Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bipolar Membrane & Fuel Cells
Uploaded by
faiz khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesBipolar Membrane and Fuel Cells
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBipolar Membrane and Fuel Cells
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesBipolar Membrane & Fuel Cells
Uploaded by
faiz khanBipolar Membrane and Fuel Cells
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Bipolar Membrane & Fuel Cells
Abdul Faiz Khan
18031D9201
Bipolar Membrane
• Definition: An ion-exchange membrane that
consist of a layered ion structure.
• The use of a bipolar membrane enables many
functionalities to be used such as anti-fouling,
water dissociation, and the separation of ions.
Bipolar Membrane
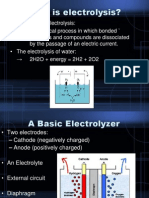
• The conventional method for generating
H+ and OH- ions from water uses electrolysis.
Electrolysis also generates O2 and H2 and the
production of these gases consumes about
half of the electrical energy of the process. In
contrast, special ion-exchange membranes
such as the bipolar membranes are capable of
splitting water directly into H+ and OH- ions
without generating O2 and H2.
Fuel Cell
• Definition: A fuel cell is an electrochemical
cell that converts the chemical energy from a
fuel into electricity through an
electrochemical reaction of hydrogen fuel with
oxygen or another oxidizing agent.
• A fuel cell uses the chemical energy of
hydrogen or another fuel to cleanly and
efficiently produce electricity.
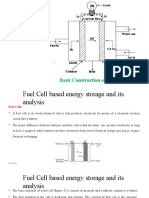
Block Diagram of a Fuel Cell
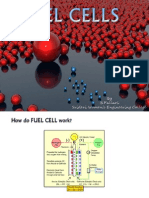
How Fuel Cell Works
• Fuel cells work like batteries, but they do not
run down or need recharging. They produce
electricity and heat as long as fuel is supplied.
A fuel cell consists of two electrodes—a
negative electrode (or anode) and a positive
electrode (or cathode)—sandwiched around
an electrolyte. A fuel, such as hydrogen, is fed
to the anode, and air is fed to the cathode.
Types of Fuel Cells
• Alkaline Fuel Cells.
• Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells.
• Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells.
• Solid Oxide Fuel Cells.
• Direct Methanol Fuel Cells.
You might also like
- Chapter 3 Fuel CellDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Fuel CellJaya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Amy Jewel, Rob Larkin and Todd HaurinDocument24 pagesElectrolysis: Amy Jewel, Rob Larkin and Todd Haurinlove_puezied4793No ratings yet
- Untitled BabaDocument82 pagesUntitled BabaKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Fuel CellsDocument7 pagesFuel Cellsmuhammadumeryaqoob16No ratings yet
- Mod7 FuelCellsDocument25 pagesMod7 FuelCellsDHANUSH KARTHIK 20BME1003No ratings yet
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell BatteryDocument20 pagesHydrogen Fuel Cell BatteryAman RaikwarNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis PresentationDocument24 pagesElectrolysis PresentationsaeikipNo ratings yet
- PGT Unit 6 (Fuel Cells)Document22 pagesPGT Unit 6 (Fuel Cells)36.Praphull DesaleNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry ProjectAPARNA GANGWARNo ratings yet
- Hev M5Document9 pagesHev M5Anandhu ANo ratings yet
- Module 4Document31 pagesModule 4Pragati ShindeNo ratings yet
- EC - Batteries & Fuel CellsDocument39 pagesEC - Batteries & Fuel CellsDr. P. Sami Associate ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Design of Fuel Cells: FUEL CELL Is An Electrochemical Cell That Converts A Source Fuel Into An ElectricalDocument4 pagesDesign of Fuel Cells: FUEL CELL Is An Electrochemical Cell That Converts A Source Fuel Into An ElectricalnirajmechgecNo ratings yet
- FC Basics Technology TypesDocument2 pagesFC Basics Technology TypesRaja RJNo ratings yet
- Fuel CellsDocument18 pagesFuel CellsAwaiz KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PPT FEDocument33 pagesUnit 3 PPT FEU N K N O W NNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis PresentationDocument21 pagesElectrolysis PresentationGopi EagaNo ratings yet
- Group10... Full CellsDocument23 pagesGroup10... Full CellsDoaa KhaledNo ratings yet
- PGT Unit 6 (Fuel Cells)Document23 pagesPGT Unit 6 (Fuel Cells)Prem ShindeNo ratings yet
- Presentation Fuel Cell Presentation 1509777151 19748Document39 pagesPresentation Fuel Cell Presentation 1509777151 19748Krishna Pavan KNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell and It's Application 2Document25 pagesFuel Cell and It's Application 2Maharghya BiswasNo ratings yet
- Fuel CellDocument19 pagesFuel CellANUJ50% (2)
- 35f23f - Batteries and Electrochemical ProcessesDocument14 pages35f23f - Batteries and Electrochemical ProcessesZainNo ratings yet
- How Fuel Cells Work?Document12 pagesHow Fuel Cells Work?Ojashwi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cells UNIT1Document49 pagesFuel Cells UNIT1Sreelatha Aihloor SubramanayamNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document12 pagesModule 5SandeepNambiarNo ratings yet
- Eee 170421171247Document12 pagesEee 170421171247Vaseline RobinsonNo ratings yet
- FulesDocument17 pagesFulesadilNo ratings yet
- By B.Pallavi Sridevi Women's Engineering CollegeDocument15 pagesBy B.Pallavi Sridevi Women's Engineering CollegeVikas Kumar SriramNo ratings yet
- Lecture9 - Energy StorageDocument47 pagesLecture9 - Energy StorageTze Long GanNo ratings yet
- Why Koh Is PreferredDocument5 pagesWhy Koh Is PreferredavaithNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2021-22 CHY1701 ETH VL2021220503815 Reference Material II 10-03-2022 Module 5 Last PartDocument42 pagesWINSEM2021-22 CHY1701 ETH VL2021220503815 Reference Material II 10-03-2022 Module 5 Last PartKillari RohithNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cells: Basic Construction of Fuel CellDocument24 pagesFuel Cells: Basic Construction of Fuel CellDinu DasNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell - WorkingDocument26 pagesFuel Cell - WorkingGunjan VarshneyNo ratings yet
- 9 ExpDocument4 pages9 ExpSuRaJ BroNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Fuel CellDocument19 pagesAlkaline Fuel CellMadan KaushishNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry, Chapter 20, ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesAP Chemistry, Chapter 20, ElectrochemistrysethisoddNo ratings yet
- Low Volatge and BatteryDocument74 pagesLow Volatge and BatteryOladokun Sulaiman OlanrewajuNo ratings yet
- Sunum Son HaliDocument24 pagesSunum Son HaliasdasfasdasdNo ratings yet
- RES - Unit-V MaterialDocument13 pagesRES - Unit-V Materialvinayroyal715No ratings yet
- Fuel CellsDocument20 pagesFuel Cells2k22cscys2213057No ratings yet
- Fuel CellDocument17 pagesFuel CellMohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Fuel CellsDocument10 pagesFuel CellsEshaNo ratings yet
- Fuel CellsDocument16 pagesFuel CellsSalim MalikNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cellelectrical - BEE-IV - Power Generation - PE-241 (17-20)Document32 pagesFuel Cellelectrical - BEE-IV - Power Generation - PE-241 (17-20)RASHEED MUHAMMADNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell 2Document10 pagesFuel Cell 2Aravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Batteries and Fuel CellsDocument31 pagesBatteries and Fuel CellsUmesh ChandraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Activity 2005557Document18 pagesChemistry Activity 2005557Sunidhi MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON Fuel Cells::Anirudh Gupta: Electrometallurgy and Corrosion.: 902 2011Document15 pagesSeminar ON Fuel Cells::Anirudh Gupta: Electrometallurgy and Corrosion.: 902 2011Devashish JoshiNo ratings yet
- Fuel CellsDocument7 pagesFuel CellsJo VialNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Fuel CellsDocument15 pagesAlkaline Fuel CellsAman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell and It's ApplicationDocument28 pagesFuel Cell and It's ApplicationMaharghya BiswasNo ratings yet
- Explain The Concept of Fuel Cells.: Advantages Over Conventional Energy SourcesDocument9 pagesExplain The Concept of Fuel Cells.: Advantages Over Conventional Energy SourcesAnusha AnandNo ratings yet
- Fuel BatteryDocument17 pagesFuel BatteryHarsha Vardhan SakalaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Fuel CellDocument27 pagesHydrogen Fuel CellVikash Mohanty100% (12)
- Fuel Cell: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument18 pagesFuel Cell: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaarief_ajahNo ratings yet
- Advanced Batteries and Fuel Cells Technology: Lecture 1: IntroductionDocument43 pagesAdvanced Batteries and Fuel Cells Technology: Lecture 1: Introductionboyproso1.1997No ratings yet
- Advances in Energy Systems and Technology: Volume 5From EverandAdvances in Energy Systems and Technology: Volume 5Peter L. AuerNo ratings yet
- Generation and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseFrom EverandGeneration and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseNo ratings yet