh – Commipholra molmol; use: astringent o Wagnner’s Reagent – iodine in KI (red-brown)
(Astring-o-sol®) o Mayer’s Reagent – potassium mercuric iodide (cream)
o Asafetida – Devil’s dung; Ferula asafetida o Valser’s Reagent – mercuric iodide (white)
Balsams – mixtures that contain cinnamic acid, benzoinc acid o Dragendorff’s Reagent – potassium bismuth iodide (orange)
or both or esters of these acids o Bouchdart’s Reagent – iodine in KI, most sensitive
BALSAM SOURCE o Marme’s Reagent – K cadmium iodide
Storax/Styrax – wound healing; Liquidambar o Sonnencheims’s Reagent – phosphotungstic acid
perfumery; storesin (α and β – Levant’s orientalis
o Hager’s Reagent – picric acid
storax 50:50); pharmaceutic and
compound benzoic tincture (benzoin, o Gold compounds
storax, tolu balsam, aloe, ethyl alcohol) o Tannic acid
Peru Balsam – parasiticide Myroxylon pereirae
Tolu Balsam – flavorant, expectorant; Myroxylon balsamum
compound benzoic tincture (benzoin,
A. PYRIDINE-PIPERIDINE ALKALOIDS
storax, tolu balsam, aloe, ethyl alcohol) Nicotine – leaves of Nicotiana tabacum; use: CNS stimulant;
Benzoin – Sumatra; Siam topical Styrax benzoin smoking deterrent (Nicoret®)
compound benzoin tincture Areca, Areca Nut or Betel Nut – dried ripe seed of Areca
Resin Acids – oxyacids (-COOH and phenik) catechu; arecoline – anthelminthic-taenicid; tannin content
Glycoresin – resin + carbohydrate causes oropharengeal cancer; catechutannin cancer
causing
IX. STEROIDS Lobella – Indian tobacco; Lobella inflata; Lobeline – CNS
Compounds with CPPP; metabolites of mevalonic pathways stimulant and smoking deterrent (Bantron®)
Sterols
o Cholesterol – animals B. TROPANE ALKALOIDS (Solaneous alkaloids)
o Ergosterol – fungi Belladona – Atropa belladonna; anticholinergic, mydriatic; (-)
o Phytosterol – plants hyoscyamine atropine]
Bile Acids Hyocyamus or Henbane – leaves of Hyscyamus niger, 0.04%;
o Primary – directly from cholesterol (liver); cholic acid, hog +bean toxic to swine
chenodeoxycholic acid Egyptian Hyoscyamus or Egyptian Henbane – hyoscyamus
muticus, 1.5%
PAGE 9 OF 11 © MANOR REVIEW CENTER NOTES (K.L)
Duboisia – Duboisia myoporoides o Hydromorphone – more potent analgesic; less frequent SE
Withania – Withania somnifera; commercial sources of o Apomorphine – condensation of morphine + HCl; use:
atropine3 emetic
Stramonium or Jimson Weed/Jamestown Weed – Datura o Hydrocodone - antitussive
stramonium Solanaceae; Talumpunay; used for asthma and o Opiates – natural source
COPD burned then vapors are obtained Morphine – Serturner; most important, most abundant,
Mandragora or European Mandrake/Satan’s Apple – roots of narcotig analgesic
Mandragora officinarum; mandragorine; potent poison Codeine – P. Robiquet; most widely used opium alkaloid;
Cocaine – Huanuco coca – Erythroxylon coca; Truxillo coca – E. obtained from methylation of morphine; methymorphine
truxillense; crack/coke; psychomotor stimulant, local – antitussive
anesthetic; Brompton’s cocktail Noscapine – non-narcotic opium alkaloid; antitussive;
Atropine – antispasmodic; antisialogogue; mydriatic and anarcotin/narcotine
cycloplegic; antidote for cholinesterase inhibitors; (+) inotropic Papeverine – smooth muscle relaxant, antitussive
agent Thebane
Scopolamine or Hyoscine – treatment form motion sickness;
Trans-scop® or Transderm® E. INDOLE ALKALOIDS (Tryptophan)
Rawolfia Serpentina – dried root of Raubolfia serpentina;
C. QUINOLINE ALKALOIDS constituent: reserpine – treatment of snake bites to insanity,
Cinchona – Red cinchona bark – Cinchona succirubra; Yellow hypotensive effects, sedative and tranquilizong properties
cinchona bark – C. calisaya; “cinchonism”; Quinine, Quinidine Chichirica/Catharanthus/Vinca – Cantharanthus roseus;
– antimalarial; Thalleioquin test = fine blue fluorescence then constituents: vinscristine and vinblastine; lymph, hodgkins;
green ppt aka Periwinkle
Cuprea – Remijia purdieana, Cupreaceae; commercial source Nux Vomica – dried ripe seed Strychnos nux vomica; Strychnos
of quinidine Ignatii (St. Ignatius Bean) – commercial source of strychnine;
constituents: strychnine (toxic central stimulant)
Mandelin’s Test = violet; Brucine (alcohol denaturant)
D. ISOQUINOLINE ALKALOIDS
Physostigmine/Eserine – local sources: calabar, ordeal, or
Ipecac – dried rhizome and rood of Cephaelis ipecacuanha; Esere Bean; from Physostigma venenosum; treatment of
constituent: emetine or methylcephaeline; use: ipecac syrup – Glaucoma
emetic
Ergot – dried sclerotium of Claviceps purpurea on rye, secale
o Ipecac fluidextract is 14 times more potent
cereal; constituents: ergonovine (ergometrine & metylsergide
o Ipecac + Opium = Dover’s Powder (diaphoretic)
– prophylaxis for migraine) – oxytoxic agent, ergotamine
o Paregoric – camphorated opium tincture o Lysergic Acid Diethylacmide – most active and most specific
o Laudanum – deodorized opium tincture psychomimetic drugs
Sanguinaria or Bloodrood – Sanguinaria Canadensis;
constituents: saguinarine; use: stimulating expectorant and
emetic F. IMIDIZOLE ALKALOIDS
Tubocurarine Chloride – aka curare or south American arrow Pilocarpine – leaflets of Pilocarpus jaborandi; treatment of
poison; Strychnos castelnaei; constituent: tubocurarine – glaucoma
skeletal muscle relaxant
o Pot – clay G. STEROIDAL ALKALOIDS
o Tube – bamboo Green Hellebore/Veratum viride – roots of Veratrum viride;
o Calabash – gourd use: cardiac depressant; (-) inotrope
o Standardization of Tubocurarine – Head Drop Assay in Black Hellebore – cardiac stimulant; (+) inotrope
Rabbits – least amount of drug capable of producing muscle White Hellebore/European Hellebore – roots of Veratum
relaxation so that head of animal drops in a characteristic album; insectesies
manner
Opium or Gum Opium – unripe poppy seed capsules of
Papaver somniferum; only legal source is India; stone of
immortality; Marquis Test: opiods (purple); synthetic
o Diacetlymorphine – Heroin; acetylation of morphin;
increase danger of habit formation (very potent)
PAGE 10 OF 11 © MANOR REVIEW CENTER NOTES (K.L)
H. ALKALOIDAL AMIDES
Ephedra/Ma Huang – ephedrine; overground portion of
Ephedra sinica; nasal decongestant; bronchodilator
Colchicine – Colchicum autumnale, Liliaceae; used in plant
genetics because it can double the chromosomes
Khat/Abyssynian Tea – fresh leaces of Catha edulis;
constituents: cathinone amphetiamine like effects
Peyote/Mescal Buttons – aka “shrooms”dried tops of
Lophophora williamsii; hallucinogenic and euphoric agent;
constituent: mescaline (psilycybe psilocybine)
I. PURINE ALKALOIDS/METHYLXANTHNES
Cannot be precipitated by any alkaloidal reagents
Caffeine – 1,3,7-trimethylxanthine *INSERT STRUCTURES*
o Kola, Cola or Kolanuts – dried cotyledon of Cola nitida
o Coffee Bean – dried seeds of Coffea Arabica
o Amaic Acid Test: Red-brown/transient purple
o C. robusta; C. liberica
Chlorogenic acid + caffeine (+ caffeole) –(∆)
Decaffenieted coffee – 0.08%
o Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors – diuresis; increase gastric
secretions; inhibit uterine contraction; weak (+)
chronotropic and inotropic effects
Theophylline – 1,3-dimethylxanthine; leaf buds of Camellia
sinensis; treatment of bronchial asthma; tocolytic agent
o Aminophylline – semi-synthetic theophylline derivative –
treatment of bronchial asthma
Green Tea (Fresh) – China and Japan
Black Tea (Fermented) – India and Sri Lanka (Ceylon)
Theobromine – 3,7-dimethylxanthine; seeds of Theobroma
cacao; diuretic in cardiac and pulmonary edema
PAGE 11 OF 11 © MANOR REVIEW CENTER NOTES (K.L)
You might also like
- Module 2 - Pharmacognosy PDFDocument22 pagesModule 2 - Pharmacognosy PDFMeg MayorNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy Lecture NoteDocument47 pagesPharmacognosy Lecture NoteAhmed Mohamed Ibrahim100% (4)
- Brex-Biopharm Best VersionDocument261 pagesBrex-Biopharm Best VersionKate Evangelista100% (2)
- Pharmacognosy NotesDocument9 pagesPharmacognosy Notessaurabh CHATURVEDI100% (2)
- Pharmacognosy NotesDocument33 pagesPharmacognosy Notesanon_888508229100% (1)
- Pharmacognosy AnswersDocument22 pagesPharmacognosy AnswersRaghu Srujann100% (4)
- Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics: Pharmacy Board Review Module 4Document73 pagesBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics: Pharmacy Board Review Module 4Kate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Phle Reviewer Module 2 - PharmacognosyDocument52 pagesPhle Reviewer Module 2 - PharmacognosyMayrigen Dominguez100% (1)
- Pharmacognosy RevisedDocument14 pagesPharmacognosy RevisedYishka ZaireahNo ratings yet
- Manor Supplementary Notes PCOGDocument32 pagesManor Supplementary Notes PCOGBenjamin TNo ratings yet
- Phle Reviewer Module 4 - Pharmacology-PharmacokineticsDocument134 pagesPhle Reviewer Module 4 - Pharmacology-PharmacokineticsMhiel Bhon RamzNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Physical PharmacyDocument7 pagesModule 5 Physical Pharmacycrayon100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry - I (5exp)Document46 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry - I (5exp)988728777950% (4)
- Manufacturing Pharmacy Lecture HandoutsDocument23 pagesManufacturing Pharmacy Lecture HandoutsKate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Jurisprudence and Ethics ManualDocument41 pagesPharmaceutical Jurisprudence and Ethics ManualMeg Gutierrez75% (16)
- Area 2 PCOG LECTURE CARBS TO LIPIDS PDFDocument172 pagesArea 2 PCOG LECTURE CARBS TO LIPIDS PDFMishella OconNo ratings yet
- Advanced PharmacognosyDocument13 pagesAdvanced Pharmacognosypharmaci88% (8)
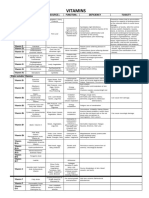
- Phle Reviewer - Minerals VitaminsDocument2 pagesPhle Reviewer - Minerals VitaminsStudy HabitNo ratings yet
- Brex Manufacturing EditedDocument291 pagesBrex Manufacturing EditedMing MingNo ratings yet
- Scope of PharmacognosyDocument6 pagesScope of PharmacognosyDr. Mussadiq Latif88% (16)
- Phle Reviewer Module 6 Qa QCDocument66 pagesPhle Reviewer Module 6 Qa QCMARIA FREDIJEAN CARIÑONo ratings yet
- Crude Drugs and Their ClassificationDocument8 pagesCrude Drugs and Their Classificationmueen hashmi100% (1)
- Pharmacognosy I (Part 1)Document38 pagesPharmacognosy I (Part 1)Andra Ispasoiu100% (1)
- Pharmacognosy Lab Manual for Pharmacy StudentsDocument53 pagesPharmacognosy Lab Manual for Pharmacy StudentsKrunal Chorey71% (7)
- Red PacopDocument74 pagesRed Pacoplyn lynNo ratings yet
- IncompatibilitiesDocument59 pagesIncompatibilitiesabdullah2020No ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy Handouts (Tannins + Lipids + Oils + Waxes) By, Sir Tanveer KhanDocument23 pagesPharmacognosy Handouts (Tannins + Lipids + Oils + Waxes) By, Sir Tanveer KhanArslan Abdullah80% (15)
- Pharmacognosy Lab ManualDocument29 pagesPharmacognosy Lab Manualjunaidniazi1100% (7)
- Pcog Answer KeyDocument7 pagesPcog Answer KeyJohn Tecson100% (2)
- Pharmaceutical Jurisprudence & Ethics Answer Key-BLUE PACOPDocument30 pagesPharmaceutical Jurisprudence & Ethics Answer Key-BLUE PACOPMelbhon Fabro RamosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacy ReviewerDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacy ReviewerMaiah Dinglasan0% (1)
- Jurisprudence and EthicsDocument22 pagesJurisprudence and EthicsRozamae Magnanao100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Care Principles for Improving Patient HealthDocument9 pagesPharmaceutical Care Principles for Improving Patient HealthJesza IgnacioNo ratings yet
- (BLUE PACOP) Pharmaceutical Jurisprudence & EthicsDocument31 pages(BLUE PACOP) Pharmaceutical Jurisprudence & EthicsDenise Yanci Demiar100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Aids and NecessitiesDocument6 pagesPharmaceutical Aids and NecessitiestriciapascualMD100% (1)
- PCOGDocument118 pagesPCOGJuliane Caniele IndiongcoNo ratings yet
- Dispensing Lecture Reviewer - MidtermDocument26 pagesDispensing Lecture Reviewer - Midtermapi-306968266No ratings yet
- UP - Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument18 pagesUP - Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryKate Evangelista100% (1)
- Perspectives in PharmacyDocument7 pagesPerspectives in Pharmacyjonette carataoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Aids and NecessitiesDocument4 pagesPharmaceutical Aids and NecessitiesJana BlueNo ratings yet
- Diploma in pharmacy Part I: Pharmaceutics I model answersDocument13 pagesDiploma in pharmacy Part I: Pharmaceutics I model answersBMohdIshaq68% (19)
- Dispensing & Medical CounselingDocument25 pagesDispensing & Medical CounselingNik Ferandos100% (1)
- Chemical Tests in PharmacognosyDocument30 pagesChemical Tests in PharmacognosyBINDU100% (9)
- Dispensing 1Document57 pagesDispensing 1janine_figueroa86% (7)
- Pharmacognosy and Plant ChemistryDocument11 pagesPharmacognosy and Plant ChemistryKaithlyn ObispoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy E-Books - PDF DriveDocument2 pagesPharmacognosy E-Books - PDF DriveRajesh singh Bhati0% (1)
- Clinical PharmacyDocument15 pagesClinical PharmacyKate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument19 pagesModule 1 - Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryMichaela100% (10)
- 4phle Reviewer Module 4 Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics 4Document48 pages4phle Reviewer Module 4 Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics 4Jayrine MonteroNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy Lecture # 1 (Glycosides) (By, Sir Tanveer Khan)Document18 pagesPharmacognosy Lecture # 1 (Glycosides) (By, Sir Tanveer Khan)Arslan Abdullah80% (5)
- Pharmacology Notes For Board Exam ReviewerDocument21 pagesPharmacology Notes For Board Exam ReviewerAnaliza100% (2)
- Perspectives On PharamcyDocument12 pagesPerspectives On PharamcyZyreeneNicoleNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Dispensing and CompoundingFrom EverandPharmaceutical Dispensing and CompoundingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Community Pharmacy: Basic Principles and ConceptsFrom EverandCommunity Pharmacy: Basic Principles and ConceptsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- MCQs in Pharmaceutical Sciences for GPAT and NIPERFrom EverandMCQs in Pharmaceutical Sciences for GPAT and NIPERRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Module 2 - Plant ChemistryDocument22 pagesModule 2 - Plant ChemistrySelena MoonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1, 2, and 3Document31 pagesChapter 1, 2, and 3hibiscus-eurie montillanaNo ratings yet
- Tamarind seeds influence oil qualityDocument232 pagesTamarind seeds influence oil qualityCecy Contreras de HernándezNo ratings yet
- Uji Aktivitas Pertumbuhan Rambut Dan Uji Iritasi Sediaan Hair TonikDocument15 pagesUji Aktivitas Pertumbuhan Rambut Dan Uji Iritasi Sediaan Hair TonikastriedamaliaamanatNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Screening in Drumstick PeelDocument9 pagesPhytochemical Screening in Drumstick PeelAllia AsriNo ratings yet
- Condurache Et Al. 2021Document16 pagesCondurache Et Al. 2021NinaNicoletaNo ratings yet
- Activity and Contents of Polyphenolic Antioxidants in The Whole Fruit, Flesh and Peel of Three Apple CultivarsDocument17 pagesActivity and Contents of Polyphenolic Antioxidants in The Whole Fruit, Flesh and Peel of Three Apple CultivarsSimon TemplarNo ratings yet
- Lifelong Vitality BrochureDocument13 pagesLifelong Vitality BrochureAtelier 35No ratings yet
- What Einstein Told His Cook 2 - The Sequel Further Adventures in Kitchen ScienceDocument448 pagesWhat Einstein Told His Cook 2 - The Sequel Further Adventures in Kitchen ScienceIsmail Adha Kesuma67% (3)
- 2329 6836 Pharmacognosy 2014 - AcceptedAbstractsDocument106 pages2329 6836 Pharmacognosy 2014 - AcceptedAbstractsColor BlackNo ratings yet
- OK - Comparative Analysis of Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Effect of Seed Coat ExtractsDocument7 pagesOK - Comparative Analysis of Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Effect of Seed Coat ExtractsOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Aim Global Business - South AfricaDocument36 pagesA Guide To Aim Global Business - South AfricaWa Tu LeeNo ratings yet
- Pomegranate Processing and Value Addition Review 2157 7110 1000565Document11 pagesPomegranate Processing and Value Addition Review 2157 7110 1000565dikadika_tans0% (1)
- Medicinal Benefits of Tamarindus Indica by Pharm Safiya A ShehuDocument14 pagesMedicinal Benefits of Tamarindus Indica by Pharm Safiya A ShehuYPS NetworkNo ratings yet
- Ajwa ReviewDocument11 pagesAjwa ReviewFhirastika AnnishaNo ratings yet
- Chitosan As A Novel Edible Coating For Fresh Fruits PDFDocument17 pagesChitosan As A Novel Edible Coating For Fresh Fruits PDFAnonymous xGc8MRRysNo ratings yet
- Phytochemicals Aging and Health (PDFDrive) - 1Document228 pagesPhytochemicals Aging and Health (PDFDrive) - 1Jorge silvaNo ratings yet
- Adhatoda Vasica: A Critical Review: Sarita M. Kapgate, Abhijit B. PatilDocument9 pagesAdhatoda Vasica: A Critical Review: Sarita M. Kapgate, Abhijit B. PatilSarita KapgateNo ratings yet
- BETEL (Piper Betle) LEAVES EXTRACT AS ANTIBACTERIAL DISINFECTANT SPRAYDocument56 pagesBETEL (Piper Betle) LEAVES EXTRACT AS ANTIBACTERIAL DISINFECTANT SPRAYAbigail MonisNo ratings yet
- Body of ResearchDocument59 pagesBody of ResearchPauline Joy Paras MorsiquilloNo ratings yet
- Kirkman DigestiveEnzymesGuideDocument40 pagesKirkman DigestiveEnzymesGuideeptanNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Inhibition by Naturally Occurring SubstancesDocument5 pagesCorrosion Inhibition by Naturally Occurring SubstancesJefree BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Olive ExtractsDocument5 pagesHealth Benefits of Olive Oil and Olive ExtractsDemar PeartNo ratings yet
- Polyphenol Content and Antioxidant Capacity of Apple Fruit: Effect of Cultivar and Storage ConditionsDocument6 pagesPolyphenol Content and Antioxidant Capacity of Apple Fruit: Effect of Cultivar and Storage ConditionsMohsinNo ratings yet
- Cocoa Processing and Impact On Composition: Jasminka Giacometti Djuro JosicDocument9 pagesCocoa Processing and Impact On Composition: Jasminka Giacometti Djuro JosicShaikh AdilNo ratings yet
- Phenolic Acids, Flavonoids and Total Antioxidant CapacityDocument9 pagesPhenolic Acids, Flavonoids and Total Antioxidant CapacityEva Mayte GuadarramaNo ratings yet
- Spinach: An Important Green Leafy Vegetable and Medicinal HerbDocument7 pagesSpinach: An Important Green Leafy Vegetable and Medicinal HerbSonia BadaNo ratings yet
- Food Research International: Shamraja S. Nadar, Priyanka Rao, Virendra K. RathodDocument22 pagesFood Research International: Shamraja S. Nadar, Priyanka Rao, Virendra K. RathodElizabeth VargasNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry: Asma Yangui, Manef AbderrabbaDocument8 pagesFood Chemistry: Asma Yangui, Manef AbderrabbaANo ratings yet
- Journal of Clinical and Experimental PharmacologyDocument13 pagesJournal of Clinical and Experimental PharmacologyCodruta Sandi100% (1)
- Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Some Traditionally Used Medicinal Plants Affected by The Extraction Time and HydrolysisDocument9 pagesPhenolic Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Some Traditionally Used Medicinal Plants Affected by The Extraction Time and HydrolysisBeatriz MelloNo ratings yet