Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ethers (Eter)
Uploaded by
Irianto Rizaldi FaturrahmanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ethers (Eter)
Uploaded by
Irianto Rizaldi FaturrahmanCopyright:
Available Formats
109.
5
0
Ethers
Definition
Nomenclature
Physical Properties
Reactions
Synthesis
Definition
What are ethers ?
A class of organic compounds in which oxygen
is bonded to 2 carbon groups
General formula: R-O-R
Examples:
CH
3
CH
2
O CH
2
CH
3
Diethyl ether
are like water, with alkyl groups replacing
both of the -Hs:
H-O-H water
R-O-H alcohol
R-O-R ether
relatively unreactive
commonly used as solvents
Structure- functional group
is a Oxygen bonded to 2
carbons
O
CH
3
H
3
C
O O
O
O
Nomenclature
IUPAC: 3-(t-butoxy)-pentane
IUPAC: Methoxyethane
IUPAC: Methoxybenzene
The R-O-R group is strongly polar.
Ethers have two C-O bonds.
Ethers cannot form internal H bonds.
Their boiling points are lower than those of
their alcohol counterparts.
Ethers are better solvents than alcohols for
nonpolar compounds.
Ethers can H bond with water and alcohols
CH
3
CH
2
OH
bp= 78
o
C
CH
3
OCH
3
bp= 36
o
C
Physical Properties
R
:O:
H
H O
R
Hydrogen bonding between
molecules of an alcohols
R
O
R
R
O
R
No hydrogen bonding
Chemical Properties of Ethers
CH
2
CH
3
O CH
3
CH
O CH
3
CH H
I CH
3
CH
2
CH3
HI, H
2
O
CH3
+
Ethyl isopropyl ether Isopropyl alcohol Iodoethane
1. Cleavage of ethers by acids
R-O-R + HX R-OH + RX
O
CH
2
CH
3
HBr, H
2
O
Reflux
OH
CH
3
CH
2
Br
+
CH
3
CHCOOH
OCH
2
CH
3
HI +
100
O
C
H
2
O
CH
3
CH
2
I CH
3
CHCOOH
O
H
+
Phenol
Bromoethane
Iodoethane Lactic acid
Ethyl phenyl ether
2-Ethoxypropanoic acid
Examples:
Examples:
If an excess of acid is used, the
alcohol initially produced is also
converted to an alkyl halide
R-O-R + HX R-OH + RX
R-O-H + HX R-X + H
2
O
2. Reaction with PCl
5
CH
3
CH
2
OCH
2
CH
3
+ PCl
5
2CH
3
CH
2
Cl + POCl
3
CH
3
CH
2
OCH
2
CH
3
+ 2HI
2CH
3
CH
2
l + H
2
O
PREPARATION OF ETHERS
1. Intermolecular dehydration of alcohols
ROH + HOR
H
+
ROR + H
2
O
CH
3
CH
2
OH
CH
2
=CH
2
+ H
2
O
CH
3
CH
2
OCH
2
CH
3
+ H
2
O
Ethene
Diethyl ether
H
2
SO
4
180
o
C
H
2
SO
4
140
o
C
The starting alcohol in the above reaction must be primary and the reaction
temperature must be kept at 140
o
C
2. The Williamson synthesis of ethers
RONa + R' X
X = Br, I
ROR' + NaX
Sodiumalkoxide
Ethers
How to synthesis of ethyl propyl ether (CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
OCH
2
CH
3
)
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
OH + Na
Propyl alcohol
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
ONa
Sodium propoxide
+ 1/2 H
2
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
ONa
+ CH
3
CH
2
I
S
N
2 reaction
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
OCH
2
CH
3
+ NaI
The Williamson synthesis
2-Methoxypropane
(Isopropyl methyl ether)
Iodomethane
(Methyl iodide)
Sodium
isopropoxide
+ +
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
I
CH
3
CHO
-
Na
+
CH
3
CHOCH
3
Na
+
I
-
S
N
2
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CO
-
K
+
CH
3
Br
S
N
2
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
COCH
3
K
+
Br
-
+
+
Potassium
tert-butoxide
Bromomethane
(Methyl bromide)
2-Methoxy-2-methylpropane
(tert-Butyl methyl ether)
Williamson ether synthesis
Important ethers
Diethyl Ether
Diethyl ether is a very low-boiling
Highly flammable liquid
Care should always be taken when diethyl ether
is used in the laboratory, because open flames or sparks
from light switches can cause explosive combustion of mixtures
of diethyl ether and air.
CH
3
CH
2
OCH
2
CH
3
O
2
CH
3
CH
2
OCHCH
3
O OH
explosive
a hydroperoxide
autoxidation
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- OC02 - Alkenes, Alkynes and Cyclic Hydrocarbons - Worksheet - ANSWERSDocument5 pagesOC02 - Alkenes, Alkynes and Cyclic Hydrocarbons - Worksheet - ANSWERSAlizay Imran80% (5)
- Classification Test For HydrocarbonsDocument3 pagesClassification Test For Hydrocarbonscyberlog21267% (3)
- Bayah PDFDocument1 pageBayah PDFIrianto Rizaldi FaturrahmanNo ratings yet
- The Lennard - Jones PotentialDocument3 pagesThe Lennard - Jones PotentialIrianto Rizaldi FaturrahmanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes (Aldehid) & Ketones (Keton)Document29 pagesAldehydes (Aldehid) & Ketones (Keton)Irianto Rizaldi FaturrahmanNo ratings yet
- Msds Benzena PDFDocument6 pagesMsds Benzena PDFIrianto Rizaldi FaturrahmanNo ratings yet
- Rekapitulasi Laporan Narkotika: NO Nama Satuan Stok Awal Pemasukan PBFDocument11 pagesRekapitulasi Laporan Narkotika: NO Nama Satuan Stok Awal Pemasukan PBFBang23 ManikNo ratings yet
- Triacylglycerol and Fatty AcidDocument6 pagesTriacylglycerol and Fatty AcidGil Angelo VillaluzNo ratings yet
- EaDocument30 pagesEaAreIf Cron BmxStreetNo ratings yet
- Word Sarcina TermicaDocument3 pagesWord Sarcina TermicaSergiu AlupoaeNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Buffer SolutionsDocument8 pagesPreparation of Buffer SolutionsStephen S. LaderaNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Polyfunctional Organic CompoundsDocument6 pagesNomenclature of Polyfunctional Organic Compoundsrahul bajajNo ratings yet
- Amines Important Questions.Document16 pagesAmines Important Questions.Rockz RockzzNo ratings yet
- Price List Bahan - Bahan Kimia Per April 2020: Abjad Nama Jenis Harga Eceran Satuan Ralat (Bila Ada) Kemasan UtuhDocument3 pagesPrice List Bahan - Bahan Kimia Per April 2020: Abjad Nama Jenis Harga Eceran Satuan Ralat (Bila Ada) Kemasan UtuhOnar Bin GegerNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Esters Lab Gina Suliman Mr. Kolesnik SCH4U12Document3 pagesSynthesis of Esters Lab Gina Suliman Mr. Kolesnik SCH4U12Gina SulimanNo ratings yet
- AaDocument152 pagesAaVishal Garg0% (1)
- Determination of The Hydroxyl NumberDocument13 pagesDetermination of The Hydroxyl NumberAstri AldelinaNo ratings yet
- PDocument4 pagesPIca zaharaNo ratings yet
- Grade12 Chemistry PA-1 35 MarksDocument4 pagesGrade12 Chemistry PA-1 35 MarkscaceyNo ratings yet
- 12.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids KCET PYQsDocument2 pages12.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids KCET PYQsPunith kumar100% (1)
- Amphoteric HydroxidesDocument3 pagesAmphoteric HydroxidesMohamed IshaqNo ratings yet
- Brain Map Aldehydes and KetonesDocument2 pagesBrain Map Aldehydes and KetonesSameer AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Libro 1Document59 pagesLibro 1YENILAYNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Identification of Functional GroupsDocument14 pagesLab 2 - Identification of Functional GroupsShamaya Murray60% (5)
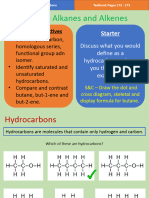
- SC22a Alkanes and AlkenesDocument10 pagesSC22a Alkanes and AlkenesEmaadB EmaadBNo ratings yet
- Name Reactions: Sandmeyer'S ReactionDocument9 pagesName Reactions: Sandmeyer'S ReactionSai Krishnan100% (1)
- Formularium Rs RoyalDocument55 pagesFormularium Rs RoyalFadril LianiNo ratings yet
- NM ObtDocument22 pagesNM ObtIlyan NastiNo ratings yet
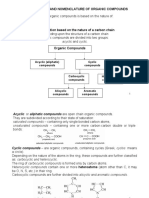
- Classification and Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument10 pagesClassification and Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsДмитрий ЛегаNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of LipidsDocument23 pagesMetabolism of Lipidssima mhammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesChapter 20: Carboxylic AcidsRobert GardnerNo ratings yet
- SCH 2108 - Organic Chemistry 2Document3 pagesSCH 2108 - Organic Chemistry 2Caleb MumohNo ratings yet
- Chem241 Final ExamDocument2 pagesChem241 Final ExamHerya EssaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Nomenclature of Organic Compounds (PB)Document10 pagesActivity 1 Nomenclature of Organic Compounds (PB)Sittie Neharah S. MapandiNo ratings yet