Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To ICT Lecture#14: Prepared by Qurat-Ul-Ain
Uploaded by
mahazkhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views15 pagesData Communication
Original Title
Data Communication
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentData Communication
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views15 pagesIntroduction To ICT Lecture#14: Prepared by Qurat-Ul-Ain
Uploaded by
mahazkhanData Communication
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Introduction to ICT
Lecture#14
Department of Computer Science
Prepared by Qurat-ul-ain
DCS
COMSATS Institute of
Information Technology
Data Communication
The process of transferring data electronically from one place
to another
Data van be transferred by using different media
Data can be text, graphics, and sound etc
Electromagnetic or light waves are used to transmit data from
one place to another is called signal
Department of Computer Science 2
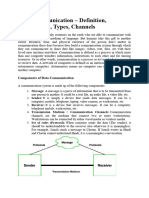
Basic Elements of Data Communication
The following components are required for successful
communication:
1. Sending device: that send message . It is also called source
or transmitter. Sending device can be a computer, fax
machine or mobile phone etc
2. Receiving device: that receive message. It is also called
sink. The receiving device can be a computer , printer, fax
machine or phone etc
3. Communication device: used to transmit message between
sending and receiving device through communication media.
Two most commonly used communication devices are
modem and network card
Department of Computer Science 3
Cont…
4. Transmission Media: is used to carry message from one
place to another. It is also called communication channel. It
can be a physical or wireless connection
5. Message: Message is the information to be communicated.
The message may consist of text, numbers, pictures audio etc
6. Protocol: A protocol is a set of rules that governs data
communication. It represents an agreement between
communication devices. Devices can not communicate
without protocol
Department of Computer Science 4
Cont…
Department of Computer Science 5
Data Transmission Modes
The way in which data is transmitted from one place to
another is called data transmission mode.
It is also called the data communication mode.
It indicates the direction of flow of information.
Sometimes, data transmission modes are also referred to as
directional modes.
There are three data transmission modes.
1. Simplex mode
2. Half-Duplex Mode
3. Full-Duplex Mode
Department of Computer Science 6
Cont…
Department of Computer Science 7
Cont…
1. Simplex mode:
In simplex mode, data can flow only in one directions
Examples of simplex communication modes are Radio and T.V
transmissions.
In computer system, the keyboard, monitor and printer are examples
of simplex devices.
2. Half-Duplex Mode:
Data can flow in both directions but not at the same time
It is transmitted one-way at a time
A device with half-duplex mode can send or receive data but not at
the same time
Example: Walkie- talkie in which message is sent one at a time and
messages are sent in both the directions.
Internet surfing
3. Department of Computer Science 8
Cont…
3. Full-Duplex Mode:
Data can travel in both directions simultaneously
It is faster way of data communication
Time is not wasted in changing the direction of data flow
Example: Telephone Network in which there is communication
between two persons by a telephone line, using which both can talk
and listen at the same time.
Department of Computer Science 9
Methods of Communication
1. Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS):
POTS, is a term which describes the voice-grade telephone service
that remains the basic form of residential and small business service
connection to the telephone network in most parts of the world.
Standard phone line
Two-way voice communication
Uses analog transmission techniques
Data communication is slow
The system was originally known as the Post Office Telephone
Service or Post Office Telephone System.
Today the term Plain Old Telephone Service is used, after the services
were removed from the control of national post offices.
Department of Computer Science 10
Modem
A modem is a hardware device that allows a computer to send
and receive data over a telephone line or a cable or satellite
connection.
Short for modulator-demodulator.
Computer information is stored digitally, whereas information
transmitted over telephone lines is transmitted in the form of
analog waves.
It converts or "modulates" an analog signal from a telephone
or cable wire to a digital signal that a computer can recognize.
Similarly, it converts outgoing digital data from a computer or
other device to an analog signal.
Speed measured in bits per second (bps)
Current fastest speed is 56 Kbps
Department of Computer Science 11
Cont…
Modem uses
Connection to the Internet
File transfer
Uploading
Downloading
Department of Computer Science 12
Digital Data Connection
1. Broadband:
This refers to high-speed data transmission in which a
single cable can carry a large amount of data at once.
Easier and faster to use
Information can be send and download must quicker then
traditional telephone and modem
Speed is measured in mega bits per second(Mbps)
The most common types of Internet broadband
connections are cable modems (which use the same
connection as cable TV) and DSL modems (which use
your existing phone line)
Department of Computer Science 13
Cont…
2. DSL:
Stands for "Digital Subscriber Line."
A technology which use the existing transmission
medium(telephone wire) to provide high speed transfer of
information across internet
Use more of the bandwidth
Allows simultaneous voice and high-speed data service
such as super fast Internet access over a single pair of
copper telephone line
Popular with home users
Speeds range from 100 Kbps to 30 Mbps
Department of Computer Science 14
Cont…
3. Cable Modem:
A cable modem is a peripheral device used to connect to
the Internet.
It operates over coax cable TV lines
Provides high-speed Internet access.
Since cable modems offer an always-on connection and
fast data transfer rates, they are considered broadband
devices.
Cable modems provided download and upload speeds of 1
to 3 Mbps
Popular with home and office users
Department of Computer Science 15
You might also like
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument9 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionCiifle CaddeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Computer NetworkingDocument42 pagesAdvanced Computer Networkingmustefa endrisNo ratings yet
- CN NotessDocument66 pagesCN NotessGRIMHEART REAPERNo ratings yet
- Data Comms & Computer Networks: Delivery, Accuracy, Timeliness & JitterDocument36 pagesData Comms & Computer Networks: Delivery, Accuracy, Timeliness & JitterDan TamiruNo ratings yet
- BSC VI Sem CN Unit IDocument33 pagesBSC VI Sem CN Unit IG51Mamatha PatlollaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Introduction To Computer Networks: M.Sc. (Computer Application) Sem-IIDocument537 pagesComputer Networks Introduction To Computer Networks: M.Sc. (Computer Application) Sem-IITanya JindalNo ratings yet
- DC_1Document19 pagesDC_1olivianatasha40No ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument103 pagesComputer NetworksNitinNo ratings yet
- Networking and Data Communication MBA Semester IIDocument91 pagesNetworking and Data Communication MBA Semester IISunit SudarsananNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworksTanmoy C0% (1)
- Unit 3Document43 pagesUnit 3Manoj pooniaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I: Fundamentals of Internet Data Communication ConceptsDocument50 pagesUNIT-I: Fundamentals of Internet Data Communication ConceptsSanthi VardhanNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument32 pagesComputer NetworkTony StarkNo ratings yet
- CH # 17 - Telecommunication NotesDocument6 pagesCH # 17 - Telecommunication Notesfarjad0% (1)
- Lect7 NetworksDocument35 pagesLect7 NetworksIdrees BharatNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking FundamentalsDocument5 pagesData Communication and Networking FundamentalsAditya KothariNo ratings yet
- Lesson7-Communications and NetworksDocument48 pagesLesson7-Communications and NetworksJennifer Diaz PendonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Network Communication TechnologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To The Network Communication TechnologyRosalyn TanNo ratings yet
- 5040 - File - COMMUNICATION AND COMPUTER NETWORK LT 3Document18 pages5040 - File - COMMUNICATION AND COMPUTER NETWORK LT 3Daniel Temitope OgunnaikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 CompntkDocument19 pagesChapter 5 Compntktekalegn barekuNo ratings yet
- Communications and The Internet: Scope of The ModuleDocument27 pagesCommunications and The Internet: Scope of The Modulejane quiambaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworkingDocument16 pagesIntroduction To NetworkingTimothy kaburuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ICTDocument19 pagesChapter 4 ICTJOHN CONo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument12 pagesData CommunicationSiddiq khanNo ratings yet
- Data Comm N NTWRKDocument13 pagesData Comm N NTWRKBishakha SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document8 pagesChapter 03Muqadas HakimNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer Network Chapter 1Document32 pagesData Communication and Computer Network Chapter 1Kalkidan SisayNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument8 pagesData Communicationlorry lamNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and NetworkDocument11 pagesData Communication and NetworkvanditaNo ratings yet
- Data Communication NotesDocument8 pagesData Communication NotesandreeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document10 pagesLesson 2Kean Rafael MarianoNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking FundamentalsDocument9 pagesData Communication and Networking FundamentalsSalman TahirNo ratings yet
- Communications and NetworksDocument14 pagesCommunications and Networksfscprimary05No ratings yet
- Lec 12Document23 pagesLec 12Aqsa gulNo ratings yet
- Csc407-Lecture Notes-1Document36 pagesCsc407-Lecture Notes-1Osinowo MosesNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument37 pagesComputer Network22MMC024 LOGESH KNo ratings yet
- MCA, CN, Unit 1Document80 pagesMCA, CN, Unit 1saithi paddeboyniaNo ratings yet
- CSA UNIT-9 CompDocument535 pagesCSA UNIT-9 CompVignesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Channels of CommunicationDocument4 pagesChannels of CommunicationHijar FahlipiNo ratings yet
- DC&N Osi CH01 PDFDocument12 pagesDC&N Osi CH01 PDFAbdiaziz QabileNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 1Document52 pagesCN Unit 1Hary DavidNo ratings yet
- ICT Lecture 11Document27 pagesICT Lecture 11Muhammad UmarNo ratings yet
- Cchapter 1 - Part IDocument21 pagesCchapter 1 - Part IBezabh AbebawNo ratings yet
- Communication Media and Devices: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesCommunication Media and Devices: Learning ObjectivesNur IzzatiNo ratings yet
- 1 Data Communication andDocument23 pages1 Data Communication andibraheemyusuf04No ratings yet
- Computer CommunicationDocument5 pagesComputer CommunicationMUGHEES BUTTNo ratings yet
- Lec 8Document15 pagesLec 8smnepalschoolNo ratings yet
- Transmission ModesDocument18 pagesTransmission ModesMedhanshu KaushikNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - Overview Chapter 1-Introduction 1.1.1 Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument31 pagesPart 1 - Overview Chapter 1-Introduction 1.1.1 Introduction To Computer NetworksMary JansiNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument13 pagesComputer NetworkParidhi GaurNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument16 pagesComputer Networkatul757012No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document8 pagesChapter 1Shubham GyawaliNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document131 pagesUnit 126 Rishabh ThakranNo ratings yet
- WCU Data Communication ChapterDocument33 pagesWCU Data Communication ChapterGetnete degemuNo ratings yet
- Communication Network and Internet ServicesDocument8 pagesCommunication Network and Internet ServicesTharankithabaskaranNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicaitonDocument6 pagesData CommunicaitonNdidiamaka Nwosu AmadiNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 1Document52 pagesCN Unit 1megha.bhoityNo ratings yet
- Shadia S. Baloch Senior Lecturer, FEST Isra University, HyderabadDocument42 pagesShadia S. Baloch Senior Lecturer, FEST Isra University, Hyderabadshadia saad balochNo ratings yet
- Advanced Long Range Proximity Reader PDFDocument1 pageAdvanced Long Range Proximity Reader PDFPhangkie RecolizadoNo ratings yet
- For Construction and Industry: Liebherr Diesel EnginesDocument8 pagesFor Construction and Industry: Liebherr Diesel EnginesGoran MatovicNo ratings yet
- RK271007 AN RXSF 1Document2 pagesRK271007 AN RXSF 1Ahmed FaragNo ratings yet
- 720-C-001 (Vent Wash Column)Document4 pages720-C-001 (Vent Wash Column)idilfitriNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 - Biomechanics in Sports Class 12Document29 pagesChapter-10 - Biomechanics in Sports Class 12Matrix craft4100% (1)
- Speed Control Methods of 3-Phase Induction MotorsDocument3 pagesSpeed Control Methods of 3-Phase Induction MotorsBenzene diazonium saltNo ratings yet
- BOYSEN® Marmorino™ Italian Marble Finish: Liters UseDocument1 pageBOYSEN® Marmorino™ Italian Marble Finish: Liters UseJohn Ray Esmama CalasicasNo ratings yet
- Node - Js 8 The Right Way: Extracted FromDocument11 pagesNode - Js 8 The Right Way: Extracted FromRodrigo Románovich FiodorovichNo ratings yet
- Simpack Off-Line and Real Time SimulationDocument23 pagesSimpack Off-Line and Real Time SimulationAnderson ZambrzyckiNo ratings yet
- 9607 Syllabus Media StudiesDocument28 pages9607 Syllabus Media StudiesmisterNo ratings yet
- Vastu House PlanDocument187 pagesVastu House Planshilpa shahNo ratings yet
- R7 Injection CheatSheet.v1Document1 pageR7 Injection CheatSheet.v1qweNo ratings yet
- Types of FuseDocument10 pagesTypes of FuseRane SiddeshNo ratings yet
- Practical Training Seminar Report FormatDocument8 pagesPractical Training Seminar Report FormatShrijeet PugaliaNo ratings yet
- June 28th Altran Capital Market Day Presentation DeckDocument52 pagesJune 28th Altran Capital Market Day Presentation Deckvenkata.krishnan100% (1)
- # Micro Pelton Turbines ! $Document93 pages# Micro Pelton Turbines ! $Nathaniel E. Barrios Fuentes100% (1)
- Six Sigma Statistical Methods Using Minitab 13 Manual4754Document95 pagesSix Sigma Statistical Methods Using Minitab 13 Manual4754vinaytoshchoudharyNo ratings yet
- CSR of DABUR Company..Document7 pagesCSR of DABUR Company..Rupesh kumar mishraNo ratings yet
- ERA News Mar 23 - Final - 0Document10 pagesERA News Mar 23 - Final - 0Băltoiu Son AlisaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis MphilDocument10 pagesSynopsis MphilAyesha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Coaching PhilosophyDocument2 pagesCoaching Philosophyapi-457181424No ratings yet
- Part 1Document3 pagesPart 1Jester NavarquezNo ratings yet
- Howden PDFDocument24 pagesHowden PDFskb2550% (2)
- Module 4.Document16 pagesModule 4.Sania MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- GE 5 Purposive Communication Course OverviewDocument10 pagesGE 5 Purposive Communication Course OverviewHarold LuceroNo ratings yet
- PqdifsdkDocument2 pagesPqdifsdkrafaelcbscribdNo ratings yet
- Crankcase Pressure SM019901095211 - en PDFDocument5 pagesCrankcase Pressure SM019901095211 - en PDFDavy GonzalezNo ratings yet
- LPDocument5 pagesLPHeizyl ann VelascoNo ratings yet
- Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 LicenseDocument4 pagesCreative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 LicenseAnindito W WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Redundant Arithmetic: Keshab K. ParhiDocument21 pagesChapter 14: Redundant Arithmetic: Keshab K. ParhiInJune YeoNo ratings yet