Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Form and Function
Uploaded by
Sharmine Poligratis Rico0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views42 pagesBiology report
Original Title
Biology Report
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBiology report
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views42 pagesPlant Form and Function
Uploaded by
Sharmine Poligratis RicoBiology report
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 42
CHAPTER 1
Plant Form and Function
PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
Plant growth, from seed
germination to maturity, involves a
combination of cellular responses
and molecular interaction
Transport System in
Plants
The Phloem....
Plant Nutrition
When we talk about plant nutrition,we
are referring to the supply and absortion
of chemical compounds for the growth
and metabolism of plants.In order for
higher plants to sustain their metabolic
processes,inorganic nutrients are
obtained from the environment via
soil,air and water.
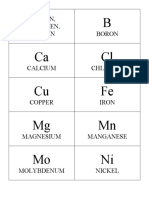
Elements Function in plants
Carbon, Hydrogen, oxygen Major constituent of organic plant material;
assimilation of oxidation – reduction reactions
Boron Cell wall synthesis; enzymatic reactions and
metabolic pathways; mitotic activity for root
development
Calcium Structural component of the cell wall and cell
membrane; counter ion in the vacuole
Chlorine Water splitting system for photosystem II;
stomatal opening regulation
Copper Co – factor for metalloproteins and enzymes;
photosynthetic electron transport; cell wall metabolism
and hormone signaling; oxidative stress response
Iron Regulatory component of proteins and metabolities in roots
and leaves
Magnesium Chloropyll synthesis; cofactor in activation of ATPase
Manganese Photodestruction of chloropyll and chloroplast structure;
enzyme activator; precursor of amino acid,
hormones(auxins) and lignins
Molybdenum Enzyme activation(e.g nitrate reductase, catalase, and
ribonuclease); chloropyll synthesis
Nickel Endosperm development and dehydrogenase activity; urease
activation for urea breakdown; root nodule growth
Nitrogen General plant growth of roots, stem, leaf, flowers and fruits;
chloropyll synthesis
phosphorus Energy transferring process for photosynthesis and respiration (ADP-
ATP synthesis); structural component of phospholipids, nucleic acids,
coenzymes, and nucleotides
Potassium Cell extension and stomatal regulation; enzyme,activation (kinase,
starch synthase, and nitrate reductase); photosynthetic activity(e.g.,
CO2 fixation and PH regulation)
SULFUR Assimilation of oxidation – reduction reactions; participates in various
enzymatic processes
Zinc Enzymatic function and reactivity; stem elongation; protein and
starch synthesis
Plant Hormones,Responses
and Feedback Mechanism
Reproduction and Modern
Biotechnological Application
Biotechnology has advance
significantly over the previous
years that breeding crops and
mass production are now aided
by plant tissue culture and
molecular biology techniques
Genetic engineering in plants was
introduced in the 1980's to create
transgenic crops that are high-
yield and persistant. This
technology utilizes Agrobacterium
tumefaciens to randomly
introduced heterologous DNA into
plants,thereby
Thank you for
listening!
Reported by: Mejares, Mae Antonette P.
You might also like
- Victorian Language of Flowers - FloriographyDocument32 pagesVictorian Language of Flowers - FloriographyOcto1100% (4)
- Red Wine ProductionDocument26 pagesRed Wine ProductionAidah NaufiaNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Poles For Engineered BambooDocument12 pagesBamboo Poles For Engineered BambooDanize Kate GimenoNo ratings yet
- Essay Titles + MarkschemesDocument49 pagesEssay Titles + MarkschemesSairah RazakNo ratings yet
- Fu Talisman For Physic HealthDocument6 pagesFu Talisman For Physic HealthmesiaNo ratings yet
- Denr Dao 97-34Document8 pagesDenr Dao 97-34ML BanzonNo ratings yet
- ESP Air in LeakDocument11 pagesESP Air in LeakRajesh Kumar MohantyNo ratings yet
- Sui Generis Protection of Plant Varieties An Indian PerspectiveDocument16 pagesSui Generis Protection of Plant Varieties An Indian PerspectiveKarthiayani A.No ratings yet
- Plant Form and FunctionDocument43 pagesPlant Form and FunctionMae MejaresNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument15 pagesPlant NutritionamieljihnNo ratings yet
- GEN. BIO. 2 Q4 Wk2A MENDELSSOHN L. AJESTA IIDocument12 pagesGEN. BIO. 2 Q4 Wk2A MENDELSSOHN L. AJESTA IIJohn Paul Luzgano AganapNo ratings yet
- Lec. 01.introductionDocument43 pagesLec. 01.introduction6ng2q6xywwNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University School of Graduate StudiesDocument25 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University School of Graduate StudiesKristoffer VillarealNo ratings yet
- B Ca CL Cu Fe MG MN Mo Ni: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen BoronDocument4 pagesB Ca CL Cu Fe MG MN Mo Ni: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen BoronWayne SalvadorNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch12 Mineral NutritionDocument5 pages11 Biology Notes Ch12 Mineral NutritionTushar RajNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and DevtDocument38 pagesPlant Growth and DevtPatriciaNo ratings yet
- 10 Homeostasis in Plant CellDocument47 pages10 Homeostasis in Plant CellMaleeha BasharatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Mineral NutritionDocument8 pagesChapter 12 - Mineral NutritionShani KumarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry2 PapersDocument31 pagesBiochemistry2 PapersShamoon HaroonNo ratings yet
- 3 PTC Medium-1Document34 pages3 PTC Medium-1HARSH MEENANo ratings yet
- Soil Science LectureDocument83 pagesSoil Science LectureMadellane MichaelisNo ratings yet
- Synoptic Essay PlansDocument21 pagesSynoptic Essay PlansBio_Joe50% (2)
- Nutrition: Animation 8.1: Nutrition Source & Credit: WikispaceDocument43 pagesNutrition: Animation 8.1: Nutrition Source & Credit: WikispaceAaa SssNo ratings yet
- Plants and Environment Factors - The PlantDocument33 pagesPlants and Environment Factors - The PlantnuningNo ratings yet
- Plants and Environment Factors-2020Document39 pagesPlants and Environment Factors-2020Angeline CallistaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry2 Past PaperDocument36 pagesBiochemistry2 Past PaperShamoon HaroonNo ratings yet
- Soil Microbiology NoteDocument21 pagesSoil Microbiology NoteOluwakemi OyinloyeNo ratings yet
- 6.1 PhotosynthesisDocument49 pages6.1 PhotosynthesisDea TjahyadiNo ratings yet
- InTech-Plant Genes For Abiotic StressDocument27 pagesInTech-Plant Genes For Abiotic StressJan Crezul BalodongNo ratings yet
- Proteome Analysis of Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) Root Under Sodium Chloride StressDocument12 pagesProteome Analysis of Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) Root Under Sodium Chloride StressMd Ashikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 8: Nutrition Short Questions: Q: Why Does An Organism Need Food?Document12 pagesUnit 8: Nutrition Short Questions: Q: Why Does An Organism Need Food?Ghulam Baqir MazariNo ratings yet
- 472 - Agboola-BIO 103 PDFDocument50 pages472 - Agboola-BIO 103 PDFAzeez quadri enesiNo ratings yet
- Plants and Environment Factors - The PlantDocument33 pagesPlants and Environment Factors - The PlantRania PrastiwiNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Management For Greenhouse VegetablesDocument19 pagesFertilizer Management For Greenhouse VegetablesMentewab EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Out Section 3 UsefulDocument18 pagesOut Section 3 UsefulkamanNo ratings yet
- 1.1.11 Nutrition in PlantsDocument6 pages1.1.11 Nutrition in PlantsAhenkan kwameNo ratings yet
- Jam ABC Dec2008Document9 pagesJam ABC Dec2008pazrroNo ratings yet
- BFE Unit 1-1Document17 pagesBFE Unit 1-1abhishek bhandareNo ratings yet
- REPORTING BiochemistryDocument6 pagesREPORTING Biochemistryclent girayNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Requirements of BacteriaDocument25 pagesNutritional Requirements of BacteriaAira MiyaNo ratings yet
- Algal NutritionDocument24 pagesAlgal Nutritionepick7No ratings yet
- Lemna SP ArmDocument16 pagesLemna SP ArmHanin Jaliyy100% (1)
- Molecular Biology of Drought StressDocument34 pagesMolecular Biology of Drought Stressvarsha pNo ratings yet
- CRSC 1 GUIDE QUESTIONS FOR CHAPTER 4Document5 pagesCRSC 1 GUIDE QUESTIONS FOR CHAPTER 4RanielJohn CollantesNo ratings yet
- Plant Respiration: April 2016Document12 pagesPlant Respiration: April 2016alfariza rfNo ratings yet
- Soil Fertility and ManagementDocument61 pagesSoil Fertility and ManagementAngge Cortes100% (1)
- Relationship Between Primary Metabolism and Secondary Metabolite AccumulationDocument47 pagesRelationship Between Primary Metabolism and Secondary Metabolite AccumulationMudit Misra100% (2)
- Mineral Nutrition in PlantsDocument4 pagesMineral Nutrition in Plantsdynamicsheetal70No ratings yet
- Overview Mega E3afaDocument19 pagesOverview Mega E3afaVolodymyrNo ratings yet
- Application of The Synechococcus NirA Promoter ToDocument8 pagesApplication of The Synechococcus NirA Promoter ToEduardo MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Selectivity of Protein Oxidative Damage During Aging in Drosophila MelanogasterDocument8 pagesSelectivity of Protein Oxidative Damage During Aging in Drosophila MelanogasterGustavo FelpeNo ratings yet
- Markers and Signals Associated With Nitrogen Assimilation in Higher PlantsDocument9 pagesMarkers and Signals Associated With Nitrogen Assimilation in Higher PlantsDewi SigalinggingNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Starch Synthesis ExperimentDocument20 pagesPhotosynthesis and Starch Synthesis ExperimentVince Adrian IlaganNo ratings yet
- Cmls 2001 58 1650 65Document17 pagesCmls 2001 58 1650 65Nadia khalizaNo ratings yet
- Unit I - BSWDocument31 pagesUnit I - BSWAshwinNo ratings yet
- Annual Plant Reviews, Biochemistry of Plant Secondary MetabolismFrom EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, Biochemistry of Plant Secondary MetabolismNo ratings yet
- Extracelular ProteinsDocument11 pagesExtracelular ProteinsKary TéllezNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influence Invidual Calorific NeedsDocument7 pagesFactors That Influence Invidual Calorific NeedsGayitri KanabiranNo ratings yet
- Drought Tolerance: Potential Due To High Solute ConcentrationDocument12 pagesDrought Tolerance: Potential Due To High Solute ConcentrationMudit MisraNo ratings yet
- Biology AssignmentDocument8 pagesBiology AssignmentpratapjaiswalshivanshuNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Requeriments - Westermann - 2005Document7 pagesNutritional Requeriments - Westermann - 2005Dario BaronaNo ratings yet
- Unit II Soil Fertility and Productivity PDFDocument20 pagesUnit II Soil Fertility and Productivity PDFArivukkarasu DhanapalNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument59 pagesPhotosynthesisAima AzharNo ratings yet
- Polyphenols Methods of ExtractionDocument6 pagesPolyphenols Methods of ExtractionWidayat WahyuNo ratings yet
- PP 501 RemovedDocument27 pagesPP 501 RemovedGulo GobindoNo ratings yet
- Identifying MicroorganismsDocument8 pagesIdentifying Microorganismsmihaela021988No ratings yet
- Regulation of Secondary Product and Plant Hormone Metabolism: FEBS Federation of European Biochemical Societies: 12th Meeting, Dresden, 1978From EverandRegulation of Secondary Product and Plant Hormone Metabolism: FEBS Federation of European Biochemical Societies: 12th Meeting, Dresden, 1978M. LucknerNo ratings yet
- DungeonYear A5 Condensed PagesDocument132 pagesDungeonYear A5 Condensed PagesU- TropuzNo ratings yet
- Trees Conservation SlogansDocument3 pagesTrees Conservation Slogansmkgarg2010100% (1)
- Wild Edible Fruits of Palpa District, West Nepal: Ras Bihari MahatoDocument10 pagesWild Edible Fruits of Palpa District, West Nepal: Ras Bihari MahatoAngel Eduardo Moreno AlboresNo ratings yet
- Vermicas Is One of The Best Fertilizer For PlantDocument3 pagesVermicas Is One of The Best Fertilizer For PlantxKingKobe24xNo ratings yet
- AsistasiaDocument8 pagesAsistasiaArabella FrondaNo ratings yet
- Wicking Guide-Cotton WicksDocument2 pagesWicking Guide-Cotton WicksJasmine EllisNo ratings yet
- "Meze" (Small Plates To Share) MenuDocument6 pages"Meze" (Small Plates To Share) Menushotokan456No ratings yet
- Horticulture - Landscaping - BonsaiDocument4 pagesHorticulture - Landscaping - BonsaiVINTAGE LOVER 17No ratings yet
- Terrariums: By: Angie BushDocument24 pagesTerrariums: By: Angie BushFaisal AnsiskaNo ratings yet
- RIEGO POR GOTEO Libro Cap24bibliografiaDocument107 pagesRIEGO POR GOTEO Libro Cap24bibliografiaIng. Luis Felipe Ferreras GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Indian ElephantDocument15 pagesIndian ElephantGanesh ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Limited Mini Ratna CompanyDocument20 pagesRashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Limited Mini Ratna CompanyRana KeyurNo ratings yet
- COMBINED SCIENCE1 Min PDFDocument100 pagesCOMBINED SCIENCE1 Min PDFLovemore MalakiNo ratings yet
- PM1282Document72 pagesPM1282waterssromNo ratings yet
- Main MenuDocument2 pagesMain MenueatlocalmenusNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Fasting Saltless and Saltless RecipesDocument12 pagesThe Importance of Fasting Saltless and Saltless RecipesAnonymous MYpy8rPNo ratings yet
- Landscaping Punch ListDocument36 pagesLandscaping Punch Listjavelio5000No ratings yet
- Written Report Cookery 10Document4 pagesWritten Report Cookery 10Andrea May IntiaNo ratings yet
- Mangrove Thesis 1st DraftDocument47 pagesMangrove Thesis 1st DraftMarie Dudan83% (6)
- Vol 2Document180 pagesVol 2ghostamirNo ratings yet
- How Can Colors Be Useful?: Unit QuestionDocument22 pagesHow Can Colors Be Useful?: Unit QuestionHà NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Easy Steps To Lawn CareDocument4 pagesEasy Steps To Lawn CareTom RisleyNo ratings yet
- FRANCISCO Manosa (TheoryDocument19 pagesFRANCISCO Manosa (TheoryShaira Reyes100% (10)