Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04 Bus
Uploaded by
Anonymous uUFY090 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views23 pagesjhijijh
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentjhijijh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views23 pages04 Bus
Uploaded by
Anonymous uUFY09jhijijh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 23
Buses
• There are a number of possible
interconnection systems
• Single and multiple BUS structures are
most common
• e.g. Control/Address/Data bus (PC)
• e.g. Unibus (DEC-PDP)
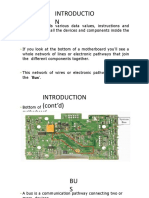
What is a Bus?
• A communication pathway connecting two
or more devices
• Usually broadcast
• Often grouped
—A number of channels in one bus
—e.g. 32 bit data bus is 32 separate single bit
channels
• Power lines may not be shown
Data Bus
• Carries data
—Remember that there is no difference between
“data” and “instruction” at this level
• Width is a key determinant of
performance
—8, 16, 32, 64 bit
Address bus
• Identify the source or destination of data
• e.g. CPU needs to read an instruction
(data) from a given location in memory
• Bus width determines maximum memory
capacity of system
—e.g. 8080 has 16 bit address bus giving 64k
address space
Control Bus
• Control and timing information
—Memory read/write signal
—Interrupt request
—Clock signals
Bus Interconnection Scheme
Big and Yellow?
• What do buses look like?
—Parallel lines on circuit boards
—Ribbon cables
—Strip connectors on mother boards
– e.g. PCI
—Sets of wires
Physical Realization of Bus Architecture
Single Bus Problems
• Lots of devices on one bus leads to:
—Propagation delays
– Long data paths mean that co-ordination of bus use
can adversely affect performance
– If aggregate data transfer approaches bus capacity
• Most systems use multiple buses to
overcome these problems
Traditional (ISA)
(with cache)
High Performance Bus
Bus Types
• Dedicated
—Separate data & address lines
• Multiplexed
—Shared lines
—Address valid or data valid control line
—Advantage - fewer lines
—Disadvantages
– More complex control
– Ultimate performance
Bus Arbitration
• More than one module controlling the bus
• e.g. CPU and DMA controller
• Only one module may control bus at one
time
• Arbitration may be centralised or
distributed
Centralised or Distributed Arbitration
• Centralised
—Single hardware device controlling bus access
– Bus Controller
– Arbiter
—May be part of CPU or separate
• Distributed
—Each module may claim the bus
—Control logic on all modules
Timing
• Co-ordination of events on bus
• Synchronous
—Events determined by clock signals
—Control Bus includes clock line
—A single 1-0 is a bus cycle
—All devices can read clock line
—Usually sync on leading edge
—Usually a single cycle for an event
PCI Bus
• Peripheral Component Interconnection
• Intel released to public domain
• 32 or 64 bit
• 50 lines
PCI Bus Lines (required)
• Systems lines
—Including clock and reset
• Address & Data
—32 time mux lines for address/data
—Interrupt & validate lines
• Interface Control
• Arbitration
—Not shared
—Direct connection to PCI bus arbiter
• Error lines
PCI Bus Lines (Optional)
• Interrupt lines
—Not shared
• Cache support
• 64-bit Bus Extension
—Additional 32 lines
—Time multiplexed
—2 lines to enable devices to agree to use 64-
bit transfer
• JTAG/Boundary Scan
—For testing procedures
PCI Commands
• Transaction between initiator (master)
and target
• Master claims bus
• Determine type of transaction
—e.g. I/O read/write
• Address phase
• One or more data phases
PCI Read Timing Diagram
PCI Bus Arbiter
PCI Bus Arbitration
Foreground Reading
• Stallings, chapter 3 (all of it)
• www.pcguide.com/ref/mbsys/buses/
• In fact, read the whole site!
• www.pcguide.com/
You might also like
- Buses and InterconnectionDocument32 pagesBuses and Interconnectionather_88100% (1)
- Sytem BusDocument24 pagesSytem BusRam RamNo ratings yet
- CH 03 p2 BusStructureDocument37 pagesCH 03 p2 BusStructureAnanda Haykel IskandarNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument25 pagesComputer Organization and ArchitectureNeel RavalNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 Edition System BusesDocument34 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 Edition System BusesShakeel AwanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Interrupts and Buses StructureDocument17 pagesMultiple Interrupts and Buses Structureapi-3801329100% (2)
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 EditionDocument62 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 EditionMD. MAHIR ABRAR KHANNo ratings yet
- Ch02 - System InterconnectionDocument29 pagesCh02 - System InterconnectionViet Quang VoNo ratings yet
- 3 BusesDocument61 pages3 BusesPuso MoletaNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 Edition System BusesDocument50 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 Edition System BusesRubeshan ShanNo ratings yet
- Unit 15 Bus StructureDocument32 pagesUnit 15 Bus StructureRennie KawanguNo ratings yet
- 4Document12 pages4Abdulaziz TilahunNo ratings yet
- Ch3 PDFDocument62 pagesCh3 PDFtesfu zewduNo ratings yet
- Arsitektur Komputer (Sistem Bus)Document51 pagesArsitektur Komputer (Sistem Bus)Dianne HarrisNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 EditionDocument55 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 EditionAthreyaNo ratings yet
- 03 - Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionDocument64 pages03 - Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnectionbree789No ratings yet
- Interconnection Structures: Collection of Paths Connecting Various Modules Is Called As Interconnection StructureDocument22 pagesInterconnection Structures: Collection of Paths Connecting Various Modules Is Called As Interconnection Structuredomainname9No ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 Edition System BusesDocument55 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 Edition System BusesLeandro MansillaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 On Chapter 3 A Top-Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection by Sameer AkramDocument37 pagesLecture 3 On Chapter 3 A Top-Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection by Sameer AkramUs ManNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 EditionDocument47 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 EditionMeena ShahNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 EditionDocument55 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 EditionMuhammad WildanNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 Edition System BusesDocument55 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 Edition System BusespuyNo ratings yet
- LectureSeries3 - BusesDocument19 pagesLectureSeries3 - BusesLamar ArnoldNo ratings yet
- BusesDocument55 pagesBusesWajahat HussainNo ratings yet
- System Bus in Computer Architecture: Goran Wnis Hama AliDocument34 pagesSystem Bus in Computer Architecture: Goran Wnis Hama AliGoran WnisNo ratings yet
- Interfacing Processors and Peripherals: CS151B/EE M116C Computer Systems ArchitectureDocument31 pagesInterfacing Processors and Peripherals: CS151B/EE M116C Computer Systems ArchitecturetinhtrilacNo ratings yet
- A Top-Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionDocument56 pagesA Top-Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionVERY YOGA MARULI TUA SIHOMBING TBANo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 Edition System BusesDocument54 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 Edition System BusesNiloy RahmanNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 Edition System BusesDocument58 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 Edition System BusesDr-Raghad Al-FahamNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 Edition System BusesDocument54 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 Edition System BusesAhmed Hassan MohammedNo ratings yet
- Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionDocument62 pagesTop Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionAhsan JameelNo ratings yet
- 03 - Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionDocument55 pages03 - Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnectionjanray1988No ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Architecture 8 Edition: Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionDocument55 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Architecture 8 Edition: Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnectionmeriem bahaNo ratings yet
- Part 04: Designing For Performance: Prof. Aaradhana DeshmukhDocument55 pagesPart 04: Designing For Performance: Prof. Aaradhana Deshmukhmadhursen99No ratings yet
- El ProcesadorDocument58 pagesEl ProcesadorCarlos Jesus Koo LabrinNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture and OrganizationDocument61 pagesComputer Architecture and OrganizationPoornima EgNo ratings yet
- 03 - Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionDocument50 pages03 - Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnectiondommy omosaNo ratings yet
- Computer Architeture Bus StructureDocument33 pagesComputer Architeture Bus StructureJbr RaheemNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 Edition System BusesDocument39 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 Edition System BusesMurtaza JamaliNo ratings yet
- 03 - Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionDocument32 pages03 - Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionflowrentsiaNo ratings yet
- 03 - Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionDocument44 pages03 - Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionMAHNOOR ATIFNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 EditionDocument55 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 EditionflowrentsiaNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 Edition System BusesDocument55 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 Edition System BusesHassan MansoorNo ratings yet
- Ecs 401 - Computer Organization Unit - I: BusesDocument8 pagesEcs 401 - Computer Organization Unit - I: BusesSannu KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization: Lec # 9: Bus System Bnar MustafaDocument29 pagesComputer Organization: Lec # 9: Bus System Bnar Mustafazara qojo (زارا)No ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document15 pagesLecture 8Syed MuneebNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2021-22 ECE3004 TH VL2021220101856 Reference Material I 20-10-2021 Module 5 - 3 DMADocument31 pagesFALLSEM2021-22 ECE3004 TH VL2021220101856 Reference Material I 20-10-2021 Module 5 - 3 DMABharath P NairNo ratings yet
- Io BusesDocument56 pagesIo Buseslalokew375No ratings yet
- Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #15 A View of Computer Function and Interconnection Interconnections StructuresDocument12 pagesComputer Organization & Architecture Lecture #15 A View of Computer Function and Interconnection Interconnections Structuresavdheshg_1No ratings yet
- Bus StructureDocument34 pagesBus StructureNoorullah ShariffNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument47 pagesIntroduction To ComputerPradhyumn ShetTilveNo ratings yet
- Lecture Microprocessor 7 - 8Document30 pagesLecture Microprocessor 7 - 8John wickNo ratings yet
- ECEG-3202 Computer Architecture and Organization: Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionDocument36 pagesECEG-3202 Computer Architecture and Organization: Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionESTIFANOS NegaNo ratings yet
- ECEG-3202 Computer Architecture and Organization: Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionDocument36 pagesECEG-3202 Computer Architecture and Organization: Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnectionδιρορα δρNo ratings yet
- Computer Buses: What Is A Bus?Document14 pagesComputer Buses: What Is A Bus?masumiNo ratings yet
- 07 Input OutputDocument63 pages07 Input Outputdeepak joshiNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 Edition Input/OutputDocument63 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 Edition Input/Outputtesos ganulNo ratings yet
- HarshadDocument61 pagesHarshadsaurabh deshmukhNo ratings yet
- Perilaku Ibu Hamil Dan KariesDocument22 pagesPerilaku Ibu Hamil Dan KarieshariyaniNo ratings yet
- HOME ECO (Decision Making 1-3)Document3 pagesHOME ECO (Decision Making 1-3)Ruth Belle HolgadoNo ratings yet
- Resolution No. 1433Document2 pagesResolution No. 1433MA. DIVINA LAPURANo ratings yet
- Henri Fayol A StrategistDocument13 pagesHenri Fayol A StrategistTerence DeluNo ratings yet
- The DimensionsDocument3 pagesThe DimensionsWilliam SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Plotting A Mystery NovelDocument4 pagesPlotting A Mystery NovelScott SherrellNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Cause List - 16.10.2023Document7 pagesSupplementary Cause List - 16.10.2023Aamir BhatNo ratings yet
- Operant Conditioning of RatsDocument7 pagesOperant Conditioning of RatsScott KaluznyNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Energy and MetabolismDocument75 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Energy and MetabolismJing LiNo ratings yet
- Soni Musicae Diato K2 enDocument2 pagesSoni Musicae Diato K2 enknoNo ratings yet
- OENDL3000007Document260 pagesOENDL3000007yoonsv100% (2)
- Tribune Publishing FilingDocument11 pagesTribune Publishing FilingAnonymous 6f8RIS6No ratings yet
- Cantilever Slab Beam Design For TorsionDocument17 pagesCantilever Slab Beam Design For TorsionNikhil100% (1)
- Present PerfectDocument1 pagePresent PerfectFrancs Fuentes100% (1)
- Scholarship ResumeDocument2 pagesScholarship Resumeapi-331459951No ratings yet
- Zalando SE Q3 2023 Financials PDFDocument7 pagesZalando SE Q3 2023 Financials PDFHjraNo ratings yet
- The Achaeans (Also Called The "Argives" or "Danaans")Document3 pagesThe Achaeans (Also Called The "Argives" or "Danaans")Gian Paul JavierNo ratings yet
- Camping Checklist: Essentials / Survival Sleep GearDocument2 pagesCamping Checklist: Essentials / Survival Sleep GearRomi Roberto100% (1)
- Lectra Fashion e Guide Nurturing EP Quality Logistics Production Crucial To Optimize enDocument8 pagesLectra Fashion e Guide Nurturing EP Quality Logistics Production Crucial To Optimize eniuliaNo ratings yet
- Torres v. People (2011)Document2 pagesTorres v. People (2011)Gigi LucilleNo ratings yet
- Shahid Change ManagementDocument1 pageShahid Change Managementtanveer azamNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Online Car Rental Management System: Presented byDocument41 pagesPresentation On Online Car Rental Management System: Presented byNikhilesh K100% (2)
- UWI St. Augustine Student Wireless Network - Instruction / Setup GuideDocument2 pagesUWI St. Augustine Student Wireless Network - Instruction / Setup GuideBrendan B. MastayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7. Linear Momentum and ImpulseDocument6 pagesLesson 7. Linear Momentum and ImpulselopomNo ratings yet
- BYD Case StudyDocument12 pagesBYD Case StudyELIZANo ratings yet
- Tatanka Oyate 2 EngDocument3 pagesTatanka Oyate 2 EngdesiNo ratings yet
- Summary Prof EdDocument19 pagesSummary Prof EdFloravie Onate100% (2)
- House Bill 4208Document1 pageHouse Bill 4208Sinclair Broadcast Group - EugeneNo ratings yet
- Induction and Training Road-Map: GenpactDocument27 pagesInduction and Training Road-Map: GenpactShrey KanungoNo ratings yet