Professional Documents
Culture Documents
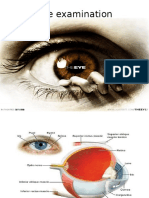
Physical Exam of The Eye
Physical Exam of The Eye
Uploaded by
Amy BobOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Exam of The Eye
Physical Exam of The Eye
Uploaded by
Amy BobCopyright:
Available Formats
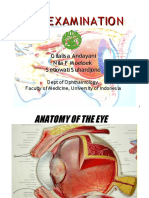
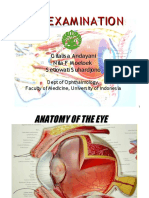
Physical Exam of the Eye
1.
Inspection
Eyes & orbits (size, shape,
symmetry, scars, swelling)
Loss of lateral 1/3 eyebrows
(hypothyroidism, leprosy,
myxedema)
Absent reflection at nasal
field of eye (extra ocular
muscle dysfunction)
Eyelids (position, swelling,
redness, lesions)
Conjunctiva (pallor,
hemorrhage, swelling,
inflammation, growths)
Lacrimal apparatus
(Sjogrens syndrome,
dacryocystitis, epiphora)
2. Pupils
3.
4.
Check direct &
consensual
response to light
Miosis
Mydriasis
Anisocoria
Check
accommodation
reflex
Check reflection
(cataract, Rb)
Extra ocular motility
H test: Have the pt
look at the 6
positions of gaze.
Test both eyes at
once to assess
versions and then
single eye at a
time Cover/uncover
test: assess for
heteropias
Intraocular pressure
If ruptured globe is
suspected, avoid
this test
Tonometry is
employed
5.
6.
Visual fields:
Temporal field : ask
pt to indicate when
he sees your
fingers appear
from beyond the
lateral margins of
orbits in horizontal
plane , & upper &
lower quadrants
Nasal field: cover
one of your eyes &
ask pt to do the
same. Repeat test
Visual acuity
Position pt about 20
feet from Snellens
chart. Test both eyes
separately with one
eye covered then
both eyes at once.
Myopia (near
sightedness)
Hyperopia
(far
sightedness)
Presbyopia
Astigmatism
7.
8.
Fundoscopy
Absent red reflex
(cataracts, corneal
scarring, Rb)
Drusen
Coloboma
Glaucoma
Hypertensive
retinopathy
Papilledema
Diabetic
retinopathy
Slit-lamp examination
Lids/lashes/lacrimal
system (anatomy,
contours)
Conjunctiva/sclera (color,
injection, lesions)
Cornea (clarity, epithelial
disruptions, stromal
opacities, endothelial
lesions)
Anterior chamber (deep,
cell or flare)
Iris (round pupil,
transillumination defects,
nodules)
Lens (clarity, nuclear,
cortical or subscapular
cataract)
Anterior vitreous
You might also like
- Opthalmology History Taking and Physical ExaminationsDocument2 pagesOpthalmology History Taking and Physical ExaminationsZi Song100% (4)
- Strab: IsmusDocument93 pagesStrab: IsmusUlquiorra SchifferNo ratings yet
- Optha Case Sheet ProformaDocument9 pagesOptha Case Sheet ProformaDebzz Pradhan86% (14)
- Assessment of Head, Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat (HEENT)Document107 pagesAssessment of Head, Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat (HEENT)Nadeem UddinNo ratings yet
- Examination of Case of StrabismusDocument76 pagesExamination of Case of StrabismusDr-SunitaVimal100% (1)
- Assessing The Eye Structures and Visual AcuityDocument5 pagesAssessing The Eye Structures and Visual Acuitymalyn1218No ratings yet
- Case History: Disturbances of Vision (Specific Complaints)Document5 pagesCase History: Disturbances of Vision (Specific Complaints)AnandNo ratings yet
- Ocular Examination: F. Francis Ma. L. Cid, MDDocument62 pagesOcular Examination: F. Francis Ma. L. Cid, MDroacruzmdNo ratings yet
- Physical AsessmentDocument15 pagesPhysical AsessmentnonelNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Exam RoutineDocument9 pagesCranial Nerve Exam Routine5kqmn798rfNo ratings yet
- The Eyes.1681642125113Document3 pagesThe Eyes.1681642125113maureensolano63No ratings yet
- Eyes and EarsDocument17 pagesEyes and Earsdlneisha61100% (2)
- Eye ExaminationDocument30 pagesEye ExaminationZuhud Zinedine PangindraNo ratings yet
- Assessment of EyeDocument34 pagesAssessment of Eyeraima ayazNo ratings yet
- Clinical Skills of Eye Examination: by Dr. Hajer Ahmed Ophthalmology Specialist Omar Almukhtar University 2019-2020Document40 pagesClinical Skills of Eye Examination: by Dr. Hajer Ahmed Ophthalmology Specialist Omar Almukhtar University 2019-2020Helene AlawamiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Skills of Eye Examination: - by Dr. Hajer AhmedDocument40 pagesClinical Skills of Eye Examination: - by Dr. Hajer AhmedHelene AlawamiNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear Assessment and DisordersDocument374 pagesEye and Ear Assessment and DisordersFirifan DiribaNo ratings yet
- Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat Assessment and Disorders Final PPT, NursingDocument489 pagesEye, Ear, Nose and Throat Assessment and Disorders Final PPT, NursingFirifan Diriba100% (1)
- Assessment-Checklist EyesDocument2 pagesAssessment-Checklist EyesJL Rebese100% (2)
- CPAC SON HA 4 EyesDocument42 pagesCPAC SON HA 4 EyesmisshalieediiNo ratings yet
- 1cranial NervesDocument48 pages1cranial NervesKaarthigan RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Ocular Motility: Department of Ophthalmology Fatima College of MedicineDocument41 pagesOcular Motility: Department of Ophthalmology Fatima College of MedicineMohammedHuzairIbunuAbidNo ratings yet
- Orientation, History Taking & Examination Dr. Yasser Al-Fakey M.D., M.SC (Ophth.), FRCSDocument8 pagesOrientation, History Taking & Examination Dr. Yasser Al-Fakey M.D., M.SC (Ophth.), FRCSscribdnotes123No ratings yet
- Assessing Special Senses - Eye (Feb 6)Document71 pagesAssessing Special Senses - Eye (Feb 6)Angelo EstanislaoNo ratings yet
- Physical Health AssessmentDocument24 pagesPhysical Health AssessmentLeofe CorregidorNo ratings yet
- Performing Physical Assessment of The EyeDocument14 pagesPerforming Physical Assessment of The Eyezyrine jhen100% (1)
- 2 - BPE - Eye ExaminationDocument50 pages2 - BPE - Eye ExaminationZauhar NurdildayevaNo ratings yet
- Anamnesa - Pengkajian KepDocument61 pagesAnamnesa - Pengkajian Kepinnekeivon24No ratings yet
- HEENT HX and P Examination (Repaired)Document77 pagesHEENT HX and P Examination (Repaired)ObsaNo ratings yet
- Eye Exam: Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOMDocument30 pagesEye Exam: Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOMDuhita Pramesthi Hayuningtyas100% (1)
- Eyes AssessmentDocument23 pagesEyes AssessmentAra AlibasaNo ratings yet
- Student Guide Ophth 12-13Document10 pagesStudent Guide Ophth 12-13Ahmad ShazwanNo ratings yet
- Inspection - Visual Acuity - Visual Fields - Pupillary Response - Fundoscopic ExamDocument34 pagesInspection - Visual Acuity - Visual Fields - Pupillary Response - Fundoscopic ExamZoya MoraniNo ratings yet
- Basic of Ophthalmology ExaminationsDocument47 pagesBasic of Ophthalmology ExaminationsAnonymous iy7I3o100% (2)
- Eye ExamDocument43 pagesEye ExamTapon Sarkar100% (1)
- Nursing Assessment For Eye DisorderDocument26 pagesNursing Assessment For Eye DisorderIrvan DwiNo ratings yet
- 8 Part Eye ExamDocument55 pages8 Part Eye ExamKim CotaocoNo ratings yet
- 8 SquintDocument46 pages8 Squintwanderer_1010No ratings yet
- Eye ExaminationDocument6 pagesEye ExaminationChellamani UmakanthanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Eyes and VisionDocument8 pagesAssessment of The Eyes and Visionmary krisNo ratings yet
- Physical Head-To-Toe AssessmentDocument138 pagesPhysical Head-To-Toe AssessmentCRISELLE KHATE TABAGO PAGATPATANNo ratings yet
- Best Aid To Ophthalmology - Pramod TK - 318Document3 pagesBest Aid To Ophthalmology - Pramod TK - 318Danielle SangalangNo ratings yet
- Mata - Eye Screening in ChildrenDocument32 pagesMata - Eye Screening in ChildrenrabinreaganNo ratings yet
- Examination Technique of The Eye & Ophthalmic EquipmentsDocument59 pagesExamination Technique of The Eye & Ophthalmic Equipmentshenok birukNo ratings yet
- EARSEYESDocument93 pagesEARSEYESZen Gesner Kenneth G. EganaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocument2 pagesCranial Nerve AssessmentTina RyanNo ratings yet
- CNS Examination: Done by DR/ Abdullah Mohd. Jan MBBS, InternDocument37 pagesCNS Examination: Done by DR/ Abdullah Mohd. Jan MBBS, InternBrajesh MouryaNo ratings yet
- Laban - Sub Kamal Salman Mahmoud Jaber Mustafa: Done byDocument40 pagesLaban - Sub Kamal Salman Mahmoud Jaber Mustafa: Done byKool Kaish100% (1)
- SquintDocument36 pagesSquintbismahNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Eye PositionDocument30 pagesAbnormal Eye PositionNimas Prita100% (1)
- Physical Ass 1Document10 pagesPhysical Ass 1andreabreeNo ratings yet
- 07 斜弱視Document72 pages07 斜弱視kenny631653No ratings yet
- Eye and Vision DisordersDocument19 pagesEye and Vision DisordersTeena Duray100% (3)
- Pemmataccm PDFDocument41 pagesPemmataccm PDFryanNo ratings yet
- Pemmataccm PDFDocument41 pagesPemmataccm PDFcloudo21No ratings yet
- Pemmataccm PDFDocument41 pagesPemmataccm PDFJimmyNo ratings yet
- Pemmataccm PDFDocument41 pagesPemmataccm PDFFauzi Ahmad HsbNo ratings yet
- Objective - Subjective Eye Examination-Referral System and When To ReferDocument56 pagesObjective - Subjective Eye Examination-Referral System and When To ReferClara Sainuka100% (1)
- Pemeriksaan MataDocument39 pagesPemeriksaan MataNadilla De PutriNo ratings yet
- Earthing Conductor SizingDocument3 pagesEarthing Conductor SizingVelavan AnnamalaiNo ratings yet
- Aops Community 2010 Albania National OlympiadDocument1 pageAops Community 2010 Albania National OlympiadMuhammad Taufan FathurrachmanNo ratings yet
- Eele461 Module 06Document42 pagesEele461 Module 06Vedran IbrahimovicNo ratings yet
- 10 Tips in Taking The Let ExamDocument14 pages10 Tips in Taking The Let ExamJom Maglente BeltranNo ratings yet
- The Radiation MechanismDocument2 pagesThe Radiation MechanismKote Bhanu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Heracell VIOS CO2 Incubator User Manual 50144132 A enDocument200 pagesHeracell VIOS CO2 Incubator User Manual 50144132 A enPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Heart of The Whau - Part 5 The Rise of The Shopping MallDocument25 pagesHeart of The Whau - Part 5 The Rise of The Shopping MallStorm Gerome100% (1)
- ANH Europe Seminar 2012 1Document208 pagesANH Europe Seminar 2012 1Abdullrahman AlzahraniNo ratings yet
- IELTS Cause-Problem and Effect-Solution Model EssayDocument17 pagesIELTS Cause-Problem and Effect-Solution Model EssaySayaf RashadNo ratings yet
- Design With Nature: Ian Mcharg. The Natural History Press, New York, Ny, 1969. Review by Ashleigh GroseDocument1 pageDesign With Nature: Ian Mcharg. The Natural History Press, New York, Ny, 1969. Review by Ashleigh Groseanusha8204No ratings yet
- MI CONEXIoN AL MUNDO EN OTRA LENGUADocument7 pagesMI CONEXIoN AL MUNDO EN OTRA LENGUAMauricio VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Axia College Material: Week One Lab Report: Topographic and Contour MapsDocument3 pagesAxia College Material: Week One Lab Report: Topographic and Contour MapschriskghtNo ratings yet
- Seamap IntroductionDocument21 pagesSeamap Introductionapi-3759466100% (2)
- Physics Investigatory Project Rough Draft: Optoelectronic Devices (Led, Solar Cell, Photodiode)Document25 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Rough Draft: Optoelectronic Devices (Led, Solar Cell, Photodiode)rahuhl100% (1)
- Grantmaker Research For Heifer Ecuador 3 September 2009Document36 pagesGrantmaker Research For Heifer Ecuador 3 September 2009Manish MehraNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 Introduction of Machines and Mechanisms: TheoryDocument23 pagesAssignment - 1 Introduction of Machines and Mechanisms: TheoryAman AmanNo ratings yet
- Ecdis - Primary Ecdis FailureDocument1 pageEcdis - Primary Ecdis FailureRiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Praise: Bagong AwitDocument2 pagesPraise: Bagong AwitgracehelenNo ratings yet
- Section A: Paper 4: Energy Performance Assessment For Equipment and Utility SystemsDocument6 pagesSection A: Paper 4: Energy Performance Assessment For Equipment and Utility Systemsmd hasanuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Science Final ReviewerDocument25 pagesScience Final ReviewerTantan Fortaleza PingoyNo ratings yet
- Armature Reaction of DC GeneratorDocument16 pagesArmature Reaction of DC GeneratorAndrew Pontanal100% (1)
- Physical Properties Interactive Word Wall Labels: Teks 4.5ADocument12 pagesPhysical Properties Interactive Word Wall Labels: Teks 4.5AAyman HomedanNo ratings yet
- Siemens CU240E ReplacementDocument23 pagesSiemens CU240E ReplacementVăn Nghĩa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- LESSON - PLANS Group 6 ACID BASEDocument6 pagesLESSON - PLANS Group 6 ACID BASEindah sinagaNo ratings yet
- Ket - Gambar Wiring BOMAKDocument3 pagesKet - Gambar Wiring BOMAKEka SukandaNo ratings yet
- Ginger On MicroorganismDocument26 pagesGinger On MicroorganismMila PearlsNo ratings yet
- Case 11F Einschmecker SauceDocument2 pagesCase 11F Einschmecker SauceDexter LiboonNo ratings yet
- BlheliDocument20 pagesBlheliseregio12No ratings yet
- Abb Price List PDFDocument128 pagesAbb Price List PDFWalter MenesesNo ratings yet
- Cutler-Hammer ATC400 AG Switch ManualDocument38 pagesCutler-Hammer ATC400 AG Switch ManualTom LeonardNo ratings yet