Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Report
Uploaded by
Franchess Isabelle Señores0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views17 pageshomeostasis
Original Title
science report
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenthomeostasis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views17 pagesScience Report
Uploaded by
Franchess Isabelle Señoreshomeostasis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
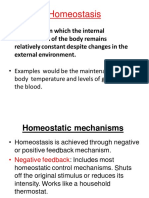
Homeostasis
A condition in which the internal
environment of the body remains
relatively constant despite changes in the
external environment.
Homeostasis is achieved through negative or
positive feedback mechanism.
Negative feedback: Includes most homeostatic
control mechanisms. Shuts of the original
stimulus, or reduces its intensity. Works like a
household thermostat.
Examples include control of blood pressure and
temperature regulation.
Positive feedback: Increases the original stimulus
to push the variable farther e.g. in blood clothing
and during the birth of a baby.
Homeostatic mechanism are designed to
reestablish homeostasis when there is an
imbalance.
There are three components to a homeostatic system
1. The Sensor which detects the stress.
2. The control center which receives information from the sensor
and sends a message to adjust the stress.
3. The effector which receives the message from the control center
and produces the response which reestablishes homeostasis.
It should be noticed that:
1. The heat produce by the furnace shuts the furnace down through
the thermostat.
2. The original stress is reduced the room warms up.
Homeostatic mechanism that show this to characteristics are
operating by negative feedback.
EXCRETION
Excretion
Is a process by which metabolic waste is
eliminated from an organism. In vertebrates
this is primarily carried out by the lungs,
kidneys and skin. This is in contrast with
secretion, where the substance may have
specific tasks after leaving the cell.
Sites of excretion
Renal:
Kidney
Others:
GIT
Lungs
Saliva
Sweat
Milk
You might also like
- Homeostasis and SkinDocument8 pagesHomeostasis and SkinHyperactive267No ratings yet
- BCH417 LN2 Homeostasis Concept in DiseasesDocument13 pagesBCH417 LN2 Homeostasis Concept in DiseasesidriscognitoleadsNo ratings yet
- Feedback MechanismsDocument1 pageFeedback MechanismsNiña VirayoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet General Biology 2 (Q4 - WK 5-6) Feedback MechanismDocument11 pagesLearning Activity Sheet General Biology 2 (Q4 - WK 5-6) Feedback MechanismJeffrey YumangNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument15 pagesHomeostasisAchira DeemanthaNo ratings yet
- HOMEOSTASISDocument10 pagesHOMEOSTASISolorunsolaolamide3No ratings yet
- Homeostasis and Control SystemsDocument2 pagesHomeostasis and Control SystemsRofekiNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument12 pagesHomeostasisTimothy StanleyNo ratings yet
- LIMCHIU - Lets Take The First Step2Document2 pagesLIMCHIU - Lets Take The First Step2Kyle LimchiuNo ratings yet
- Temperature Homeostasis (Thermoregulation)Document7 pagesTemperature Homeostasis (Thermoregulation)Fadilah Cuinta FisikaNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument16 pagesHomeostasisMerly MorgianaNo ratings yet
- What Happens If Stability Is Disrupted?: Human BodyDocument4 pagesWhat Happens If Stability Is Disrupted?: Human BodyDanooyyNo ratings yet
- 7 HomeostasisDocument7 pages7 HomeostasisAmy SuarezNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument16 pagesHomeostasisDr M K GuptaNo ratings yet
- Homeostatis: What Is Homeostasis?Document3 pagesHomeostatis: What Is Homeostasis?Uzair SoomroNo ratings yet
- ANFISDocument463 pagesANFISns.sara.alfarsaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Physiology Name:: Nowal ChoudharyDocument12 pagesAssignment Physiology Name:: Nowal ChoudharyhammdNo ratings yet
- 1 HomeostasisDocument14 pages1 HomeostasisBareera iftekharNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument46 pagesHomeostasisHeswer RajNo ratings yet
- FEEDBACK MECHANISM Module 5Document44 pagesFEEDBACK MECHANISM Module 5Xin Ssai XaveraNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Dr.P.HamambuluDocument15 pagesHomeostasis: Dr.P.HamambuluDevina SariNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument6 pagesHomeostasisLuqman Nul HakimNo ratings yet
- Environmental Homeostasis Homeostasis: Acting On An OrganismDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Homeostasis Homeostasis: Acting On An OrganismAtifMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Oral Physioloy Lecture 1 PDFDocument33 pagesOral Physioloy Lecture 1 PDFHabeeb AL-AbsiNo ratings yet
- GenBio 2 FinalsDocument7 pagesGenBio 2 FinalsPanot na BilogNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: A State of Balance in The BodyDocument13 pagesHomeostasis: A State of Balance in The BodyJedidah JongNo ratings yet
- Homeostatic RegulationDocument2 pagesHomeostatic RegulationGiyo RamosNo ratings yet
- Physiology Homeostasis: Presented By: Ms Kanwal QaiserDocument53 pagesPhysiology Homeostasis: Presented By: Ms Kanwal QaiserMuhammad SheerazNo ratings yet
- Bio2 WK 2Document53 pagesBio2 WK 2Crisha JelleNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument3 pagesHomeostasisAffie SaikolNo ratings yet
- Set PointDocument3 pagesSet PointMaria Katrinka Sophia MartiresNo ratings yet
- Joan Mam ActivityDocument5 pagesJoan Mam ActivitySheshira Reddy YeruvaNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument16 pagesHomeostasisAloysius RajNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument2 pagesHomeostasisGlaizel PanalNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Homeostasis: Denny Agustiningsih Dept. of PhysiologyDocument27 pagesGeneral Principles of Homeostasis: Denny Agustiningsih Dept. of Physiologyabdul qadirNo ratings yet
- A2 Biology Homeostasis Assignment: by Samir BabaldinDocument13 pagesA2 Biology Homeostasis Assignment: by Samir BabaldinNurhafidzah Shaiful HaqNo ratings yet
- A2 Biology Homeostasis Assignment: by Samir BabaldinDocument13 pagesA2 Biology Homeostasis Assignment: by Samir BabaldinNahla TammamNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument5 pagesPhysiologyEric KihiuNo ratings yet
- 4.01 HomeostasisDocument3 pages4.01 HomeostasisIbrahim Adel zaidNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and OsmoregulationDocument11 pagesHomeostasis and OsmoregulationMaria ChrisnaNo ratings yet
- Feedback MechanismsDocument7 pagesFeedback MechanismsClem Aisha Mae FajardoNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and Physiological Processes - ScholisticoDocument23 pagesHomeostasis and Physiological Processes - ScholisticojoffuhNo ratings yet
- Thermoregulation and HomeostasisDocument1 pageThermoregulation and Homeostasiskim trippNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument25 pagesHomeostasisCooper Puno100% (1)
- Lesson 5 Principles of Homeostasis and ThermoregulationDocument28 pagesLesson 5 Principles of Homeostasis and ThermoregulationKristie CorpusNo ratings yet
- PBLDocument5 pagesPBLlourdes kusumadiNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument25 pagesHomeostasisZhedriex EspirituNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HomeostasisDocument25 pagesIntroduction To HomeostasisSerrano, John DanielleNo ratings yet
- Oral Physioloy Lecture 3Document49 pagesOral Physioloy Lecture 3Habeeb AL-AbsiNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis, AnatomyDocument16 pagesHomeostasis, AnatomyKapemba White BothaNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and Feedback - OfFLINE STATIONDocument3 pagesHomeostasis and Feedback - OfFLINE STATIONLyn GomezNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument25 pagesHomeostasisJoey II Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Feedback Mechanism LESSON 1: Feedback Loops: General Biology 2Document6 pagesChapter 3: The Feedback Mechanism LESSON 1: Feedback Loops: General Biology 2Kylene RossNo ratings yet
- 3 HomeostasisDocument8 pages3 HomeostasisNoor ul aminNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document24 pagesBiology 1maleeha shahzadNo ratings yet
- Effector Response To Low Temperature Response To High TemperatureDocument6 pagesEffector Response To Low Temperature Response To High TemperatureBeth RespicioNo ratings yet
- The Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseFrom EverandThe Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Intro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1From EverandIntro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1No ratings yet
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- The Level of Satisfaction in The ImplemeDocument10 pagesThe Level of Satisfaction in The ImplemeFranchess Isabelle SeñoresNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER I II III Scope and Limitation UnfinishedDocument31 pagesCHAPTER I II III Scope and Limitation UnfinishedLourene Jauod- Guanzon100% (1)
- Theories of Health BehaviorDocument24 pagesTheories of Health BehaviorkitsilcNo ratings yet
- QualitativeDocument9 pagesQualitativeFranchess Isabelle SeñoresNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument6 pagesEnglishFranchess Isabelle SeñoresNo ratings yet
- Science ReportDocument14 pagesScience ReportFranchess Isabelle SeñoresNo ratings yet