Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metal Casting Processes (Continue #1) : Mata Kuliah Proses Manufaktur Ii Jurusan Teknik Industri Itenas
Uploaded by
Anggita Novitasari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views17 pagesPermanent mold casting uses reusable metal molds to produce castings through high-volume production. Molten metal is poured into the mold and allowed to solidify. This process produces parts with close tolerances, fine grain structure, and good surface finish. However, it is limited to lower melting point metals and simpler part geometries. Variations include slush casting, which drains liquid from a partially solidified casting, and die casting which forces molten metal into a mold under high pressure. Centrifugal casting also uses rotation to distribute molten metal through molds.
Original Description:
Ini adalah power point ttg proses pengecoran.
Original Title
Proses Pengecoran
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPermanent mold casting uses reusable metal molds to produce castings through high-volume production. Molten metal is poured into the mold and allowed to solidify. This process produces parts with close tolerances, fine grain structure, and good surface finish. However, it is limited to lower melting point metals and simpler part geometries. Variations include slush casting, which drains liquid from a partially solidified casting, and die casting which forces molten metal into a mold under high pressure. Centrifugal casting also uses rotation to distribute molten metal through molds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views17 pagesMetal Casting Processes (Continue #1) : Mata Kuliah Proses Manufaktur Ii Jurusan Teknik Industri Itenas
Uploaded by
Anggita NovitasariPermanent mold casting uses reusable metal molds to produce castings through high-volume production. Molten metal is poured into the mold and allowed to solidify. This process produces parts with close tolerances, fine grain structure, and good surface finish. However, it is limited to lower melting point metals and simpler part geometries. Variations include slush casting, which drains liquid from a partially solidified casting, and die casting which forces molten metal into a mold under high pressure. Centrifugal casting also uses rotation to distribute molten metal through molds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
Metal Casting Processes
(continue #1)
1
MATA KULIAH PROSES MANUFAKTUR II
JURUSAN TEKNIK INDUSTRI ITENAS
1. Permanent Mold Casting Processes
2
The economic disadvantage of any of the expendable
mold processes is that a new mold is required for
every casting.
In the permanent mold casting, the mold is reused
many times.
1.1 Permanent Mold Casting
3
It uses a metal mold constructed of two section that are
designed for easy, precise opening and closing.
These mold are commonly made of steel or cast iron.
The cavity, with gating system included, is machined into the
two halves to provide accurate dimensions and good surface
finish.
Metal commonly cast in permanent mold include aluminum,
magnesium, cooper-based alloy, and cast iron.
Cast iron requires pouring temperature. 2300 to 2700 F
(1250 to 1500 C), which take a heavy toll on mold life. The
very high temperature of steel make permanent mold
unsuitable for this metal unless the mold is made of refractory
material.
1.2 Semi-permanent mold casting
4
In the permanent mold casting, a core can be made
of metal, but either their shape must allow for
removal from the casting, or they must be
mechanically collapsible to permit removal.
If withdrawal of a metal core would be difficult or
impossible, sand cores can be used. The mold is
called semi-permanent mold.
1.3 Advantages, limitations, and applications of
permanent mold casting
5
Advantages:
good surface finish, close dimensional control, more rapid
solidification (caused by the metal results in finer grain
structure), strong casting are produced.
Limitations:
The process is generally limited to metal of lower melting
point, simple part (because of the need to open the mold) and
the expense of the mold
Applications:
This is best suited to high-volume production and can be
automated accordingly.
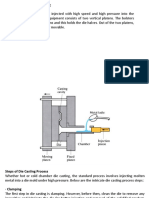
1.4 Steps in permanent-mold casting
6
1.5 Variation in Permanent-Mold Casting
7
Slush Casting
A hollow casting is formed by inverting the mold after partial
freezing at the surface to drain out the liquid metal in center.
Solidification begins at the mold wall since they are relatively
cool and progress over time toward in the middle of the
casting.
Slush casting is used to make statues, lamp pedestals, and toy
out of low-melting-point metals.
The exterior is important, but the strength and interior
geometry of the casting are minor considerations.
1.5 Variation in Permanent-Mold Casting
(continue)
8
Low-pressure casting
1.5 Variation in Permanent-Mold Casting
(continue)
9
Vacuum permanent-mold casting
variation of low-pressure casting in which a vacuum is used to
draw the molten metal in to cavity.
The difference is that reduced air pressure from the vacuum in
the mold is used to draw the liquid metal into cavity, rather
than forcing it by positive air pressure from below.
1.6 Die Casting
10
Permanent mold casting process in which the molten
metal into mold cavity under high pressure.
General configuration:
1.6 Die Casting (continue)
11
There two main types of die casting machine: (I) hot
chamber and (2) cold chamber.
Hot Chamber
1.6 Die Casting (continue)
12
Cold-chamber die casting machines
1.7 Centrifugal Casting
13
Several casting methods in which the mold is rotated
at high speed so that centrifugal force distributed the
molten metal to the outer region of the die cavity.
The group includes (1) true centrifugal casting, (2)
semi-centrifugal casting, and (3) centrifugal casting
1.7 Centrifugal Casting (continue)
14
True centrifugal casting molten metal is poured
into rotating mold to produce a tubular part.
1.7 Centrifugal Casting (continue)
15
Semi-centrifugal Casting used to produce solid
casting rather than tubular parts. G factor are
obtained and the mold are designed with risers at the
center to supply the feed metal.
1.7 Centrifugal Casting (continue)
16
Centrifuge Casting Design with cavities located
away from the axis of rotation so that the molten
metal poured into the mold is distributed to these
cavities by centrifugal force. Used for small part
Thank You
17
You might also like
- CH 7-Methods of CastingDocument44 pagesCH 7-Methods of CastingGosaye DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Special Casting ProcessesDocument31 pagesSpecial Casting Processesdarshan_rudraNo ratings yet
- Permanent Mold CastingDocument15 pagesPermanent Mold CastingEka RosmitaliaNo ratings yet
- Metal CastingDocument28 pagesMetal CastingAngel ChanteyNo ratings yet
- Pressure Die CastingDocument62 pagesPressure Die CastingARUNSFRH83% (6)
- 8 Centrifugal & Die Casting-2Document53 pages8 Centrifugal & Die Casting-2Monsieur PoopNo ratings yet
- Sess 9 (Ceramic Mould - Pressure Die Casting - Centrifugal Casting)Document7 pagesSess 9 (Ceramic Mould - Pressure Die Casting - Centrifugal Casting)Prakash RagupathyNo ratings yet
- DM-1 CO-1 Special Castings MaterialDocument9 pagesDM-1 CO-1 Special Castings MaterialSree vishnu Sai chandan guntupalliNo ratings yet
- Drilling BitsDocument9 pagesDrilling BitsAli AbdelrahemNo ratings yet
- Pressure Die CastingDocument62 pagesPressure Die CastingChetan Nehete100% (2)
- Casting in Manufacturing ProcessesDocument106 pagesCasting in Manufacturing ProcessesAhsan MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Equipment Design and Drawing: Project ReportDocument40 pagesEquipment Design and Drawing: Project Reportsurajagtap01No ratings yet
- Allowable Stresses of Typical ASME Materials - Carbon Steel PDFDocument3 pagesAllowable Stresses of Typical ASME Materials - Carbon Steel PDFMSNo ratings yet
- 1.6.1 Die Casting (Pressure Die Casting) : Module-I of Manufacturing Science-IDocument8 pages1.6.1 Die Casting (Pressure Die Casting) : Module-I of Manufacturing Science-IChinmay Das100% (2)
- Nmos and Cmos FabricationDocument33 pagesNmos and Cmos FabricationmannsloveNo ratings yet
- EIM Electrical Tools Winstonjun N. TuliaoDocument57 pagesEIM Electrical Tools Winstonjun N. Tuliaowinstonjun n. TuliaoNo ratings yet
- Continuous Casting and Mould Level ControlDocument15 pagesContinuous Casting and Mould Level Controlsalvador2meNo ratings yet
- Die CastingDocument6 pagesDie Castingkutik3bugerNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Part C RevisedDocument72 pagesUnit3 Part C Revisedraymon sharmaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice 2 Heat Treatment Carbon Content PreheatDocument10 pagesMultiple Choice 2 Heat Treatment Carbon Content PreheatAhmed Ben Nouma100% (1)
- Unit2 - Limits Fits & Tolerance NotesDocument19 pagesUnit2 - Limits Fits & Tolerance NotesvrmgiteduNo ratings yet
- Hot Working of MetalsDocument27 pagesHot Working of MetalsRommel Blanco100% (1)
- Final Metal CastingDocument38 pagesFinal Metal CastingishanNo ratings yet
- Casting Process: Steps of Casting AreDocument10 pagesCasting Process: Steps of Casting AreReham Emad Ezzat MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lec 5Document39 pagesLec 5Omar AssalNo ratings yet
- ( (Manufacturing) ) : Permanent Mold Casting ProcessesDocument15 pages( (Manufacturing) ) : Permanent Mold Casting ProcessesKarthikeyan MuthukumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Project Document EiDocument66 pagesProject Document EiPrathap ReddyNo ratings yet
- L-13 Dasar-Dasar Proses PengecoranDocument21 pagesL-13 Dasar-Dasar Proses PengecoranGusti Ryanda FazrinNo ratings yet
- 04 CastingDocument26 pages04 CastingSports GloballyNo ratings yet
- Valery Marinov, Manufacturing TechnologyDocument168 pagesValery Marinov, Manufacturing TechnologyAbir Roy100% (3)
- Permanent Mold Casting Processes: Usually Made From Metal Gas Pressure or A Vacuum UsedDocument57 pagesPermanent Mold Casting Processes: Usually Made From Metal Gas Pressure or A Vacuum UsedJacob KussiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document22 pagesLecture 11Huraira AbidNo ratings yet
- 2.14. Multiple-Use-Mould Casting ProcessesDocument3 pages2.14. Multiple-Use-Mould Casting Processesaman chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Metal Mould-Casting Processes: Unit Iv Moulding ProcessesDocument26 pagesMetal Mould-Casting Processes: Unit Iv Moulding ProcessesMr. T. Anjaneyulu Mr. T. AnjaneyuluNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 - Special Moulding Processes PART-2Document25 pagesUnit-3 - Special Moulding Processes PART-2mahammad kamaluddeenNo ratings yet
- CastingDocument8 pagesCastingTody IsfitazliNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and CoolingDocument37 pagesFundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and CoolingSachin RanaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and CoolingDocument40 pagesFundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and Coolingalemu170No ratings yet
- Topic 4 Contemporary Casting ProcessesDocument47 pagesTopic 4 Contemporary Casting ProcesseslucasNo ratings yet
- Types of CastingDocument14 pagesTypes of CastingRamoji Aditya Chary100% (1)
- Permanent Mold CastingDocument4 pagesPermanent Mold CastingcpprodNo ratings yet
- Ch10 Casting Fund WileyDocument38 pagesCh10 Casting Fund WileyAbdur Rahman SultanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - METAL WORK, CASTING PROCESS AND HEAT TREATMENT ON STEELDocument21 pagesChapter 3 - METAL WORK, CASTING PROCESS AND HEAT TREATMENT ON STEELتاج نيسهاNo ratings yet
- ME 330 Manufacturing Processes Casting Processes (Cont.)Document39 pagesME 330 Manufacturing Processes Casting Processes (Cont.)Sibu SibuNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document21 pagesLab Report 2Cherif ChokeirNo ratings yet
- 05 CastingDocument19 pages05 CastingSports GloballyNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy CH 12 and 13 Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesMetallurgy CH 12 and 13 Lecture Notesayaan.works76No ratings yet
- Special Casting MethodsDocument73 pagesSpecial Casting Methods359 Srinivasa RamanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Casting IDocument38 pagesChapter 10 Casting IMinhaj UllahNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Advanced Workshop PracticeDocument28 pagesWeek 2 Advanced Workshop PracticeBasit AliNo ratings yet
- ميحرلا نمحرلا الله مسب Manufacturing Processes 0703314: Solidification and Casting ProcessesDocument45 pagesميحرلا نمحرلا الله مسب Manufacturing Processes 0703314: Solidification and Casting ProcessesAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Ae15301 AMMTDocument98 pagesAe15301 AMMTDurai Raj KumarNo ratings yet
- Valery Marinov Manufacturing Technology PDFDocument168 pagesValery Marinov Manufacturing Technology PDFMostafa Adil50% (2)
- 7continuous CastingDocument10 pages7continuous CastingrushabhkhotNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ten - Fundamental of Metal CastingDocument35 pagesChapter Ten - Fundamental of Metal CastingWael W. AlsousNo ratings yet
- 2nd Class Notes 17.01Document48 pages2nd Class Notes 17.01EDISON OCHIENGNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Moulding Processes: StructureDocument18 pagesUnit 3 Moulding Processes: StructureChethan Madappady75% (4)
- 1st Class 13.01.2020Document18 pages1st Class 13.01.2020EDISON OCHIENGNo ratings yet
- Long AnswerDocument3 pagesLong AnswerVarinder MouryaNo ratings yet
- Applications & Processing of Metal AlloysDocument17 pagesApplications & Processing of Metal AlloysSohaibNo ratings yet
- PNC3 - Casting IIDocument4 pagesPNC3 - Casting IIAlpNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Summaries: Expendable Mold and Permanent MoldDocument4 pagesManufacturing Summaries: Expendable Mold and Permanent MoldSanguinius28No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222Document66 pagesManufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222shahnawaz875No ratings yet
- Thixoforming: Semi-solid Metal ProcessingFrom EverandThixoforming: Semi-solid Metal ProcessingGerhard HirtNo ratings yet
- Single Head Nest Detail: Turbonest F644 20Mm S355 04Document3 pagesSingle Head Nest Detail: Turbonest F644 20Mm S355 04Vv ZzNo ratings yet
- CrystallizersDocument14 pagesCrystallizersAbhishekAyareNo ratings yet
- Defectos de Inclusiones en FundicionDocument31 pagesDefectos de Inclusiones en Fundicionjose.figueroa@foseco.comNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its SettingDocument50 pagesThe Problem and Its SettingSherren Marie Nala100% (1)
- Docslide - Us CH 5 Drilling SK MondalDocument31 pagesDocslide - Us CH 5 Drilling SK MondalKumar UjjwalNo ratings yet
- 980 TDocument6 pages980 TDiego Fernando Cadena ArangoNo ratings yet
- SRU6501 - List of Standard SpecificationDocument3 pagesSRU6501 - List of Standard Specificationstamboli9No ratings yet
- Test Report On Ordinary Portland CementDocument2 pagesTest Report On Ordinary Portland CementjayadushNo ratings yet
- Fabrication Course OutlineDocument4 pagesFabrication Course OutlineOmarNo ratings yet
- Printmaking NotesDocument16 pagesPrintmaking Notesapi-279660401100% (1)
- Engineering Workshop Lab ManualDocument37 pagesEngineering Workshop Lab ManualsaiNo ratings yet
- Br20 - B.Tech. - Mechanical Engineering Syllabus: Course ObjectivesDocument2 pagesBr20 - B.Tech. - Mechanical Engineering Syllabus: Course ObjectivesBashu Dev SanjelNo ratings yet
- Kit B - Edition 12 - Jan 2021Document37 pagesKit B - Edition 12 - Jan 2021Thitikorn WassanarpheernphongNo ratings yet
- 100 Penetration Grade BitumenDocument1 page100 Penetration Grade BitumenJohn SnowNo ratings yet
- BET Katalog-2018 Grabenfraesen 4webDocument44 pagesBET Katalog-2018 Grabenfraesen 4webHUZEYFENo ratings yet
- Case Study Anti Spatter AMPCOLOY® MylarDocument3 pagesCase Study Anti Spatter AMPCOLOY® MylarashwanidusadhNo ratings yet
- MillingDocument3 pagesMillingafif lahNo ratings yet
- SSPC ChartDocument2 pagesSSPC ChartajuhaseenNo ratings yet
- Polymeric Coating For Prevention of Hydrogen Permeation - Science Direct ArticleDocument11 pagesPolymeric Coating For Prevention of Hydrogen Permeation - Science Direct ArticleSAUGAT DUTTANo ratings yet
- Unit V Powder Metallurgy and Plastic MoldingDocument48 pagesUnit V Powder Metallurgy and Plastic MoldingGayatri KanwadeNo ratings yet
- CH 15Document44 pagesCH 15Ramez MezNo ratings yet
- Lapox AR 101 PDFDocument2 pagesLapox AR 101 PDFOsama GabrNo ratings yet
- Sikaflex Pro 3 I CureDocument5 pagesSikaflex Pro 3 I Curemuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- Effects of Fabric Alkalinity in Resin FinishingDocument4 pagesEffects of Fabric Alkalinity in Resin Finishingviathung02No ratings yet