Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Environmental Pollution Control (ET ZC362 - WILP Course) : BITS Pilani
Uploaded by
sa_arunkumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Environmental Pollution Control (ET ZC362 - WILP Course) : BITS Pilani
Uploaded by
sa_arunkumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Environmental Pollution Control
(ET ZC362 – WILP Course)
BITS Pilani Lakshmi Sirisha
Department of Chemical Engineering
Hyderabad Campus
Session 5
25th August, 2018
Topics to be covered:
Chapter 4 : Air Pollution Sampling and
Measurement
• Ambient Air Sampling
• Stack Sampling
• Analysis of Air Pollutants
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Introduction
Air quality monitoring: Sampling and measurement of air
pollutants
It is helpful for us to implement control measures for reducing
pollutant concentrations
Both long term pollution trends and short term sampling are
required
Two types of air quality measurement:
• Ambient air quality measurement: Pollutant levels in ambient
atmosphere are measured
• Stack sampling: Pollutants emitted from a source such as
smoke stack
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Introduction
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Air sampling system
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
BITS Pilani
Pilani|Dubai|Goa|Hyderabad
Ambient air sampling
12/9/2018 ET ZC 362 Environmental Pollution Control 6
Sampling methods for gaseous pollutants
• Grab sampling
• Absorption in liquids
• Adsorption on solids
• Freeze out sampling
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Grab sampling
In grab sampling, sample is collected in an evacuated
bag/flask/plastic container
Some times, water displacement methods is used
Grab sampling is used to take out a relatively small sample,
over a very short period of time, for instantaneous
analysis.
Bag sampling is prone to moisture condensation, diffusion
through walls of the bag which can be avoided by using
rigid wall containers
Moisture condensation can be avoided by wrapping the
containers with heating tapes, nichrome wires.
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Absorption in liquids
Air pollutants are collected and absorbed by liquids based
on solubility, or a chemical reaction with the liquid.
Most common method
Different types of collectors like simple bubblers to more
complex fritted glass or impingers are used.
In fritted glass absorbers, the gas stream is broken into
extremely small bubbles promoting an intimate contact
between gas and the liquid
In impingers, a high velocity gas stream is impinged
(striking hard) onto a flat surface, providing a good gas-
liquid contact
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Absorption in liquids
Impingers
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Adsorption on solids
Sample air is first passed through solid adsorbent bed and
then desorbed for analysis
Solid adsorbent beds are basically columns packed with
granular porous solids
Activated carbon/silica gel having large surface areas are
used as adsorbents
Adsorption is exothermic reaction. Removal of heat favors
adsorption of gases on solids
Desorption can be carried out by heating the adsorbent.
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Freeze out sampling
A series of cold traps with progressively lower temperatures
are used to collect samples and the condensed samples
are later analysed on GC/IR/UV etc. techniques.
Coolants such as liquid nitrogen, liquid oxygen, dry ice and
acetone etc. are used based on the temperature attained
(0 to -196oC)
This technique is generally not used as the system might
get plugged due to ice formation from water vapr present
in gas samples
High energy intensive process
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Sampling of particulate matter
• Sedimentation
• Filtration Used for
• Impingement particulate matter
that remain
• Electrostatic precipitation suspended as
• Thermal precipitation aerosols.
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Sedimentation
Mainly used for particulate matter > 10 microns
Funnel type plastic jar ( typically 20 m in height with 10-15
m diameter)
Sample is deposited over a period of 1 month and then
dried and weighed
The dust fall jars must be closely spaced, within a km
distance
Advantages: Simple, inexpensive method
Disadvantage: Less accurate, usually non repeatable
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Sedimentation
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Filtration
Hi-vol. sampler
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Filtration
Mainly used for particulate matter < 10 microns
Known volume of pollutant air is sucked by a blower
through a fine mess filter for a period of approx. 24 hrs
The filter is made of fibrous or granular material, through
which the air stream passes, while the particles are
entrained on the filter
Dust weight is calculated from filter weight.
A glass fibre filter typically has an efficiency of 99% for
particles of size 0.3 micron
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Filtration
Design
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Impingement
Separation of particulates from air stream takes place by
collision against a flat surface.
A high velocity gas stream impinges on a fat surface,
causing gas bubbles to break (in wet impingement) and
particulate matter gets collected due to change in
direction of flow.
Types:
• Wet impingement
• Dry impingement
• Cascade impactors (dry impingers)
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
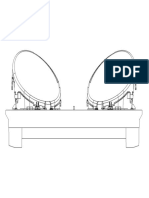
Impingement
Cascade impinge ( Four stage)
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Electrostatic precipitator
Electrostatic precipitator removes particulate matter in the
size range 0.01<d<20 microns from a gas based on
inducted electrostatic charge.
It contains a row of thin vertical wires and large flat metal
plates oriented vertically
Gas stream flows horizontally through the paces between
the wires and then passes through the positively charged
plates.
During operation a negative voltage is applied to the wire
and corona effects ionizes the gas particles
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Negatively charged particle
moves to the grounded
plates gets neutralized
and deposited on it
The performance of
electrostatic precipitator
mainly depends on
• Particle resistivity
• Particle size distribution
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Other techniques
Tape sampler
COH is calculated
by evaluating amount
of light that can pass
through the spot
Thermal precipitation: Small particulate matter under the
influence of strong temperature gradient between two
surfaces, have a tendency to move to lower temperature and
get deposited on the colder of the two surfaces.
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
BITS Pilani
Pilani|Dubai|Goa|Hyderabad
Stack sampling
12/9/2018 ET ZC 362 Environmental Pollution Control 24
Stack sampling
Deq = 4 X cross sectional area of flow/ wetted perimeter
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Stack sampling
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Stack sampling-Traverse points
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Stack sampling system
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Isokinetic sampling
(for Particulate sampling)
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Isokinetic sampling
(for Particulate sampling)
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
BITS Pilani
Pilani|Dubai|Goa|Hyderabad
Analysis of air pollutants
12/9/2018 ET ZC 362 Environmental Pollution Control 31
Analysis of pollutants
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Analysis of SO 2(Colorimetric)
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Analysis of SO 2(Colorimetric)
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Analysis of Nitrogen oxides
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Analysis of Nitrogen oxides
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Analysis of CO
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Analysis of CO
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Analysis of CO
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
Analysis of O3, HC, stack PM
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
End
Any Questions?
mail to
sirisha@hyderabad.bits.pilani.ac.in
BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus
You might also like
- SQL-Problems Solutions PDFDocument11 pagesSQL-Problems Solutions PDFManpreet Singh100% (1)
- Upgrade DB 10.2.0.4 12.1.0Document15 pagesUpgrade DB 10.2.0.4 12.1.0abhishekNo ratings yet
- Statistical Process Control Study: Data Collection: - Sample D2 A2 D4Document1 pageStatistical Process Control Study: Data Collection: - Sample D2 A2 D4sa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- English 8-Q3-M3Document18 pagesEnglish 8-Q3-M3Eldon Julao0% (1)
- Comparing Different Biogas Upgrading TechniquesDocument56 pagesComparing Different Biogas Upgrading Techniquesengrabdulhanan100% (5)
- PDF Reply Position Paper For ComplainantDocument4 pagesPDF Reply Position Paper For ComplainantSheron Biase100% (1)
- Historical Heritage of Kancheepuram DistrictDocument65 pagesHistorical Heritage of Kancheepuram DistrictMurugesan PalrajNo ratings yet
- SHIPPING TERMSDocument1 pageSHIPPING TERMSGung Mayura100% (1)
- FlexSim 7.7.2 ManualDocument1,456 pagesFlexSim 7.7.2 Manualsa_arunkumar0% (1)
- Self Heall PPT EditedDocument34 pagesSelf Heall PPT EditedYASHAS K CNo ratings yet
- List of Automotive Test PDFDocument147 pagesList of Automotive Test PDFsa_arunkumar100% (1)
- Environmental Pollution Control (ET ZC362 - WILP Course) : BITS PilaniDocument33 pagesEnvironmental Pollution Control (ET ZC362 - WILP Course) : BITS Pilanisa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Population GrowthDocument29 pages1 Population GrowthKrishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- PD Mid Sem PresentationDocument34 pagesPD Mid Sem PresentationMD AZHARUDDIN MONDULNo ratings yet
- S1-18-Et ZC362-L3Document29 pagesS1-18-Et ZC362-L3sa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Filtration PDFDocument13 pagesFiltration PDFAyush PorwalNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Control TechDocument58 pagesAir Pollution Control TechvivekNo ratings yet
- Lecture Class 1 - ME F 112Document25 pagesLecture Class 1 - ME F 112OPM RockyNo ratings yet
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: Granular Filtration StrategiesDocument48 pagesWater and Wastewater Treatment: Granular Filtration StrategiesGHANTASALA VARUNNo ratings yet
- L6 MMZG534 DMZG534 - L6 - Pollution Prevention PDocument27 pagesL6 MMZG534 DMZG534 - L6 - Pollution Prevention PsureshNo ratings yet
- Removing Color from Textiles Effluent Using Coagulants and Activated CarbonDocument7 pagesRemoving Color from Textiles Effluent Using Coagulants and Activated Carbonsecondary twoNo ratings yet
- Design-Fabrication-and-Testing-of-Waste-Plastic-Pyrolysis-PlantDocument10 pagesDesign-Fabrication-and-Testing-of-Waste-Plastic-Pyrolysis-Plantbabiato41No ratings yet
- IoT-Lecture-5. SlidesDocument24 pagesIoT-Lecture-5. SlidesPrithviraj ChiripalNo ratings yet
- Lec Rolling ForgingDocument43 pagesLec Rolling Forgingadityaagr2910No ratings yet
- Design Fabrication and Testing of Waste Plastic Pyrolysis PlantDocument10 pagesDesign Fabrication and Testing of Waste Plastic Pyrolysis PlantMatthues Ace MartinezNo ratings yet
- Production Techniques 1 ME F243: BITS PilaniDocument16 pagesProduction Techniques 1 ME F243: BITS PilaniShubham AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 3025 (Part19 RA2018)Document7 pages3025 (Part19 RA2018)qdqwdqwdNo ratings yet
- Bio-Reactor Septic Tank Treats Domestic Waste WaterDocument14 pagesBio-Reactor Septic Tank Treats Domestic Waste WaterHlaine Ko KoNo ratings yet
- Bio-Reactor Septic Tank Treats Domestic Waste WaterDocument14 pagesBio-Reactor Septic Tank Treats Domestic Waste WaterDHARANI SHANMUGAMNo ratings yet
- Thesesaastu 2019 175Document76 pagesThesesaastu 2019 175Zemenu PiltoNo ratings yet
- Ioegc 2017 37Document9 pagesIoegc 2017 37ounassNo ratings yet
- Khulna University of Engineering & Technology (KUET), KhulnaDocument6 pagesKhulna University of Engineering & Technology (KUET), Khulna17018 Md. Shahariar KabirNo ratings yet
- Study of Sustainable Materials For Low Cost Housing-Compressed Earth Blocks (Ceb'S)Document48 pagesStudy of Sustainable Materials For Low Cost Housing-Compressed Earth Blocks (Ceb'S)ravali chinthaNo ratings yet
- Ioegc 2017 37Document9 pagesIoegc 2017 37Niti KlinkaewNo ratings yet
- N Ironmental: TudiesDocument4 pagesN Ironmental: TudiesWX YZNo ratings yet
- Yasmeen 1042015 IRJPAC23315Document15 pagesYasmeen 1042015 IRJPAC23315Bethmage KasunNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Grey Water Treatment Through Fecl3-Activated Carbon Obtained From Cotton Stalks and River SandDocument10 pagesSynthetic Grey Water Treatment Through Fecl3-Activated Carbon Obtained From Cotton Stalks and River SandRohit UbnareNo ratings yet
- Adsorptionandits Isotherm Theory 1227Document6 pagesAdsorptionandits Isotherm Theory 1227ArmaanNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Textile Wastewater by Coagulation PreDocument12 pagesTreatment of Textile Wastewater by Coagulation PreSakibNo ratings yet
- Yasmeen 1042015 I RJ Pac 23315Document15 pagesYasmeen 1042015 I RJ Pac 23315vanbanbinhdinhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document13 pagesLecture 1Aryan SonthaliaNo ratings yet
- Developing An Intelligent Waste Sorting System With Robotic Arm A Step Towards Green EnvironmentDocument7 pagesDeveloping An Intelligent Waste Sorting System With Robotic Arm A Step Towards Green EnvironmentREYES, PATRICK HENDRYNo ratings yet
- Certificate: Government Polytechic, SolapurDocument32 pagesCertificate: Government Polytechic, SolapurCM5I53Umeidhasan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- APC 2nd Batch-1 PDFDocument54 pagesAPC 2nd Batch-1 PDFABHISHEK SINGHNo ratings yet
- Lecture Class 4 - ME F 112Document43 pagesLecture Class 4 - ME F 112Vivekananda NandamNo ratings yet
- Adsoprtion EA13Document11 pagesAdsoprtion EA13sharemwNo ratings yet
- Non Destructive Testing using Vibration AnalysisDocument19 pagesNon Destructive Testing using Vibration AnalysisVijay GouthamNo ratings yet
- ProfileDocument3 pagesProfileVijay PathakNo ratings yet
- MDCPSS_Webinar_Slides_ISO_18562Document18 pagesMDCPSS_Webinar_Slides_ISO_18562Vickysh MevawalaNo ratings yet
- Air Sampling MethodsDocument124 pagesAir Sampling MethodsalokNo ratings yet
- 5 - Sampling For Air Borne Contaminants - pptx-1Document76 pages5 - Sampling For Air Borne Contaminants - pptx-1lim boon tikNo ratings yet
- Waste plastic pyrolysis plant design and testingDocument9 pagesWaste plastic pyrolysis plant design and testingSamee UllahNo ratings yet
- CFD Analysis of A Wickless Heat Pipe: January 2018Document8 pagesCFD Analysis of A Wickless Heat Pipe: January 2018Optimuz TsNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Sampling and Measurement: - by G.Naga ThulasiDocument19 pagesAir Pollution Sampling and Measurement: - by G.Naga ThulasisaiganeshmadasuNo ratings yet
- Progress On The Extraction Techniques of BromineDocument6 pagesProgress On The Extraction Techniques of Brominejaveria masoodNo ratings yet
- CO2 Capture From Flue Gas by A PSA Process Using A Novel StructurDocument167 pagesCO2 Capture From Flue Gas by A PSA Process Using A Novel StructurChia-YiiNo ratings yet
- Pollution Control and Effluent Treatment 03602267: Unit I Basics of Environmental PollutionDocument4 pagesPollution Control and Effluent Treatment 03602267: Unit I Basics of Environmental PollutionSMIT CHRISTIANNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 AnpcDocument50 pagesUnit 2 AnpcRajiv kumar KushwahaNo ratings yet
- A Non-Destructive FTIR Method For The Determination of Ammonium and Sulfate in Urban PM2.5 SamplesDocument8 pagesA Non-Destructive FTIR Method For The Determination of Ammonium and Sulfate in Urban PM2.5 SamplesIksan AfrizalNo ratings yet
- Range of ParameterDocument6 pagesRange of Parameterআমি স্নেহাশীষNo ratings yet
- CE4810-Air Pollution Control Concepts-W5Document13 pagesCE4810-Air Pollution Control Concepts-W5Khimavath BharathNo ratings yet
- 14-Curve SurveyingDocument76 pages14-Curve SurveyingVinayaka RamNo ratings yet
- Viki Micro ProjectDocument11 pagesViki Micro ProjectRavindra SalunkheNo ratings yet
- CFD Optimization of Airflow in Baghouse FiltersDocument5 pagesCFD Optimization of Airflow in Baghouse FiltersYhaneNo ratings yet
- Ie 181Document13 pagesIe 181nminhhanh03No ratings yet
- Simtec Silicone PartsDocument70 pagesSimtec Silicone Partssa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Pot Plant Infographics PGo 16 - 9Document3 pagesPot Plant Infographics PGo 16 - 9sa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- How to receive DD Free Dish and tune old STBDocument9 pagesHow to receive DD Free Dish and tune old STBkPrasad8100% (1)
- S1-18-Et ZC417-L2Document49 pagesS1-18-Et ZC417-L2sa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Aditi Agarwal - An Expert Guide To Problem-Solving - With Practical Examples (Learn Brainstorming, Fishbone, SWOT, FMEA, 5whys + 6 More) - Aditi Agarwal Books LLC (2016)Document55 pagesAditi Agarwal - An Expert Guide To Problem-Solving - With Practical Examples (Learn Brainstorming, Fishbone, SWOT, FMEA, 5whys + 6 More) - Aditi Agarwal Books LLC (2016)sa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution Control (ET ZC362 - WILP Course) : BITS PilaniDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Pollution Control (ET ZC362 - WILP Course) : BITS Pilanisa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Ventilation SpecificationsDocument1 pageVentilation Specificationssa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Shreegandha Dinner Food MenuDocument1 pageShreegandha Dinner Food Menusa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Resuscitation BagDocument4 pagesResuscitation Bagsa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Excellence: BITS PilaniDocument49 pagesManufacturing Excellence: BITS Pilanisa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- M Hybrid SolutionsDocument8 pagesM Hybrid Solutionssa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- S1-18-Et ZC362-L1Document27 pagesS1-18-Et ZC362-L1sa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Cluster Layout1Document1 pageCluster Layout1sa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution Control (ET ZC362 - WILP Course) : BITS PilaniDocument31 pagesEnvironmental Pollution Control (ET ZC362 - WILP Course) : BITS Pilanisa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Afdex Tutorial 2Document8 pagesAfdex Tutorial 2sa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Gluing GuideDocument36 pagesGluing Guidesa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document9 pagesTutorial 1sa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Material Details FoamDocument4 pagesMaterial Details Foamsa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Version Control FILENAME: Version Control Example V3 Date Changed by Revisions Made Change Ref V1 17-Jul-17 Arun Draft and Released N/ADocument2 pagesVersion Control FILENAME: Version Control Example V3 Date Changed by Revisions Made Change Ref V1 17-Jul-17 Arun Draft and Released N/Asa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Reducing LCD Chopin Rear Cover Painting DefectsDocument25 pagesReducing LCD Chopin Rear Cover Painting Defectssa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Design To SOP-Process Flow and Estimates-1Document1 pageDesign To SOP-Process Flow and Estimates-1sa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Fuel Systems FundamentalDocument26 pagesFuel Systems Fundamentalsa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Reducing LCD Chopin Rear Cover Painting DefectsDocument25 pagesReducing LCD Chopin Rear Cover Painting Defectssa_arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Anomaly Sell Out Remap December 2019 S SUMATRA & JAMBIDocument143 pagesAnomaly Sell Out Remap December 2019 S SUMATRA & JAMBITeteh Nha' DwieNo ratings yet
- Amos Code SystemDocument17 pagesAmos Code SystemViktor KarlashevychNo ratings yet
- Laporan Mutasi Inventory GlobalDocument61 pagesLaporan Mutasi Inventory GlobalEustas D PickNo ratings yet
- The Punjab Commission On The Status of Women Act 2014 PDFDocument7 pagesThe Punjab Commission On The Status of Women Act 2014 PDFPhdf MultanNo ratings yet
- SABIC Ethanolamines RDS Global enDocument10 pagesSABIC Ethanolamines RDS Global enmohamedmaher4ever2No ratings yet
- EE3331C Feedback Control Systems L1: Overview: Arthur TAYDocument28 pagesEE3331C Feedback Control Systems L1: Overview: Arthur TAYpremsanjith subramani0% (1)
- Statement of PurposeDocument2 pagesStatement of Purposearmaan kaurNo ratings yet
- A CASE STUDY OF AU SMALL FINANCE BANK'S SHRIRAMPUR BRANCHDocument9 pagesA CASE STUDY OF AU SMALL FINANCE BANK'S SHRIRAMPUR BRANCHprajakta shindeNo ratings yet
- Siyaram S AR 18-19 With Notice CompressedDocument128 pagesSiyaram S AR 18-19 With Notice Compressedkhushboo rajputNo ratings yet
- DX133 DX Zero Hair HRL Regular 200 ML SDS 16.04.2018 2023Document6 pagesDX133 DX Zero Hair HRL Regular 200 ML SDS 16.04.2018 2023Welissa ChicanequissoNo ratings yet
- Instruction/Special Maintenance Instruction (IN/SMI)Document2 pagesInstruction/Special Maintenance Instruction (IN/SMI)ANURAJM44No ratings yet
- Dewatering Construction Sites Below Water TableDocument6 pagesDewatering Construction Sites Below Water TableSOMSUBHRA SINGHANo ratings yet
- Coa - Ofx-8040a (H078K5G018)Document2 pagesCoa - Ofx-8040a (H078K5G018)Jaleel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Borneo United Sawmills SDN BHD V Mui Continental Insurance Berhad (2006) 1 LNS 372Document6 pagesBorneo United Sawmills SDN BHD V Mui Continental Insurance Berhad (2006) 1 LNS 372Cheng LeongNo ratings yet
- Tps65070X Power Management Ic (Pmic) With Battery Charger, 3 Step-Down Converters, and 2 LdosDocument98 pagesTps65070X Power Management Ic (Pmic) With Battery Charger, 3 Step-Down Converters, and 2 Ldosmok waneNo ratings yet
- Rtlo 18918B 1202Document42 pagesRtlo 18918B 1202gustavomosqueraalbornozNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument32 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Computer NetworksHuluNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument50 pagesTransformerبنیاد پرست100% (8)
- Pike River Case StudyDocument7 pagesPike River Case StudyGale HawthorneNo ratings yet
- Why Companies Choose Corporate Bonds Over Bank LoansDocument31 pagesWhy Companies Choose Corporate Bonds Over Bank Loansতোফায়েল আহমেদNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Charges General Banking 2022Document18 pagesSchedule of Charges General Banking 2022Shohag MahmudNo ratings yet
- BUSN7054 Take Home Final Exam S1 2020Document14 pagesBUSN7054 Take Home Final Exam S1 2020Li XiangNo ratings yet
- Exercise Manual For Course 973: Programming C# Extended Features: Hands-OnDocument122 pagesExercise Manual For Course 973: Programming C# Extended Features: Hands-OnAdrian GorganNo ratings yet
- The Causes of Cyber Crime PDFDocument3 pagesThe Causes of Cyber Crime PDFInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 2016 04 1420161336unit3Document8 pages2016 04 1420161336unit3Matías E. PhilippNo ratings yet