Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Overview of Immunity and Its Different Types
Uploaded by
Palwasha Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views11 pagesimmunity and its types
Original Title
Specific Defenses
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentimmunity and its types
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views11 pagesOverview of Immunity and Its Different Types
Uploaded by
Palwasha Khanimmunity and its types
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Overview of immunity and
its different Types
it is an ability of a body to fight against
the foreign invaders and ward them off.
The Immune Response
Immunity: Free from burden. Ability of an
organism to recognize and defend itself against
specific pathogens or antigens.
Immune Response: Third line of defense. Involves
production of antibodies and generation of
specialized lymphocytes against specific antigens.
Antigen: Molecules from a pathogen or foreign
organism that provoke a specific immune
response.
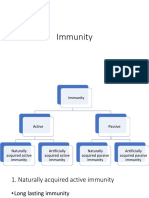
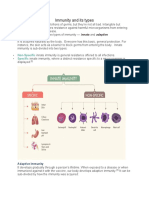
Types of immunity:
1. Natural or innate (non specific)
2. Acquired or adaptive (specific
immunity).
Acquired immunity is further divided into
following:
Naturally acquired Active immunity.
Naturally acquired passive immunity
Artificially acquired active immunity
Artificially acquired passive immunity.
Innate or Genetic Immunity: Immunity an
organism is born with.
Genetically determined.
May be due to lack of receptors or other molecules
required for infection.
Innate human immunity to canine distemper.
Immunity of mice to poliovirus.
Acquired Immunity: Immunity that an
organism develops during lifetime.
Not genetically determined.
May be acquired naturally or artificially.
Development of immunity to measles in response to infection or
vaccination.
Types of Acquired Immunity
I. Naturally Acquired Immunity: Obtained in the course of daily life.
A. Naturally Acquired Active Immunity:
Antigens or pathogens enter body naturally.
Body generates an immune response to antigens.
Immunity may be lifelong (chickenpox or mumps) or temporary
(influenza or intestinal infections).
B. Naturally Acquired Passive Immunity:
Antibodies pass from mother to fetus via placenta or breast
feeding (colostrum).
No immune response to antigens.
Immunity is usually short-lived (weeks to months).
Protection until childs immune system develops.
Types of Acquired Immunity (Continued)
II. Artificially Acquired Immunity: Obtained by receiving a vaccine or
immune serum.
1. Artificially Acquired Active Immunity:
Antigens are introduced in vaccines (immunization).
Body generates an immune response to antigens.
Immunity can be lifelong (oral polio vaccine) or temporary (tetanus
toxoid).
2. Artificially Acquired Passive Immunity:
Preformed antibodies (antiserum) are introduced into body by
injection.
Snake antivenom injection from horses or rabbits.
Immunity is short lived (half life three weeks).
Host immune system does not respond to antigens.
Thank You
You might also like
- Acquired Immunity: Dr. Mejbah Uddin AhmedDocument13 pagesAcquired Immunity: Dr. Mejbah Uddin Ahmedapi-19969058No ratings yet
- Immunity and Immunization ProgramDocument11 pagesImmunity and Immunization ProgramĦajra KhaŋNo ratings yet
- Acquired Imm and Infection - BPTDocument15 pagesAcquired Imm and Infection - BPTKathal 66No ratings yet
- Ayan Das 16401722005 BO-303Document4 pagesAyan Das 16401722005 BO-303Ayan DasNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument2 pagesImmunityHi HelloNo ratings yet
- Micro Assignment Unit 3 Group BDocument12 pagesMicro Assignment Unit 3 Group Bnabeelpatras19No ratings yet
- (PPT) DPC 1.4.2 Immunity and Disease - Dr. Cabanos PDFDocument83 pages(PPT) DPC 1.4.2 Immunity and Disease - Dr. Cabanos PDFJennifer Pisco LiracNo ratings yet
- Acquired ImmunityDocument22 pagesAcquired ImmunityWilliam C ChishaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 Specific Host Defense MechanismsDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 16 Specific Host Defense MechanismsedemcantosumjiNo ratings yet
- Immunity NewDocument17 pagesImmunity NewWijesiri D WNo ratings yet
- Immunization: (Document Subtitle)Document5 pagesImmunization: (Document Subtitle)Abigail BascoNo ratings yet
- Immunity Vaccination: Public HealthDocument41 pagesImmunity Vaccination: Public HealthBaraa AbosamraNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument31 pagesImmunityattiarph23No ratings yet
- Immunization (Immunisasi)Document27 pagesImmunization (Immunisasi)Andhy Andha Dhyan HardhyantiNo ratings yet
- Immunity PPT FinalDocument20 pagesImmunity PPT FinalVarsha SharmaNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITY - 5th FormDocument21 pagesIMMUNITY - 5th FormKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- Immune System (Inn & Adapt)Document53 pagesImmune System (Inn & Adapt)Bushra Khan100% (1)
- Lec # 4 Body Defence SystemsDocument31 pagesLec # 4 Body Defence SystemssamotherlianNo ratings yet
- Biologics: by DR TanginaDocument41 pagesBiologics: by DR TanginaAnam AbidNo ratings yet
- H.S.Z.H Govt (Autonomous) Unani Medical College Bhopal: Immunity and Immunization ScheduleDocument18 pagesH.S.Z.H Govt (Autonomous) Unani Medical College Bhopal: Immunity and Immunization ScheduleĦajra KhaŋNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 Infection and Host Resistance PDFDocument22 pagesMODULE 3 Infection and Host Resistance PDFVillanueva, AbegailNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument9 pagesImmunologyNivedita DasNo ratings yet
- 9-3-23 Immunity, Epi, Disease Control, Delivered Lec by DR Shumaila Humayun, 09-03-23Document65 pages9-3-23 Immunity, Epi, Disease Control, Delivered Lec by DR Shumaila Humayun, 09-03-23Dr Sarah Bakhsh - Resident FCPS Community MedicineNo ratings yet
- Specific Host Defense Mechanism: ImmunologyDocument35 pagesSpecific Host Defense Mechanism: ImmunologyLouie O. DomingoNo ratings yet
- Immunization (Immunisasi)Document27 pagesImmunization (Immunisasi)DindaalifiahNo ratings yet
- Immunization (Immunisasi)Document27 pagesImmunization (Immunisasi)Dinda FirdasariNo ratings yet
- A. ImunitasDocument1 pageA. Imunitasbaiq elmalia mislah putriNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Principles of Immunology and Immunization - April 20 2018Document13 pages2.0 Principles of Immunology and Immunization - April 20 2018Ranjan YadavNo ratings yet
- Biologics 2 PDFDocument24 pagesBiologics 2 PDFmuhammad ihtisham ul hassanNo ratings yet
- Immunity 180603063305Document38 pagesImmunity 180603063305Musfira KhalidNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument10 pagesImmune Systemailyn regaladoNo ratings yet
- Immunisation NotesDocument11 pagesImmunisation NotesCynthia WilsonNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument46 pagesImmunityLalyn Balasbas100% (2)
- Immuno AssgtDocument2 pagesImmuno Assgtapi-3727388No ratings yet
- The Role of The Circulatory System in The Body's Defence MechanismDocument22 pagesThe Role of The Circulatory System in The Body's Defence MechanismSyamsamaria AzizNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGICS LectureDocument36 pagesBIOLOGICS LectureRao Salman LatifNo ratings yet
- l3 Immunization & Cold ChainDocument53 pagesl3 Immunization & Cold ChainNur AinaaNo ratings yet
- l2.1 Immunization Cold ChainDocument53 pagesl2.1 Immunization Cold Chainsinuaish syaNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument40 pagesImmunitydrkhalidfcps100% (5)
- Che 224 Immunity and ImmunizationDocument54 pagesChe 224 Immunity and ImmunizationAbdullahi Bashir SalisuNo ratings yet
- Veterinary ImmunologyDocument20 pagesVeterinary ImmunologyJennifer Bumagat-BermudezNo ratings yet
- Infection ControlDocument1 pageInfection ControlGab AbalosNo ratings yet
- Chap 16 Part 1Document4 pagesChap 16 Part 1clrssNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 ImmunizationDocument45 pagesUnit 11 ImmunizationBikash Kandel100% (1)
- ImmunityDocument17 pagesImmunityNAVEEN DHIMANNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument3 pagesMICROBIOLOGYbritishsam57No ratings yet
- Avian ImmunityDocument65 pagesAvian Immunityarmanda06No ratings yet
- Innate Immunity: Is Present at The Time of Birth. There Are 4 Types of Barriers Present inDocument2 pagesInnate Immunity: Is Present at The Time of Birth. There Are 4 Types of Barriers Present inSTEFFY MARY JOHNSON 2031844No ratings yet
- Immunity and Its TypesDocument3 pagesImmunity and Its TypesBenazir SheikhNo ratings yet
- The Immune SystemDocument4 pagesThe Immune SystemSseguya Lubega YaqubNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument6 pagesImmunitySahir Seemab ZafarNo ratings yet
- Adaptive ImmunityDocument6 pagesAdaptive ImmunityAvinash SahuNo ratings yet
- Comment On The Following ProverbsDocument4 pagesComment On The Following ProverbsArina CucuruzaNo ratings yet
- Immunology Lecturs 27Document27 pagesImmunology Lecturs 27Rolls SaeedNo ratings yet
- Disease-ImmunityDocument10 pagesDisease-ImmunityAshantiwa EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 Immunity and VaccinationDocument15 pagesUnit 13 Immunity and VaccinationcyumadripNo ratings yet
- Active ImmunityDocument1 pageActive ImmunityshaliniNo ratings yet
- 10.0 Diseases - ImmunityDocument5 pages10.0 Diseases - ImmunityBianca Astrid AndoneNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 2 PDFDocument33 pagesPDF Document 2 PDFKendrix FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle QuizDocument2 pagesMenstrual Cycle QuizPalwasha Khan100% (1)
- CounsellingDocument37 pagesCounsellingPalwasha Khan100% (1)
- 8577 00Document17 pages8577 00Palwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Result of B.S English 3rd Semester: Percentage 83% CGP 3.56 UNIVERSITY OF Education (Multan Campus)Document2 pagesResult of B.S English 3rd Semester: Percentage 83% CGP 3.56 UNIVERSITY OF Education (Multan Campus)Palwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Question No 2: Morbidity and Mortality Among Older AdultsDocument3 pagesQuestion No 2: Morbidity and Mortality Among Older AdultsPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Family Planning NepalDocument5 pagesFamily Planning NepalPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- PractocleDocument10 pagesPractoclePalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Nursingethics2 150728122850 Lva1 App6892Document43 pagesNursingethics2 150728122850 Lva1 App6892Palwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Family Planning Research 210Document68 pagesFamily Planning Research 210Palwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Hospital 130918083157 Phpapp01Document13 pagesHospital 130918083157 Phpapp01Palwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- The Story of An HourDocument11 pagesThe Story of An HourPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- MCQs Test of 1st Professionals College of Nursing NMCH MultanDocument7 pagesMCQs Test of 1st Professionals College of Nursing NMCH MultanPalwasha Khan100% (1)
- Fluid Electrolytes and Acid Base BalanceDocument108 pagesFluid Electrolytes and Acid Base BalancesayednourNo ratings yet
- Scope of Educational PsychologyDocument2 pagesScope of Educational PsychologyAgrippa Mungazi81% (16)
- Poster Presentation Handbook PDFDocument6 pagesPoster Presentation Handbook PDFPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- WWW - Plus100years: How To Prevent Hypertensive Heart Disease Through Heart Care Tips?Document68 pagesWWW - Plus100years: How To Prevent Hypertensive Heart Disease Through Heart Care Tips?Palwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- CareerDevelopment InterviewsDocument5 pagesCareerDevelopment InterviewsAneesh RaviNo ratings yet
- Nursing Leadership and ManagementDocument283 pagesNursing Leadership and ManagementRuth Jazelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Sample CurriculumDocument1 pageSample CurriculumPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoruesDocument67 pagesNursing TheoruesPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Abstract WrittingDocument32 pagesAbstract WrittingPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Personalityassessment 120415223237 Phpapp02Document49 pagesPersonalityassessment 120415223237 Phpapp02Jean ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Wagner EthicsDocument14 pagesWagner EthicsPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Sociology Unit 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesSociology Unit 1 Multiple ChoiceDookhan_TT75% (8)
- Management DevelopmentDocument24 pagesManagement DevelopmentPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Ting-Toomey UIC SSM Ch08Document20 pagesTing-Toomey UIC SSM Ch08Palwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment NegotiationDocument8 pagesAssignment Negotiationhimanshu4jun100% (1)
- Managementinformationsysteminhealthcare 120114161332 Phpapp01Document20 pagesManagementinformationsysteminhealthcare 120114161332 Phpapp01Palwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Work Load ManagementDocument12 pagesWork Load ManagementPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Psychological TestingDocument654 pagesPsychological TestingMaymay Lindayao88% (16)
- Digital ThermometerDocument12 pagesDigital Thermometershahpatel19No ratings yet
- Job Sheet 1Document5 pagesJob Sheet 1Sue AzizNo ratings yet
- Review Problems On Gas TurbineDocument9 pagesReview Problems On Gas TurbinejehadyamNo ratings yet
- Bank OD Account in Tally 1Document3 pagesBank OD Account in Tally 1yashusahu180No ratings yet
- Grammar Review A2-B1Document5 pagesGrammar Review A2-B1Lena Silva SouzaNo ratings yet
- Grange Fencing Garden Products Brochure PDFDocument44 pagesGrange Fencing Garden Products Brochure PDFDan Joleys100% (1)
- Norma Geral Astm Bronze Alumínio - b150b150m.19198Document7 pagesNorma Geral Astm Bronze Alumínio - b150b150m.19198EduardoNo ratings yet
- Permutation, Combination & ProbabilityDocument9 pagesPermutation, Combination & ProbabilityVicky RatheeNo ratings yet
- SOP For Operation & Calibration of PH Meter - QualityGuidancesDocument9 pagesSOP For Operation & Calibration of PH Meter - QualityGuidancesfawaz khalilNo ratings yet
- JHS Integrated Science Preamble, Jan 2012 - FinalDocument15 pagesJHS Integrated Science Preamble, Jan 2012 - Finalfrank adamsNo ratings yet
- (AVA Academia) Lorraine Farrelly - The Fundamentals of architecture-AVA Academia (2012) - Trang-137-161Document25 pages(AVA Academia) Lorraine Farrelly - The Fundamentals of architecture-AVA Academia (2012) - Trang-137-161Thảo VyNo ratings yet
- Loan Agreement: Acceleration ClauseDocument2 pagesLoan Agreement: Acceleration ClauseSomething SuspiciousNo ratings yet
- A Dessertation Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofDocument65 pagesA Dessertation Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofMadhavpokale100% (1)
- 1evolution of O and M TheoryDocument27 pages1evolution of O and M TheoryTracy AdraNo ratings yet
- Q1. What Is JDBC? Explain Different Types JDBC Drivers With Suitable DiagramDocument64 pagesQ1. What Is JDBC? Explain Different Types JDBC Drivers With Suitable DiagramjyebbwycqmfkuxNo ratings yet
- DD 3600 3500 3000 Parts CatalogDocument46 pagesDD 3600 3500 3000 Parts CatalogAndres Fdo Mora D100% (2)
- Cross System Create Supplier ProcessDocument14 pagesCross System Create Supplier ProcesssakthiroboticNo ratings yet
- Perfect Picture SummaryDocument3 pagesPerfect Picture SummaryReiaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Ashok LeylandDocument120 pagesFinancial Analysis of Ashok LeylandSiva Kumaravel0% (1)
- The Incidence of COVID-19 Along The ThaiCambodian Border Using Geographic Information System (GIS), Sa Kaeo Province, Thailand PDFDocument5 pagesThe Incidence of COVID-19 Along The ThaiCambodian Border Using Geographic Information System (GIS), Sa Kaeo Province, Thailand PDFInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Calculate Breakeven Point in Units and Revenue Dollars: Intermediate Cost Analysis and ManagementDocument52 pagesCalculate Breakeven Point in Units and Revenue Dollars: Intermediate Cost Analysis and ManagementNavice Kie100% (1)
- UniFi Quick GuideDocument2 pagesUniFi Quick GuideAndhika TharunaNo ratings yet
- CV Old NicDocument4 pagesCV Old NicTensonNo ratings yet
- One God One People February 2013Document297 pagesOne God One People February 2013Stig DragholmNo ratings yet
- Castle CrashesDocument21 pagesCastle Crasheswicked wolfNo ratings yet
- Data Analyst Chapter 3Document20 pagesData Analyst Chapter 3Andi Annisa DianputriNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesEngineering Mathematics Questions and AnswersZaky Muzaffar100% (1)
- VRF Mv6R: Heat Recovery Outdoor UnitsDocument10 pagesVRF Mv6R: Heat Recovery Outdoor UnitsTony NguyenNo ratings yet
- Check List For Design Program of A Parish ChurchDocument11 pagesCheck List For Design Program of A Parish ChurchQuinn HarloweNo ratings yet
- WHITE TOWN GROUP-4 FinalDocument112 pagesWHITE TOWN GROUP-4 Finalaswath manojNo ratings yet