Professional Documents
Culture Documents
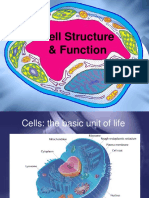
Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell Organisation
Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell Organisation
Uploaded by
mayakefliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell Organisation
Chapter 2 Cell Structure and Cell Organisation
Uploaded by
mayakefliCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell
Organisation
2.1 Cell Structure And Function
ITeach Biology Form 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Structure And Function
Cells Structure
Cells are basic units of life.
Both plant and animal cells have protoplasm which surrounded
by plasma membrane and made up of cytoplasm and nucleus.
Cytoplasm contains organelles which can perform specific
function.
In plant cells, plasma membrane is surrounded by cell wall.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Struktur dan Fungsi Sel
Struktur Sel
Sel merupakan unit asas bagi hidupan.
Kedua-dua sel haiwan dan tumbuhan mempunyai protoplasma
yang dikelilingi oleh membran plasma dan terbina daripada
sitoplasma dan nukleus.
Sitoplasma mengandungi organel yang dapat menjalankan
fungsi tertentu.
Pada sel tumbuhan, membran plasma dikelilingi oleh dinding
sel.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Structure And Function
Animal
AnimalCell
Cell
Centrioles
Rough endoplasmic
reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic
reticulum
Ribosomes
Nuclear membrane
Nucleolus
Cytoplasm
Mitochondrion
Golgi apparatus
Plasma membrane
Overview of an Animal Cell
IIlustration of a
generalized animal
cell
ITeach Biology Form 4
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Struktur dan Fungsi Sel
Sel
SelHaiwan
Haiwan
Sentriol
Jalinan endoplasma
kasar
Jalinan endoplasma
licin
Ribosom
Membran nukleus
Nukleolus
Sitoplasma
Mitokondrion
Jasad Golgi
Membran plasma
Gambaran Struktur Sel Haiwan
Ilustrasi
struktur
umum sel haiwan
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Structure And Function
Plant Cell
Mitochondria
Vacuole
Chloroplast
Cell sap
Tonoplast
Nucleus
Plasma
membrane
Cell wall
Plant cells have chloroplasts in addition to all
organelles in animal cells except centrioles.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Illustration of a generalized
plant cell
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Struktur dan Fungsi Sel
Sel Tumbuhan
Mitokondrion
Vakuol
Kloroplas
Sap sel
Tonoplas
Nukleus
Membran
plasma
Dinding sel
Sel tumbuhan mempunyai kloroplas sebagai
tambahan kepada semua organel yang terdapat
pada sel haiwan kecuali sentriol.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Ilustrasi struktur umum sel
tumbuhan
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Structure And Function
Functions
Functionsof
ofCellular
CellularComponents
Components
Plant
PlantCell
Cell
Chloroplast
Vacuole
Cell sap
Tonoplast
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Plasma membrane
Cell wall
Filled with cell sap which maintain turgidity of cells in plants.
Contains
Acts
as as
a selective
barrier.
which determines
Acts
a genetic
medium
forinformation
biochemical
reactions.
Maintain
shape
of
a
plant
cell.
Traps and vacuoles
convert
light
to chemical
energy
characteristics
and functions
cell.
Contractile
help energy
toof a
regulate
organisms
water
during
photosynthesis.
Provides
substances
required
bysupport.
organelles.
balance.
Controls
movement
Provide of
mechanical
substances
into and out of
Controls all activities of cell.
cytoplasm.
Storage place of water, sugar, mineral salts.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Struktur dan Fungsi Sel
Fungsi
FungsiKomponen
KomponenSel
SelSel
SelTumbuhan
Tumbuhan
Kloroplas
Sap sel
Vakuol
Tonoplas
Sitoplasma
Nukleus
Membran plasma
Dinding sel
Bertindak
sebagai
rintangan
berpilih.
Mengandungi
maklumat
genetik
yang
menentukan
ciri
Dipenuhi
dengan
sap medium
sel yang
mengekalkan
kesegahan
sel
Bertindak
sebagai
bagi
tindak
balas
biokimia.
Mengekalkan
bentuk
sel
tumbuhan.
Memerangkap
dan menukarkan tenaga cahaya kepada
dan
fungsi
sel.
pada tumbuhan.
tenaga
kimia
sewaktu
fotosistesis.
Mengawal
Menyediakan
Memberi
pergerakan
bahan
sokongan
yang
bahan
diperlukan
mekanikal.
ke dalam
oleh dan
organel.
ke luar
Mengawal
semua
aktiviti
sel.
Tempat
simpanan air, gula dan garam mineral
sitoplasma.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Structure And Function
Functions
Functionsof
ofCellular
CellularComponents
Components
Animal
AnimalCell
Cell
Lysosome
Ribosomes
Centrioles
Endoplasmic
reticulum
Mitochondrion
Golgi apparatus
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER).
Synthesis and transport protein.
Eliminate
mitochondria
other
damage
Hasworn
ribosomes
attached
totransports
itsand
surface.
Processes,
packages
and
molecule
Siteout
of protein
synthesis.
organelles.
synthesises
inspindle
cell.
Smooth
endoplasmic
reticulum
Produce
Involve
in cellular
fibres
respiration.
during cell(Smooth
division. ER).
Does
not
have
ribosomes.
Consist
of
RNA. the break down of protein.
Contain
enzymes
which
control
Forms lysosomes.
Sites of metabolic reaction such as lipid synthesis.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Struktur dan Fungsi Sel
Fungsi
FungsiKomponen
KomponenSel
SelSel
SelHaiwan
Haiwan
Lisosom
Ribosom
Sentriol
Jalinan
endoplasma
Mitokondrion
Jasad Golgi
Jalinan endoplasma kasar
Memproses,
membungkus
dan
molekul
Mengangkut
dan menghasilkan
Menyingkirkan
mitokondrion
yang mengangkut
lusuhprotein.
dan organel
yang
yang disintesis
di
dalam
sel. protein.
Terlibat
Tapak
dalam
sintesis
respirasi
sel.
rosak.
Terdapat
ribosom
permukaannya.
Menghasilkan gelendongmelekat
sewaktupada
pembahagian
sel.
Menghasilkan
lisosom.
Jalinan endoplasma
licin
Mengandungi
enzim
yang
mengawal
penguraian protein.
Mengandungi
RNA.
Tidak mempunyai ribosom.
Tapak tindak balas metabolik.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Structure And Function
Comparison
Comparisonbetween
betweenthe
theStructure
Structureof
ofan
an
Animal
Cell
and
a
Plant
Cell
Animal Cell and a Plant Cell
Similarities
Both have nucleus, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, cytoplasm,
plasma membrane, vacuole and endoplasmic reticulum
Differences
Animal cell
Structure
Plant cell
No fixed shape
Shape
Fixed shape
No cell wall
Cell wall
Has cellulose
cell wall
Small vacuole
Vacuoles
Large vacuole
No chloroplast
Chloroplast
Has chloroplast
Glycogen
Food storage
Starch
ITeach Biology Form 4
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Struktur dan Fungsi Sel
Perbezaan
PerbezaanAntara
AntaraStruktur
StrukturSel
SelHaiwan
Haiwandan
dan
Sel
Tumbuhan
Sel Tumbuhan
Persamaan
Kedua-duanya mempunyai nukleus, jasad Golgi, ribosom,
sitoplasma, membran plasma, vakuol dan jalinan endoplasma
Perbezaan
Sel Haiwan
Struktur
Sel Tumbuhan
Tidak tetap
Bentuk
Tetap
Tiada dinding
sel
Dinding sel
Dinding sel
berselulosa
Vakuol kecil
Vakuol
Vakuol besar
Tiada kloroplas
Kloroplas
Ada kloroplas
Glikogen
Simpanan
makanan
Kanji
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell
Organisation
2.2 Cell Organisation
ITeach Biology Form 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Small and simple organisms made up
of single cell.
Unicellular
Organisms
Example : Amoeba sp., Paramecium
sp., yeast and Chlamydomonas.
Amoeba sp. live in freshwater
environment as well as in soil water.
Amoeba sp.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Chlamydomonas sp.
Paramecium sp.
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Organisma kecil dan ringkas yang
terdiri daripada satu sel sahaja.
Organisma Unisel
Contoh: Amoeba sp., Paramecium sp.,
yis dan Chlamydomonas sp..
Amoeba sp. hidup dalam kawasan air
tawar dan air tanah.
Amoeba sp.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Chlamydomonas sp.
Paramecium sp.
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Amoebasp.
sp.- -Movement
Movement
Amoeba
Form pseudopodia that help it to move forward.
It moves by extending temporary pseudopodia.
The shape of amoeba changes as it moves.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Amoebasp.
sp.- -Pergerakan
Pergerakan
Amoeba
Membentuk pseudopodium yang membantunya untuk
bergerak.
Amoeba bergerak dengan mengunjurkan pseudopodium
(kaki palsu).
Bentuk Amoeba akan berubah-ubah ketika ia bergerak.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Amoebasp.
sp.- -Feeding
Feeding
Amoeba
Amoeba extending
pseudopodia
Surrounds and
engulf food particle
Formation of food
vacuole
Microscopic
view:
AmoebaPhagocytosis
feeding
on
protista
Food is digested and nutrients
are absorbed into cytoplasm
ITeach Biology Form 4
Lysozyme secreted
into food vacuole
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Amoebasp.
sp.- Amoeba
Pemakanan
Pemakanan
Amoeba
mengunjurkan
pseudopodium
Mengelilingi dan
meliputi partikel
makanan
Pembentukan
vakuol makanan
Fagositosis
Pemerhatian di bawah
mikroskop: Amoeba
memakan protista
Lisozim dirembeskan
Makanan dicerna dan nutrien
ke dalam vakuol
diserap ke dalam sitoplasma
makanan
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Amoebasp.
sp.- Amoeba
Reproduction
Reproduction
Amoeba sp. reproduces asexually by binary fission.
Form spores under unfavorable condition.
Amoeba sp. divides
after it has grown
to a certain size
ITeach Biology Form 4
Nucleus divides
Cytoplasm divides
Two new cells are
formed
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Amoebasp.
sp.- -Pembiakan
Pembiakan
Amoeba
Amoeba sp. membiak melalui belahan dedua.
Membentuk spora dalam keadaan buruk
Amoeba sp.
membahagi selepas
ia mencapai suatu
saiz tertentu
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Nukleus
membahagi
Sitoplasma
membahagi
Dua sel baru
terbentuk
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Cell Specialisation In Multicellular Organisms
Multicellular organisms have more than one
cell.
Each type of cell is different in size, shape
and structure.
To perform their task effectively, cells will go
through
differentiation
process
and
specialisation.
For example: Nerve cells have long, thin
fibres called axons which conduct nerve
impulse.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Pengkhususan Sel Bagi Organisma Multisel
Organisma multisel
daripada satu sel.
mempunyai
lebih
Setiap jenis sel berbeza dari segi saiz,
bentuk dan struktur.
Untuk menjalankan tugas mereka dengan
berkesan, sel akan melalui proses
pembezaan dan pengkhususan.
Sebagai contoh: Sel saraf mempunyai
gentian yang panjang dan nipis dipanggil
akson yang mengawal saraf impuls.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation In Multicellular Organisms
Cells
Cells
Basicunits
unitsofoflife
life
Basic
Tissues
Tissues
Similarcell
cellcarry
carryout
outaaparticular
particular
Similar
function.
function.
Organ
Organ
groupofoftissues
tissuesthat
thatexecute
execute
AAgroup
specialisedfunction.
function.
aaspecialised
Severals organ
System
System
ITeach Biology Form 4
All system work
together
Multicellular
Multicellular
Organism
Organism
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel dalam Organisma Multisel
Sel
Sel
Unitasas
asaskehidupan.
kehidupan.
Unit
Tisu
Tisu
Sel khusus
khusus yang
yang menjalankan
menjalankan
Sel
fungsitertentu.
tertentu.
fungsi
Organ
Organ
Sekumpulan
tisu
yang
Sekumpulan
tisu
yang
menjalankanfungsi
fungsikhusus.
khusus.
menjalankan
Beberapa organ
Sistem
Sistem
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Semua
sistem
bekerjasama
Organisma
Organisma
multisel
multisel
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation in Animals
Cell Organisation in Animals
Tissues
Tissues
Epithelial
tissue
Nerve tissue
Muscle tissue
ITeach Biology Form 4
Connective
tissue
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel Dalam Haiwan
Organisasi Sel Dalam Haiwan
Tisu
Tisu
Tisu epitelium
Tisu saraf
Tisu otot
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Tisu
penghubung
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Consist of epithelial cells arranged in a continuous layer.
Epithelial tissue
Form exocrine and endocrine glands which produce
secretions.
Structure of an epithelial tissue is adjusted to its function.
Example: Epithelial lining of skin protect underlying cells
from infections.
Epithelial lining
of skin
ITeach Biology Form 4
Epithelial
of glands
lining
Epithelial lining
of trachea
Epithelial lining of
small intestine
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Terdiri daripada sel epitilium yang disusun dalam lapisan
berterusan.
Tisu Epitelium
Membentuk kelenjar endokrin
menghasilkan rembesan.
dan
eksokrin
yang
Struktur tisu epitelium disesuaikan dengan fungsinya.
Cth: Tisu epitelium
jangkitan
Epitelium pengalas
pada kulit
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Epitelium pengalas
pada kelenjar
kulit melindungi sel daripada
Epitelium pengalas Epitelium pengalas
pada trakea
pada usus kecil
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Made up of cells called muscle fibres.
Muscle tissue
Most abundant tissue in the body.
3 types of muscle tissues
Smooth muscle
Can be found in blood
vessels, intestines.
Responsible
for
involuntary
body
activities.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Skeletal muscle
Can be found in arms
and legs.
Involved in voluntary
movement.
Cardiac muscle
Found in the wall of
heart.
Contract to pump
blood to all parts of
body.
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Terdiri daripada sel gentian otot.
Tisu Otot
Tisu yang paling banyak dalam badan
3 jenis tisu otot
Otot licin
Terdapat pada salur
darah, usus.
Bertanggungjawab
terhadap aktiviti luar
kawal badan
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Otot rangka
Didapati pada lengan
dan kaki.
Terlibat
dalam
pergerakan terkawal.
Otot kardiak
Terdapat
pada
dinding jantung
Mengecut
untuk
mengepam darah ke
seluruh
bahagian
badan.
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Connective Tissue
Specialized connective tissue
Blood cells
Adipose tissue
Cartilage
Produce in bone
marrow.
Acts as an energy
reserve.
Strong,
flexible
connective tissue.
Function
:
regulate, transport
and protective.
Found in dermis of
skin.
Provides support to
the nose, ears and
bones at joints.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Bone
Provides
protection
and
give support to the
body.
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Tisu penghubung
Tisu Penghubung Khusus
Sel darah
Tisu adipos
Dihasilkan dalam
tulang sum-sum.
Fungsi
mengawal,
mengangkut
melindungi.
Bertindak
sebagai
simpanan tenaga.
:
dan
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Didapati pada dermis
kulit.
Rawan
Tisu
penghubung
yang
kuat
dan
fleksibel.
Memberi sokongan
pada hidung, telinga
dan sendi di tulang
Tulang
Memberi
perlindungan dan
menyokong
badan
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Nerve tissue
Made up of neurones or
nerve cells.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Send and receive impulse
to
coordinate
bodys
activities.
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Tisu Saraf
Terdiri daripada neuron
atau sel saraf.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Menghantar
dan
menerima impuls untuk
mengkoordinasi
aktiviti
badan.
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
A group of different tissues that work
together to perform a particular function.
Organ
Organ
Epithelial cells
Examples: Heart, skin, kidneys, eyes and
ears.
Epithelial tissue
Skin
Muscle cells
Muscle tissue
Formation of Human Skin
ITeach Biology Form 4
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Sekumpulan
tisu-tisu
berbeza
yang
bekerjasama untuk menjalankan suatu fungsi
khusus.
Organ
Organ
Sel epitelium
Contoh: Jantung, kulit, buah pinggang, mata
dan telinga.
Tisu epitelium
Kulit
Sel otot
Tisu otot
Pembentukan Kulit Manusia
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Several organs which work together to do
a specific function.
System
Human body has 11 major system.
Skeletal
system
Muscular
system
Circulatory
system
Nervous Reproductive Lymphatic
system
system
system
ITeach Biology Form 4
Digestive
system
Excretory
system
Endocrine Respiratory
system
system
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Beberapa organ bekerjasama untuk
melakukan satu fungsi yang khusus.
Sistem
Badan manusia mempunyai 11 sistem
utama.
Sistem
rangka
Sistem
saraf
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Sistem
otot
Sistem
peredaran
darah
Sistem
Sistem limfa
pembiakan
Sistem
Sistem
pencernaan perkumuhan
Sistem
endokrin
Sistem
pernafasan
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
CellOrganisation
OrganisationIn
InPlants
PlantsTissues
Tissues
Cell
Meristematic tissue
ITeach Biology Form 4
Permanent tissue
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
OrganisasiSel
SelPada
PadaTumbuhan-Tisu
Tumbuhan-Tisu
Organisasi
Tisu meristem
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Tisu kekal
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
CellOrganisation
OrganisationIn
InPlants
Plants
Cell
Tissues
Tissues
Meristematic
tissue
Consist of undifferentiated
cells which are able to divide.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Produces new cells by cell
division.
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
OrganisasiSel
SelDalam
DalamTumbuhan
Tumbuhan
Organisasi
Tisu
Tisu
Tisu meristem
Mengandungi sel yang tidak
membeza tetapi berupaya
untuk membahagi.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Menghasilkan
sel
baru
melalui pembahagian sel.
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
CellOrganisation
OrganisationInInPlants
Plants
Cell
Permanent
tissue
Epidermal
tissues
Covers
stems,
leaves and roots of
young plants.
Ex : Guard cells of
stomata.
Parenchyma tissue
Phloem
Store sugar and starch.
Give support and shape to herbaceous
plant.
Transport
nutrient
such as glucose
from leaves to root
and stems.
Collenchyma tissue
Have unevenly thickened cell walls.
Support non-woody plants, young stems
and petioles.
Xylem
Transport water and
mineral salts from
roots to stems and
leaves.
Provides support to
plant.
Scleronchyma tissue
ITeach Biology Form 4
Vascular
tissues
Cuticle
lessens
water loss.
Protect plant from
mechanical
injury
and infection.
Ground tissues
Have cell walls uniformly thickened by
lignin.
Give support to mature region plant.
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
OrganisasiSel
SelDalam
DalamTumbuhan
Tumbuhan
Organisasi
Tisu kekal
Menutupi
batang,
daun
dan
akar
tumbuhan muda.
Kutikel
mengurangkan
kehilangan air.
Melindungi
tumbuhan daripada
kecederaan
mekanikal.
Cth : Sel pengawal
pada stomata.
Tisu Parenkima
Menyimpan gula dan kanji.
Floem
Memberi sokongan dan bentuk pada
tumbuhan herba.
Mengangkut nutrien
seperti glukosa dari
daun ke akar dan
batang.
Tisu kolenkima
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Tisu vaskular
Tisu asas
Tisu epidermis
Mempunyai
dinding
sel
yang
berketebalan tidak sekata.
Memberi sokongan kepada tumbuhan
tak berkayu, batang muda dan petiol.
Tisu skelenkima
Menpunyai dinding sel yang ditebalkan
oleh lignin secara tidak sekata.
Memberi sokongan kepada bahagian
tumbuhan yang matang.
Xilem
Mengangkut air dan
garam mineral dari
akar ke batang dan
daun.
Memberi sokongan
kepada tumbuhan.
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Organs And Systems In Plant
Organ
Organinin
plants
plants
Leaf
Stem
Root
Flower
Flower
Fruit
System
Systeminin
plants
plants
Root system
Consist of taps roots
and lateral roots of
plant.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Shoot
system
Shoot system
Consist
of
stems,
leaves, buds, flowers Root
and fruit.
system
Stem
Leaf
Root
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Organ dan Sistem Tumbuhan
Organ
Organ
tumbuhan
tumbuhan
Daun
Batang
Akar
Bunga
Bunga
Buah
Sistem
Sistem
tumbuhan
tumbuhan
Sistem akar
Terdiri daripada akar
tunjang
dan
akar
lateral tumbuhan.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Sistem
pucuk
Sistem pucuk
Terdiri
daripada
batang, daun, tunas, Sistem
bungan dan buah.
akar
Batang
Daun
Akar
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
RegulatingThe
TheInternal
Internal
Regulating
Environment
Environment
The Internal Environment Of Multicellular Organisms
Internal environment refer to reaction inside organism to external changes by its
own metabolism.
Consists of the interstitial fluid and the blood plasma.
Chemical Factors
Salt and sugar content.
pH value
ITeach Biology Form 4
Physical Factors
Factors affecting
internal
environment
Temperature
Blood pressure
Osmotic pressure
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
MengawalaturPersekitaran
Persekitaran
Mengawalatur
Dalaman
Dalaman
Persekitaran Dalaman Organisma Multisel
Persekitaran dalaman merujuk kepada tindak balas di dalam organisma terhadap
perubahan luaran oleh metabolismenya sendiri.
Terdiri daripada bendalir tisu dan plasma darah.
Faktor kimia
Kandungan garam dan
gula
Nilai pH
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Faktor yang
memberi kesan
kepada
persekitaran
dalaman
Faktor fizikal
Suhu
Tekanan darah
Tekanan osmosis
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Regulating The Internal Environment
The Necessity For Maintaining An Optimal Internal Environment
Regulation of physical and chemical factors in internal
environment so that it is always constant for the cell to
function best.
Changes in glucose, oxygen levels and temperature of
body will affect the metabolism of the body.
Homeostasis
These changes regulated by homeostatic mechanisms
so that metabolic processes can proceed at optimum
rate.
The mechanism that controls homeostasis is called
negative feedback mechanism.
In negative feedback, any different from normal range
of function is opposed.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Mengawalatur Persekitaran Dalam
Keperluan Mengekalkan Persekitaran Dalaman Yang Seimbang
Pengawalaturan faktor fizikal dan kimia dalam
persekitaran dalaman supaya ia sentiasa malar untuk
sel berfungsi dengan baik.
Perubahan glukosa, aras oksigen dan suhu akan
memberi kesan kepada metabolisma badan.
Homeostasis
Perubahan ini dikawal oleh mekanisme homeostasis
supaya proses metabolisma dapat diteruskan pada
kadar optimum.
Mekanisme yang mengawal homeostatis dipanggil
mekanisme tindak balas negatif.
Dalam tindak balas negatif, sebarang perbezaan
daripada julat normal akan ditentang.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Involvement Of Various Systems In Maintaining An
Optimal Internal Environment
Systems in the body work together to maintain a stable internal
environment.
Example :
Body
temperature
rises above normal
level.
Skins
receptor
detect changes.
Transmit
information
to
Normal
body
temperature 37C.
Body
temperature
drops
towards
normal
through
evaporation.
Nervous
system
signals blood vessel
to dilate and sweat
gland to secrete.
Hypothalamus
Normal body temperature is maintained by the negative feedback
mechanism.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Penglibatan Pelbagai Sistem Dalam Mengekalkan
Persekitaran Dalaman Optimum
Sistem di dalam badan bekerjasama untuk mengekalkan persekitaran
dalaman yang stabil.
Contoh :
Suhu
badan
meningkat melebihi
aras normal.
Reseptor
mengesan
perubahan.
kulit
Maklumat
dipindahkan
kepada
Suhu badan normal
37C.
Suhu badan turun ke
tahap normal melalui
penyejatan.
Sistem saraf memberi
isyarat kepada salur
darah
untuk
mengembang
dan
kelenjar peluh untuk
perembesan.
Suhu badan normal dikekalkan oleh mekanisme tindakbalas negatif.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Hipotalamus
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Cell Organisation
Normal Regulation Of Blood Sugar
Blood
rises
sugar
level
Promotes
release
Normal sugar level
Blood
falls
sugar
Stimulate formation
of glycogen.
sugar
level
Normal sugar level
Stimulate
glucose
uptake from blood.
level
Promotes glucagon
release
ITeach Biology Form 4
insulin
Blood
falls
Blood
rises
Stimulates glycogen
break down.
sugar
level
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Organisasi Sel
Pengawalaturan Normal Gula Darah
Aras
gula
meningkat
darah
Menggalakkan
pembebasan insulin
Aras gula normal
Arah
gula
menurun
Menggalakkan
pembebasan
glukagon
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Meransang
pembentukan
glikogen.
Merangsang
pengambilan glukosa
daripada darah
darah
Aras
gula
menurun
Aras gula normal
Arah
gula
meningkat
Meransang penguraian
glikogen.
darah
darah
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell
Organisation
2.3 Appreciating The Uniqueness Of The Cell
ITeach Biology Form 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Appreciating The Uniqueness Of The Cell
Every cellular component has its own
specific function.
Uniqueness
UniquenessOf
Of
The
TheCell
Cell
Survival of cell will be threatened if cell
lacks particular component.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Menghargai Keunikan Sel
Setiap komponen sel mempunyai fungsi
yang khusus.
Keunikan
KeunikanSel
Sel
Kemandirian sel akan diancam sekiranya
sel kekurangan komponen tertentu.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Appreciating The Uniqueness Of The Cell
Production Of Secretion In The Cell
Nucleus send information to ribosomes
to build protein.
Nucleus
Cell membrane
Protein expelled
Rough endoplasmic
reticulum
Protein is synthesised and transported
by endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi
apparatus in small vesicles.
Secretory
vesicle
Ribosome
Proteins are modified into specific
secretions by Golgi apparatus.
Product is sorted and packaged in
vesicles which are then budded off
from Golgi apparatus.
Vesicles are transferred to plasma
membrane and fused with it to release
their contents outside cell.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Transport
vesicle
Smooth
endoplasmic
reticulum
Golgi
apparatus
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Menghargai Keunikan Sel
Penghasilan Rembesan Dalam Sel
Nukleus
menghantar
maklumat
kepada ribosom untuk menghasilkan
protein.
Nukleus
Protein disintesis dan diangkut oleh
jalinan endoplasma ke jasad Golgi
dalam vesikel kecil.
Membran sel
Protein yang
dikeluarkan
Jalinan endoplasma
kasar
Vesikel
rembesan
Ribosom
Protein diubah menjadi
tertentu oleh jasad Golgi.
rembesan
Produk disusun dan dibungkus dalam
vesikel dan kemudiannya dikeluarkan
dari jasad Golgi.
Vesikel tersebut dipindahkan kepada
membran plasma dan bergabung
dengannya
untuk
membebaskan
kandungannya ke luar sel.
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Vesikel
angkutan
Jalinan
endoplasma
licin
Jasad Golgi
Chapter 2 Cell Structure And Cell Organisation
Appreciating The Uniqueness Of The Cell
Predicted state of a cell
without
a
particular
cellular component
Motichondria
Not have enough
energy for cell
activities.
Nucleus
The cells would
not be able to
reproduce.
All cell activities
are affected.
The cell dies.
ITeach Biology Form 4
Cytoplasm
Endoplasmic
Reticulum
(ER)
Cells would lose
their shapes and
rigidities.
Synthesis
and
transport
of
proteins
would
stop.
Enzyme
production
become fewer.
Bab 2 Struktur Sel dan Organisasi Sel
Menghargai Keunikan Sel
Jangkaan Keadaan Sel
Tanpa Komponen Sel
Tertentu
Motikondrion
Tidak
mempunyai
tenaga
yang
cukup
untuk
aktiviti sel.
Jalinan
endoplasma
Nukleus
Sel
tidak
berupaya untuk
membiak.
Semua
aktiviti
sel akan terjejas.
Sel akan mati
ITeach Biologi Tingkatan 4
Sitoplasma
Sel
akan
kehilangan
bentuk
dan
kesegahan.
Penghasilan dan
pengangkutan
proteins
akan
terhenti.
Penghasilan
enzim
akan
berkurangan.
The End
i - Teach
You might also like
- Meiosis RubricDocument1 pageMeiosis RubricJeniffer De Guzman GadiomaNo ratings yet
- Plant EmbryogenesisDocument19 pagesPlant EmbryogenesisJosiahBriz-Rull100% (1)
- Notes Calvin CycleDocument2 pagesNotes Calvin Cycleneelp331No ratings yet
- Syllabus in Chemical Biology III (Biomolecules) (TCB3)Document12 pagesSyllabus in Chemical Biology III (Biomolecules) (TCB3)Yuri PaderesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument44 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistryFrance Jan First SaplacoNo ratings yet
- Pig Heart Dissection Lab - Final PDFDocument15 pagesPig Heart Dissection Lab - Final PDFapi-1127245210% (1)
- Study This To Ace The Pre-Quarterly Test in Biology!Document70 pagesStudy This To Ace The Pre-Quarterly Test in Biology!Rose MendizabalNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument14 pagesActive TransportRjay CruzNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Phloem & XylemDocument6 pagesLab Report - Phloem & XylemAriadna ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument38 pagesChemical Basis of LifeFernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument112 pagesPlant CellAlfonso PlantillaNo ratings yet
- PNotes Success Bio F4-OkDocument32 pagesPNotes Success Bio F4-Okdineshooish100% (1)
- EnzymeDocument16 pagesEnzymePrecious DerainNo ratings yet
- 4NA - Heat TransferDocument24 pages4NA - Heat TransferChico AlvesNo ratings yet
- 8 & 9: Cell Structure and Function: CellsDocument13 pages8 & 9: Cell Structure and Function: CellsEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - LipidsDocument56 pagesWeek 5 - LipidsPaula LouiseNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes Vs EukaryotesDocument4 pagesProkaryotes Vs EukaryotesDhuran ModhaNo ratings yet
- Network Structure in Root, Stem, and LeafDocument5 pagesNetwork Structure in Root, Stem, and LeafMarwana SuaibNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Biomolecules: Major Types of Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, andDocument12 pagesLesson 4: Biomolecules: Major Types of Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, andJuselle Faith AtaNo ratings yet
- General Biology Practice Lab Mnaul.. (Copy)Document94 pagesGeneral Biology Practice Lab Mnaul.. (Copy)Misgana Warku Iggii100% (1)
- Basic Plant Processes (Laboratory)Document70 pagesBasic Plant Processes (Laboratory)anon_228573261No ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument18 pagesCell As A Unit of LifeMohamad Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- The Energy Flows Within Cells: ExampleDocument4 pagesThe Energy Flows Within Cells: ExamplesydjjNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument4 pagesBotanyRejie Canny CariasoNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and FunctionDocument25 pagesCell Parts and FunctionGerald N EstradaNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Cell MembranesDocument60 pagesCh5 Cell MembranesAdrian Aguilera GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8.dynamic EcosystemDocument45 pagesChapter 8.dynamic EcosystemNur Bahiyah Binti Abdul Wahab IPGKTINo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument38 pagesCell Structure & Functiongundogan21100% (1)
- Zoology Animal TissueDocument54 pagesZoology Animal TissueasuhassNo ratings yet
- BIO 127 General Microbiology:: Course Description and ObjectivesDocument24 pagesBIO 127 General Microbiology:: Course Description and Objectivescheramae ancesNo ratings yet
- General BotanyDocument5 pagesGeneral BotanyKNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Notes.Document12 pagesCell Biology Notes.Aranyani SwamiNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Lab ActivityDocument5 pagesPlant Cells Lab ActivityHaris KhanNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument19 pagesSexual ReproductionjojopebblesNo ratings yet
- Mitosis in Onion Root Tips LabDocument4 pagesMitosis in Onion Root Tips LabJohn Osborne40% (5)
- Group 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsDocument4 pagesGroup 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsClaire Angelie Ruaya100% (1)
- Plant Tissue SystemsDocument2 pagesPlant Tissue SystemsJohn0% (1)
- Chapter 6: Cell Division: 6.2: Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument18 pagesChapter 6: Cell Division: 6.2: Cell Cycle and MitosisMohammed Ridzuwan0% (1)
- 2.1. Cell Structure and Function of OrganellesDocument66 pages2.1. Cell Structure and Function of OrganellesNama Saya100% (1)
- LESSON 1 Explain The Postulates of The Cell TheoryDocument28 pagesLESSON 1 Explain The Postulates of The Cell Theorysophia DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Comparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyDocument1 pageComparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyFVCproductionsNo ratings yet
- NSB BOT 20 Intro Chapter 1A Plant PhysiologyDocument21 pagesNSB BOT 20 Intro Chapter 1A Plant PhysiologyZeldeign ManuelNo ratings yet
- Cell and TransportDocument77 pagesCell and TransportEugenie Francisco100% (1)
- PHCG 201 CytologyDocument113 pagesPHCG 201 CytologyIbn HaarūnNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 - Cell Cycle & Cell Division PDFDocument3 pagesActivity 7 - Cell Cycle & Cell Division PDFKiro ZeroNo ratings yet
- Modern Bio II - Nutrition Plant and AnimalsDocument77 pagesModern Bio II - Nutrition Plant and AnimalsLavander BlushNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For BiochemistryDocument8 pagesSyllabus For BiochemistryJenny Lyn Nebres100% (1)
- Active TransportDocument10 pagesActive TransportSylvia DuzonNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1 Cell Notes.Document6 pagesBiology Chapter 1 Cell Notes.Jyoti AmbwaniNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets For Changes in Chromosome NumberDocument11 pagesActivity Sheets For Changes in Chromosome NumberGu Jun PyoNo ratings yet
- Cell 2Document15 pagesCell 2teaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ApparatusDocument35 pagesLaboratory ApparatusAdrian MiclatNo ratings yet
- Respiration Bio21Document32 pagesRespiration Bio21yayreeeNo ratings yet
- Meiosis & MitosisDocument8 pagesMeiosis & MitosisAna Melisa DorueloNo ratings yet
- 10 EmbryogenesisDocument14 pages10 EmbryogenesisPhenyo MmerekiNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal CellHera Lopez100% (1)
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Carbohydrates LPDocument32 pages3.3 Carbohydrates LPjnfjngsdj100% (1)
- Cell Biology NotesDocument6 pagesCell Biology Notessaadc786100% (1)
- Cell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDocument54 pagesCell Structure AND Cell OrganisationAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Week4 - Predefined Classes and ObjectsDocument75 pagesWeek4 - Predefined Classes and ObjectsMohd HaidilNo ratings yet
- PBI 1082 EOP Sem 2-1920 - Slides 3.2 Week 11Document34 pagesPBI 1082 EOP Sem 2-1920 - Slides 3.2 Week 11Mohd HaidilNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Kem Pecutan Kimia SBP - T5Document24 pages2015 - Kem Pecutan Kimia SBP - T5Mohd HaidilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Endangered EcosystemDocument28 pagesChapter 9 Endangered EcosystemMohd HaidilNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Paper 2 ExerciseDocument16 pagesSPM Chemistry Paper 2 ExerciseMohd HaidilNo ratings yet