Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Computer Aided Process Planning
Introduction To Computer Aided Process Planning
Uploaded by
Mayur Raut0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views26 pagesOriginal Title
53822448-CAPP.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views26 pagesIntroduction To Computer Aided Process Planning
Introduction To Computer Aided Process Planning
Uploaded by
Mayur RautCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
Introduction to Computer
Aided Process Planning
Computer Integrated Manufacturing
(CIM)
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
2D
3D
Concurrent Engineering
Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP)
Variant
Generative
Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM)
CNC
Robotics
Material Handling
Just in Time (JIT)
Group Technology
Flexible Manufacturing Systems
What is process planning?
Recipe/Algorithm/Step-by-step instructions
Fast Food Chain
Same taste everywhere from NY to New
Delhi
How do they do it?
Customization in formal dinner restaurant
Manufacturing Environment
Role of the master machinist in small batch
manufacturing
Manufacturing is more complex than cooking yet
the planning for it is similar
Job shop: group machines which perform same
operation together
Routing of parts through the various
departments
Process plan defines the route
Reduction in the necessary skill of operator can
be achieved by using a detailed process plan
Formal Definition
Process planning can be defined as an act of
preparing processing documentation for the
manufacturing of a piece, part or an assembly
depending on the production environment can
be
Rough
Detailed
When process planning is done using a
computer : Computer Aided Process Planning
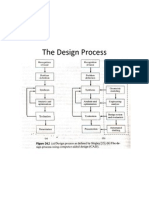
Step-by-step
operations in
a sample
part
Manufacturing a part to meet design specs.
Selection of initial block
Sequence of operations
Selection of machine, process
Surface finish
Quality
Tolerance
Hardness
Life
Cost
A Rough Process Plan
A Detailed Process Plan
Components of Process Planning
Selection of machining operations
Sequencing of machining operations
Selection of cutting tools
Determining the setup requirements
Calculation of cutting parameters
Tool path planning and generation of
NC/CNC programs
Design of Jigs/Fixtures
Process Planning in different
environments
In tool-room type manufacturing
make part as per drawing is sufficient
In metal-forming type operations
The process planning requirements are embedded
directly into the die.
Process planning is fairly trivial
Job-shop type manufacturing requires most
detailed process planning
Design of tools, jigs, fixtures and manufacturing
sequence are dictated directly by the process plan.
Requirements for process planner
Must be able to analyze and understand
part requirements
Have extensive knowledge of machine
tools, cutting tools and their capabilities
Understand the interactions between the
part, manufacturing, quality and cost
Traditional process planning
Experienced based and performed manually
Variability in planners judgment and experience
can lead to differences in the of what constitutes
best quality
Problem facing modern industry is the current
lack of skilled labor force to produce machined
parts as was done in the past
Hence Computer Integrated Manufacturing and
Computer Aided Process Planning
Advantages of CAPP
Reduces the demand on the skilled
planner
Reduces the process planning time
Reduces both process planning and
manufacturing cost
Creates consistent plans
It produces accurate plans
It increases productivity
Approaches to CAPP
Variant
Generative
Automatic
Variant Process Planning
based on the valid conjecture that similar
parts will have similar process plans
Preparatory stage
GT-based part coding
Families of similar parts are created
Family matrix
A process plan is to manufacture the entire
family is created
Variant Process Planning
Production Stage
Incoming part is coded
Part family is identified
Process plan is edited to account for the different needs
of the part
Salient points of variant process planning
Easy to build, learn and use
Experienced process planners are still required to edit
the process plan
Cannot be used in an entirely automated manufacturing
system without additional process planning
Variant Process Planning
Generative Process Planning
a system which automatically synthesizes a
process plan for a new component
Requires
Part description
Part to be produced must be clearly and precisely
defined in a computer compatible format
(OPITZ,AUTAP)
Manufacturing databases
Logic of manufacturing must be identified and
captured
The captured logic must be incorporated in a unified
manufacturing database
Generative Process Planning
Decision making
logic and
algorithms
Decision trees
Expert Systems:
AI based
approaches
Automatic Process Planning
generate a complete process plan directly from a
CAD drawing
Requires:
Automated CAD interface
Take a general CAD model ( 3D for unambiguous
data) and develop an interface to develop a
manufacturing interface for this model : Feature
Recognition of CAD
Design the parts with available manufacturing
features : Feature based CAD
Dual: useful features of both approaches
Intelligent (computer based) process planner
Some process
planning
approaches
SUMMARY
CAPP is a highly effective technology for
discrete manufacturers with a significant
number of products and process steps.
Rapid strides are being made to develop
generative planning capabilities and
incorporate CAPP into a computer-
integrated manufacturing architecture.
SUMMARY
The first step is the implementation of GT
and coding.
Commercially-available software tools
currently exist to support both GT and
CAPP.
SUMMARY
As a result, many companies can achieve
the benefits of GT and CAPP with minimal
cost and risk.
Effective use of these tools can improve a
manufacturer's competitive advantage.
References
Systems Approach To Computer Integrated
Design and Manufacturing
Author: Nanua Singh
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons
Expert Process Planning For Manufacturing
Author: Tien-chien Chang
Publisher: Addison-Wesley Publishing
Company
You might also like
- The CNC Handbook: Digital Manufacturing and Automation from CNC to Industry 4.0From EverandThe CNC Handbook: Digital Manufacturing and Automation from CNC to Industry 4.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successFrom EverandThe New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Computer Aided Process Planning-IDocument19 pagesComputer Aided Process Planning-IShamsir Ibni ShukriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Aided Process PlanningDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Computer Aided Process Planningmuniraju mNo ratings yet
- Processplanning 140517022639 Phpapp02 PDFDocument33 pagesProcessplanning 140517022639 Phpapp02 PDFNiroshaNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Process PlanningDocument33 pagesComputer Aided Process PlanningDanish SaifiNo ratings yet
- 18MEC207T - Unit 5 - Rev - W13Document52 pages18MEC207T - Unit 5 - Rev - W13Asvath GuruNo ratings yet
- Process PlanningDocument32 pagesProcess PlanningBalto YesurethnamNo ratings yet
- Cad CamDocument19 pagesCad Camrohit singhNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP)Document22 pagesComputer Aided Process Planning (CAPP)fear to face100% (1)
- CAPPDocument27 pagesCAPPRajeshwar DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 (A) : ObjectivesDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 1 (A) : ObjectivesMuhammadRamdanMohdSulaimanNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Process Planning CAPPDocument32 pagesComputer Aided Process Planning CAPPعبدالله عبداللهNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam Cat 1-MergedDocument52 pagesCad Cam Cat 1-MergedJude JohnNo ratings yet
- Draft 1Document8 pagesDraft 1Girish JainNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Process Planning CAPP PDFDocument32 pagesComputer Aided Process Planning CAPP PDFMuizzuddin Rosli100% (1)
- Cim M5 1Document17 pagesCim M5 1shamsabdullah2031No ratings yet
- Introduction To CAD/CAMDocument40 pagesIntroduction To CAD/CAMdsathiyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Aided Process PlanningDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Computer Aided Process PlanningJayasimmanNo ratings yet
- Cad CamDocument31 pagesCad CamPratik PaniNo ratings yet
- Group 9: Ch. 38: Computer-Aided Manufacturing Ch. 40: Product Design and Process Selection in A Competitive EnvironmentDocument53 pagesGroup 9: Ch. 38: Computer-Aided Manufacturing Ch. 40: Product Design and Process Selection in A Competitive Environmentkbkaran5955No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 CAPPDocument31 pagesChapter 6 CAPPtrần thị ngọc trâmNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On: Unit VI: CAD Customization & Automation By, ByDocument41 pagesA Presentation On: Unit VI: CAD Customization & Automation By, Byvishwajeet patilNo ratings yet
- Cam LectureDocument48 pagesCam LectureSam LastNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Design and ManufacturingDocument62 pagesComputer Aided Design and Manufacturingmanu33% (3)
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing Courseresume 04Document2 pagesComputer Integrated Manufacturing Courseresume 04api-246809582No ratings yet
- ON Product Design and Manufacturing: Prepared byDocument25 pagesON Product Design and Manufacturing: Prepared byChinmay BeheraNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Process Planning-IDocument19 pagesComputer Aided Process Planning-IAnoop SavantNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Process Planning: Date: 2/27/03 Room: MSE Computer Lab Presenters: Cem Toma Anthony NguyenDocument23 pagesComputer Aided Process Planning: Date: 2/27/03 Room: MSE Computer Lab Presenters: Cem Toma Anthony NguyenRjose PortilloNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. VII-Sem: Cad/CamDocument162 pagesB.Tech. VII-Sem: Cad/CamSushanthNo ratings yet
- Ship Computer Aided Design L-00 Introduction To CAEDocument21 pagesShip Computer Aided Design L-00 Introduction To CAEMohamed BarakatNo ratings yet
- Cims BasicsDocument69 pagesCims BasicsprepinstaitdudesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CAMDocument42 pagesIntroduction To CAMapoorva.choudhary02No ratings yet
- Computer Aided Process Planning-IDocument19 pagesComputer Aided Process Planning-IelkhawadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CAD/CAMDocument31 pagesIntroduction To CAD/CAMJOHN RICHMOND DIZONNo ratings yet
- CIMSDocument24 pagesCIMSAaryan MoreNo ratings yet
- CAD CAM CAE Notes PDFDocument101 pagesCAD CAM CAE Notes PDFSatyaprakash Dinesh VisputeNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP)Document30 pagesComputer Aided Process Planning (CAPP)brijkishor2017100% (1)
- CO: 6: Adapt Recent Practices Like CAPP, CIM, AI, RP and FOF For Effective ProductionDocument8 pagesCO: 6: Adapt Recent Practices Like CAPP, CIM, AI, RP and FOF For Effective ProductionDivyeshparmar9077No ratings yet
- DF Lecture 22-25Document44 pagesDF Lecture 22-25riya.3No ratings yet
- Computer Aided Process Planning Full Seminar ReportDocument32 pagesComputer Aided Process Planning Full Seminar ReportSarath Chandran100% (7)
- CH - 1 Intro CAD CAM CNCDocument55 pagesCH - 1 Intro CAD CAM CNCNhư TâmNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 CADCAMDocument31 pagesLecture 8 CADCAMAnand P DwivediNo ratings yet
- Process PlanningDocument12 pagesProcess Planningselva_raj215414No ratings yet
- Cad / Cam: Presented byDocument19 pagesCad / Cam: Presented byRaunak DoshiNo ratings yet
- Cad, Cam, CimDocument37 pagesCad, Cam, CimSolomon Ngussie0% (1)
- Cad CamDocument14 pagesCad CamTarikbusefiNo ratings yet
- Process Planning and Cost EstimationDocument44 pagesProcess Planning and Cost Estimationshanjith balakrishnanNo ratings yet
- MEC435 Chapter1Document49 pagesMEC435 Chapter1najmi_najmi_muhammad96No ratings yet
- MSC Design Presentation-March 2017Document137 pagesMSC Design Presentation-March 2017GooftilaaAniJiraachuunkooYesusiinNo ratings yet
- Process Planning, CAPPDocument67 pagesProcess Planning, CAPPNahugirsh ZozNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument50 pagesDownloadSAJITH NFNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To CAD-CAMDocument4 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To CAD-CAMabbas6063No ratings yet
- Computer-Aided Process Planning (CAPP)Document26 pagesComputer-Aided Process Planning (CAPP)Akatew Haile MebrahtuNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Process Planning (Capp)Document21 pagesComputer Aided Process Planning (Capp)raviNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam - CADDocument40 pagesCad Cam - CADAdyakanta SahooNo ratings yet
- Cad, Cam CimDocument16 pagesCad, Cam CimSurya SNo ratings yet
- Cad For Manufacturing: Dr. Sankha DebDocument31 pagesCad For Manufacturing: Dr. Sankha Debkiran03pachpandeNo ratings yet
- The PTC Creo Suite of NC and Tooling Solutions: Data SheetDocument5 pagesThe PTC Creo Suite of NC and Tooling Solutions: Data Sheetbranet_adrianaNo ratings yet
- UNIT I 1.2 Process Planning and Production PlanningDocument52 pagesUNIT I 1.2 Process Planning and Production Planningprof_panneerNo ratings yet
- UNIT I 1.9 Production Flow AnalysisDocument13 pagesUNIT I 1.9 Production Flow Analysisprof_panneerNo ratings yet
- UNIT I 1.6 Group-TechnologyDocument78 pagesUNIT I 1.6 Group-Technologyprof_panneerNo ratings yet
- Unit I 1.5 Group Technology, Part Classi, CodingDocument36 pagesUnit I 1.5 Group Technology, Part Classi, Codingprof_panneer0% (1)
- UNIT I 1.1 Process Planning in The Manufacturing CycleDocument34 pagesUNIT I 1.1 Process Planning in The Manufacturing Cycleprof_panneer100% (1)
- Geometric Tolerances and DimensionsDocument40 pagesGeometric Tolerances and Dimensionsprof_panneerNo ratings yet
- Design For MachiningDocument43 pagesDesign For Machiningprof_panneer50% (2)
- Theory of Metal CuttingDocument69 pagesTheory of Metal Cuttingprof_panneer0% (1)
- Measuring Cutting Forces PDFDocument14 pagesMeasuring Cutting Forces PDFprof_panneerNo ratings yet
- Unit I 1-Cutting Tool Angles and Their SignificanceDocument48 pagesUnit I 1-Cutting Tool Angles and Their Significanceprof_panneer50% (2)
- Group TechnologyDocument27 pagesGroup TechnologyVelsami AmmasaiGounder100% (1)
- Group Technology - Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocument11 pagesGroup Technology - Flexible Manufacturing SystemGiovani CarpinNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 CRCDocument21 pagesUnit 9 CRCEr Manpreet ChahalNo ratings yet
- Review On Heat TransferDocument76 pagesReview On Heat Transferprof_panneer100% (1)
- Applications of Finite Element Methods For Academic & Industrial ResearchDocument2 pagesApplications of Finite Element Methods For Academic & Industrial Researchprof_panneerNo ratings yet