Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Larva
Types of Larva
Uploaded by
Israr Khan Musakhail0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views12 pagesOriginal Title
TYPES-OF-LARVA.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views12 pagesTypes of Larva
Types of Larva
Uploaded by
Israr Khan MusakhailCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
A larva (Latin; plural larvae) is a distinct juvenile
form many animals undergo before metamorphosis
into adults. Animals with indirect developments such
as insects, amphibians or cnidarians specially have a
larval phase of their lifecycle Larva is Latin for
"ghost".
Larvae are frequently adapted to environments
separate from adults. For example, some larvae
such as tadpoles live exclusively in aquatic
environments, but as adults can live outside
water as frogs. By living in distinct
environments, larvae may be given shelter from
predators and reduce competition for resources
with the adult population.
1. Protopod larva:- It shows ill-defined segmentation and has
rudimentary caphalic and thoracic appendages.
It occurs in some parasitic forms of insects.
It has is merely a precociously hatched embryo.
It feed on nutritive fluid of the host.
2. Apod larva:- Its is called maggot in housefly.
Apod larva lacks legs.
In mosquitoes, larva is free swimming and is called
wriggler.
Body is elongated, cylindrical and is divisible into
head, thorax and abdomen.
In culex larva, the abdoment is without palmate
hairs.
It head may be well-developed, reduced or absent.
An apod larva wit ha fully developed had is say be eucephalous
as in red wasp
An apod larva with a reduced head is say to be hemicephalous as
in honeybee
An apod larva with no head is called acephalous as in housefly
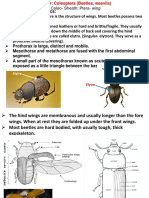
3. Oligopod larva:- It has true thoracic legs. It is further of two
kinds:
A. Scrabraiform larva:- it has cylindrical body with short thoracic
legs.
The terminal processes on abdomen are absent.
example in many beetles.
B. Compodiform larva:- It has long, depressed body with prominent
thoracic legs and also bear prominent terminal processes.
Example in may Neuropterans and coleopterans.
c. Elateriform larva:- it has an elongated, smooth,
cyclindrical,hardened body.
It is a root pest of many crops.
It occur in the click beetle.
D. Triongulin larva:- it has an elongated body with very
well developed legs, each bearing three claws.
Its found in the soil beetles
It’s a parasite in the nest of solitary bees or on the egg
masses of grasshopper.
4. Polypod larva:- It possesses stumpy, unjointed
prolegs on the abdomen in addition to true
segmented thoracic legs.
Mouth part are of chewing type
Antenna are short.
Its found in Lepidoptera and Hymenoptera.
They are also called eruciform and have 3 pair of
sclerotised, jointed legs and fleshy, abdominal ‘prolegs'.
Polypod larvae are usually caterpillars i.e. larvae of
butterflies or moths.
Most of caterpillar have cylindrical
bodies consisting of multiple
segments, with three pairs of true legs
on the thorax and several pairs of
short, fleshy prolegs on the abdomen.
The head has six small eyes
(stemmata) on each side that function
in light detection but not in image
formation
They generally eat leaves of various
types of plants, though some species
eat insect or other small animals.
The beetle larvae can be of
different shapes and sizes.
Some are wormlike and
legless, and other are more
like caterpillar, with thoracic
legs and abdominal prolegs.
Many larvae have C-shaped
bodies and are usually soft.
This form of larva, which is
present in scarabs and other
beetles, often is called a grub.
Healthy larvae are snowy
white and resemble small
grubs curled up in the cells.
Tiny at first the larvae
grow quickly, shedding their
skin five times.
The larvae are helpless
little creatures and have
voracious appetites,
consuming 1300 meals a
day.
The mosquito larva has a well
developed head with mouth
brushes used for feeding, a large
segmented abdomen.
Larvae breathe through
spiracles located on the eight
abdominal segment, or through a
siphon, and therefore must come
to the surface frequently.
The larvae spend most of their
time feeding on algae, bacteria,
and other microbes in the surface
micro layer.
The integument of the house fly
larva consist of an outer acellular
cuticle and inner single layer of
epithelium which rest on a basement
membrane. The cuticle is covered
with an epicuticle and has are
stratified structure.
The larva is white and cylindrical,
which the posterior end broad and
flattened. It tapers anteriorly.
They are no eyes or appendages,
although they are some ventral spiny
ridges which aid locomotion.
The larvae have 13 segments, but
the first two are partially fused so
that only 12 segments are
appearance.
You might also like
- (Bloomsbury Advances in Translation) Helen Julia Minors - Music, Text and Translation-Bloomsbury Academic (2013) PDFDocument242 pages(Bloomsbury Advances in Translation) Helen Julia Minors - Music, Text and Translation-Bloomsbury Academic (2013) PDFRocío CortésNo ratings yet
- ColeopteraDocument23 pagesColeopterapurbali100% (1)
- Fungi Characteristics of Fungi Key Points Ascus. Reproduction Key PointsDocument4 pagesFungi Characteristics of Fungi Key Points Ascus. Reproduction Key PointsPrincess Z. DaelNo ratings yet
- 15 January 2004 1st Lecture Herpetology ECOL 483/583 University of Arizona Spring 2004Document14 pages15 January 2004 1st Lecture Herpetology ECOL 483/583 University of Arizona Spring 2004andreaweiler1No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Mycology I PDFDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Mycology I PDFWpj JanuNo ratings yet
- Insect OrderDocument5 pagesInsect OrderkarinadegomaNo ratings yet
- Puma - Class AssignmentDocument6 pagesPuma - Class AssignmentUmang Zehen100% (1)
- Cat A PillarDocument26 pagesCat A PillartgeerawoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document28 pagesLecture 1Mamun_Abdullah_1612100% (1)
- Introductory Entomology: Third Semester Lamjung CampusDocument206 pagesIntroductory Entomology: Third Semester Lamjung Campusnishan khatriNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Entomology 10Document9 pagesStudy Guide For Entomology 10Alex TunqueNo ratings yet
- Seeds DisperselDocument9 pagesSeeds DispersellovleshrubyNo ratings yet
- Incredible Insects - How Do Flies Breathe With No Lungs?Document1 pageIncredible Insects - How Do Flies Breathe With No Lungs?Kelsey WosnitzkaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in EntomologyDocument9 pagesBasic Concepts in Entomologyjyc roseNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and Classification....Document8 pagesTaxonomy and Classification....Andrew MarariaNo ratings yet
- Ento Lab Midterms HandoutsDocument8 pagesEnto Lab Midterms Handoutshumanupgrade100% (1)
- Morphology and Life Cycle of Puccinia and The Symptoms of SmutsDocument21 pagesMorphology and Life Cycle of Puccinia and The Symptoms of SmutsRuchika PokhriyalNo ratings yet
- Phthiraptera - Johari JalinasDocument24 pagesPhthiraptera - Johari JalinasJohari Jalinas100% (1)
- Insect MorphologyDocument10 pagesInsect MorphologyDragan GrčakNo ratings yet
- Dispersal of Seeds by FruitsDocument6 pagesDispersal of Seeds by FruitsAnil PantNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Orthoptera and Allied Insects:, IncludingDocument9 pagesA Guide To Orthoptera and Allied Insects:, IncludingMaria Angela Caisapanta PachecoNo ratings yet
- EntomologyDocument37 pagesEntomologytariNo ratings yet
- 2010 MG EntomologyDocument11 pages2010 MG EntomologyhundohanNo ratings yet
- Seminar 1 - Ecosystems and Human InterferenceDocument3 pagesSeminar 1 - Ecosystems and Human InterferenceStefanNo ratings yet
- PollinationDocument9 pagesPollinationMia MadiaNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO ENTOMOLOGY DEGREE 3yrsDocument132 pagesINTRODUCTION TO ENTOMOLOGY DEGREE 3yrsMalikNo ratings yet
- M.a.part - II - Paper ViiDocument174 pagesM.a.part - II - Paper Viinv_xp750% (2)
- Bryophytes (Liverworts) PDFDocument7 pagesBryophytes (Liverworts) PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Lec4 SocialInsects TheSociety NotesDocument3 pagesLec4 SocialInsects TheSociety NotesAlexandra LvNo ratings yet
- Entomology: Naming of TaxaDocument19 pagesEntomology: Naming of TaxaAliah Alleyne Canals - BSA - 1ANo ratings yet
- Clasification of InsectsDocument68 pagesClasification of InsectsMarie Serena McConnellNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy 3 PDFDocument18 pagesTaxonomy 3 PDFJessa BelleNo ratings yet
- Swallowtail ButterflyDocument8 pagesSwallowtail Butterflymineiro_quimica2007No ratings yet
- Phylum PoriferaDocument17 pagesPhylum PoriferaRhiZhal SquDetto FrizTalNo ratings yet
- Exercise 10-11 (Lice of Mammals and Birds)Document92 pagesExercise 10-11 (Lice of Mammals and Birds)Jelika Raakin100% (2)
- GN 310 EntomologyDocument49 pagesGN 310 EntomologyKaira Mae CamiletNo ratings yet
- Invert Lab 2Document1 pageInvert Lab 2Beruk BerhaneNo ratings yet
- Polytene ChromosomeDocument21 pagesPolytene Chromosomestevensb055No ratings yet
- Linnean - Nomenclature - Week - One - Docx Filename - UTF-8''Linnean Nomenclature Week OneDocument32 pagesLinnean - Nomenclature - Week - One - Docx Filename - UTF-8''Linnean Nomenclature Week OneKaydina GirNo ratings yet
- Fungi Complete NotesDocument22 pagesFungi Complete NotesAli Akber FerokeNo ratings yet
- Nematode Biology, Physiology & Ecology - Conversion GateDocument42 pagesNematode Biology, Physiology & Ecology - Conversion GatePra YoudhaNo ratings yet
- Phylogeny and EvolutionDocument12 pagesPhylogeny and EvolutionKathryn Palmerton0% (1)
- Agr 154 C1Document28 pagesAgr 154 C1Fatin Aisyah SulaimanNo ratings yet
- ICNDocument18 pagesICNDr. Vineet GoswamiNo ratings yet
- A History of EntomologicalDocument20 pagesA History of EntomologicalBarzola HerlissNo ratings yet
- Lab+3+Taxonomy+Lab ACDocument42 pagesLab+3+Taxonomy+Lab ACJustinSantostefanoNo ratings yet
- Entomology Lab HandoutsDocument13 pagesEntomology Lab Handoutshumanupgrade100% (1)
- Synonym (Taxonomy)Document5 pagesSynonym (Taxonomy)Constantin TodiNo ratings yet
- Botanical NomenclatureDocument4 pagesBotanical NomenclatureKanak SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Hierarchical Classification: Linnaean HierarchyDocument3 pagesHierarchical Classification: Linnaean HierarchyanunglaNo ratings yet
- ButterflyDocument13 pagesButterflyashisb444No ratings yet
- Cnidaria: Body Cavity Known As The CoelenteronDocument21 pagesCnidaria: Body Cavity Known As The CoelenteronLakshya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Why Name Changes in PlantsDocument27 pagesWhy Name Changes in PlantsPhani Bhusan SahooNo ratings yet
- ChordataDocument28 pagesChordatatinchu guptaNo ratings yet
- Full TextDocument295 pagesFull TextkanNo ratings yet
- Flowering PlantDocument21 pagesFlowering PlantAhmed SharifNo ratings yet
- Key Psocoptera PDFDocument83 pagesKey Psocoptera PDFkhawla zedNo ratings yet
- Aphids as Virus VectorsFrom EverandAphids as Virus VectorsKerry F. HarrisNo ratings yet
- Review of Invertebrate Biological Control Agents Introduced into EuropeFrom EverandReview of Invertebrate Biological Control Agents Introduced into EuropeNo ratings yet
- Colombia Culture ResumeDocument5 pagesColombia Culture ResumeVictoria BritoNo ratings yet
- Saint Saens Organ Symphony - Google SearchDocument6 pagesSaint Saens Organ Symphony - Google SearchlanguageinfinityNo ratings yet
- Arutunian Trompete BBDocument8 pagesArutunian Trompete BBAbdalan da Gama100% (1)
- Cópia de 30 Day Monthly Habit TrackerDocument7 pagesCópia de 30 Day Monthly Habit TrackerJosesitoleNo ratings yet
- Between Two Skies by Joanne O'Sullivan Discussion GuideDocument3 pagesBetween Two Skies by Joanne O'Sullivan Discussion GuideCandlewick PressNo ratings yet
- Final Upper-Inermediate Exam BDocument5 pagesFinal Upper-Inermediate Exam BgalinaNo ratings yet
- Midway Metals CatalogueDocument10 pagesMidway Metals CataloguegarrybieberNo ratings yet
- Lesson A Around Town: 1. Label The Pictures With The Correct Words From The BoxDocument6 pagesLesson A Around Town: 1. Label The Pictures With The Correct Words From The BoxANTHONY STIVEN GAVILEMA TIPANTUÑANo ratings yet
- Liquid Yeast Comparison Chart UpdatedDocument2 pagesLiquid Yeast Comparison Chart UpdatedJose G VegaNo ratings yet
- HP Odu PDFDocument7 pagesHP Odu PDFarielp31No ratings yet
- FO - Assist & Duty Manager (AM, PM, Night) ChecklistDocument7 pagesFO - Assist & Duty Manager (AM, PM, Night) ChecklistTaco CompanyNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument1 pageReported SpeechMartabm29No ratings yet
- Kismet's Guide To Sex & Romance in Fantasy GamingDocument89 pagesKismet's Guide To Sex & Romance in Fantasy GaminggoroNo ratings yet
- Rizal Provincial Government: Republic of The Philippines Provincial Engineer's OfficeDocument2 pagesRizal Provincial Government: Republic of The Philippines Provincial Engineer's OfficeNikki CalumaNo ratings yet
- Press Release: 2018 Provisional Calendar Date Grand Prix VenueDocument1 pagePress Release: 2018 Provisional Calendar Date Grand Prix VenueYonatanPutraNo ratings yet
- Economic Impact of The Fashion IndustryDocument8 pagesEconomic Impact of The Fashion Industryan nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Whipping Cream PowderDocument2 pagesWhipping Cream PowderSALCON ConsultancyNo ratings yet
- JollibeeeeDocument2 pagesJollibeeeeKrishna Dasi GarciaNo ratings yet
- t2 T 8355 ks2 ST Patricks Day Party Games PowerpointDocument7 pagest2 T 8355 ks2 ST Patricks Day Party Games PowerpointjuvervanderleiNo ratings yet
- Dell Poweredge ServerDocument3 pagesDell Poweredge ServerSimlim SqNo ratings yet
- Uniarch Mobile Surveillance App Datasheet - V1.0Document3 pagesUniarch Mobile Surveillance App Datasheet - V1.0groupaura850No ratings yet
- The Summer Girl Elle KennedyDocument349 pagesThe Summer Girl Elle KennedyMariana GodinhoNo ratings yet
- Gertie Food MenuDocument2 pagesGertie Food MenuEater NYNo ratings yet
- EXERCISES - Reported Speech With InfinitiveDocument2 pagesEXERCISES - Reported Speech With InfinitiveThu TangNo ratings yet
- Business Models and Capturing Value: 6.1. What Is A Business Model?Document6 pagesBusiness Models and Capturing Value: 6.1. What Is A Business Model?Melkamu AbiyuNo ratings yet
- NovelsDocument16 pagesNovelsWeiNo ratings yet
- Lí Thuyết Tiếng Anh - Chức Năng Giao Tiếp - Lời Khen Ngợi, Chúc Mừng Và Động ViênDocument3 pagesLí Thuyết Tiếng Anh - Chức Năng Giao Tiếp - Lời Khen Ngợi, Chúc Mừng Và Động ViênHồ Viết TiênNo ratings yet
- BER Analysis OfNakagami M Channels WithDocument3 pagesBER Analysis OfNakagami M Channels WithÖzge Buse CoşkunNo ratings yet