Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ito Na Talaga Totoo Pramis Teksman Mamatay Man-2
Uploaded by
ReveRie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views11 pagesOriginal Title
ito na talaga totoo pramis teksman mamatay man-2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views11 pagesIto Na Talaga Totoo Pramis Teksman Mamatay Man-2
Uploaded by
ReveRieCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
CUBA –COMMAND ECONOMY
• Fidel Castro – introduced the concept of a
command economy
• The economy of this government controls all
means of production and determines prices
for most of the goods in the economy
• Cuba does not have proper property rights in
place
Fidel
Castro
FLASHBACK!
• Cuba, once a colony of US, gained its independence through Cuban
Revolution in 1959
• They nationalised three US oil refineries in June 1960
• On July 3, 1960, US suspended trading sugar with Cuba
• On July 5, they retaliated by nationalising all US businesses and
commercial property
• The following day, US cancelled tones of sugar remaining in Cuba’s quota
• Sugar-for-oil exchange between Cuba and USSR was born
• In September & October 1960, Fidel nationalised all US banks and local
firms
• Following this, US imposed a trade and economic embargo on Cuba
• Cuba defeated the US army at Bay of Pigs on April 17, 1961 after 3 days of
fighting
FLASHBACK!
• On May 1, 1961, Fidel declared Cuba as socialist country
and declared himself as “Marxist-Leninist and extended his
personal dominion over every dimension of government”
• Agricultural production remained high with USSR buying
sugar from it
• But in 1990, as the USSR collapsed, so did Cuban economy
and its agricultural production
• Instead of choosing to open up its markets, Cuban
government continued to control agricultural production
and marketing
• Sugar production started falling. Sugar industry fell from 8.1
million metric tonnes in 1989 to 3.5 million metric tonnes
in 1995
ALL ABOUT CUBA: STRENGTHS
• Non-Tariff Barriers to Trade are very Restrictive
• Equitable Distribution of Income and Wealth
Income gap between the farmers and the urban workers
decreased
Employment for all
All Cuban children go to school
Remote village has a school
Literacy Rate of 99.8%
Good healthcare and achieved many breakthroughs in the field
of biotechnology
• Cuba’s Gini Coefficient of 0.25
• Low Unemployment Rate
• Moderate Level of Inflation
CUBA’S HUMAN DEVELOPMENT INDEX - 2006
HDI Value Life expectancy Adult literacy Combined GDP per capita
2006 at birth (years) rate (ages 15 primary, (PPP in $)
2006 and above (%)) secondary and 2006
2006 tertiary gross
enrolment
ratio (%)
2006
0.855 77.9 99.8 94.8 6,876
Source:”2008 Statistical Update Cuba”, http://hdrstats.undp.org/2008/countires/country_fact_sheets/cty_fs_CUB.html
INFLATION AND UNEMPLOYMENT FIGURES OF SWITZERLAND,
CUBA AND INDIA - 2008
Country Inflation (CPI) (%) Unemployment Rate (%)
Switzerland 0.9 2.5
Cuba 3.6 1.8
India 6.4 7.2
Compiled by the author from 2009 Index of Economic Freedom
ALL ABOUT CUBA: WEAKNESSES
• Governmental Spending for the year 2008
equaled 72.6% of GDP
• Poorly Run State Factories and Firms that
Results in Shortages
• Difficult Investment Environment
• Freedom of Expression (Freedom of Speech &
Press) are Denied
ALL ABOUT CUBA: OPPORTUNITIES
• Exercise Control Over Employment Issues
• Introduction of Market Reforms
Legalisation of dollar
Allowing foreign investment
Opening of the country for tourism
Legalisation of some private enterprises
Self-employment for 150 occupants
ALL ABOUT CUBA: THREATS
• Continuous and Rapid Flourishing of
Shadow/Black Markets
• “Established Soviet-Style Rationing of
Housing, Goods, and Food”
ANNOUNCEMENT MADE BY RAUL CASTRO
Expanding access to public land for private farmers
Permitting some Cubans to own their homes
Increasing wages and retirement pensions
Licensing private taxis to operate
Limited deregulation of the construction industry
Expanding access to certain previously restricted consumer goods
Launching a new-24 hr. television station to include mostly foreign-produced
content
Compiled by the author from:”Background Note: Cuba”, http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/2886.htm, August 2008
You might also like
- Summary Of "Economy Between Two Centuries" By Jorge Saborido: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Economy Between Two Centuries" By Jorge Saborido: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Country Specific Business Analysis of Cuba and IndiaDocument29 pagesCountry Specific Business Analysis of Cuba and IndiaDeepthi TammannagariNo ratings yet
- (Contemporary Cuba) Al Campbell-Cuban Economists On The Cuban Economy-University Press of Florida (2013) PDFDocument357 pages(Contemporary Cuba) Al Campbell-Cuban Economists On The Cuban Economy-University Press of Florida (2013) PDFHernán Riccioppo0% (1)
- República de CubaDocument13 pagesRepública de CubaSiddhartha BothraNo ratings yet
- Country Presentation On Cuba: By, Kapish Gaba JKPS/PGDM/10/07Document19 pagesCountry Presentation On Cuba: By, Kapish Gaba JKPS/PGDM/10/07sainiprateek88No ratings yet
- Cuba: Economic Restructuring, Recent Trends and Main ChallengesDocument14 pagesCuba: Economic Restructuring, Recent Trends and Main ChallengesRobert WileyNo ratings yet
- Ind AagDocument2 pagesInd Aagadmin.maldivesNo ratings yet
- Cuba'S Economy After Raúl Castro: A Tale of Three Worlds: Richard E. FeinbergDocument21 pagesCuba'S Economy After Raúl Castro: A Tale of Three Worlds: Richard E. FeinbergMilton-GenesisNo ratings yet
- Brazil Vs Costa RicaDocument10 pagesBrazil Vs Costa RicaChaiNo ratings yet
- BNB Press Release December 2009Document2 pagesBNB Press Release December 2009Chola MukangaNo ratings yet
- Economic SystemsDocument7 pagesEconomic SystemszawaloveathoiNo ratings yet
- P15738coll2 129344Document20 pagesP15738coll2 129344Rhea SimoneNo ratings yet
- EconDocument3 pagesEconAimee CapinpuyanNo ratings yet
- Etude Econometrique RDCDocument55 pagesEtude Econometrique RDCchafik bouberrimaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Key Sectors and Policies Driving India's EconomyDocument17 pagesAnalysis of Key Sectors and Policies Driving India's EconomyApoorvJainScribdNo ratings yet
- Bolivia Poverty Report 1996Document56 pagesBolivia Poverty Report 1996ARKNo ratings yet
- Cuba 2Document1 pageCuba 2vskywokervsNo ratings yet
- Presentation Doing Business Brazil PFM December 2020Document53 pagesPresentation Doing Business Brazil PFM December 2020Giulia CamposNo ratings yet
- Economic Briefing - CubaDocument14 pagesEconomic Briefing - CubaAlex HirstNo ratings yet
- IT 304 IT in The Global Economy: Dr. Harold D. CampDocument13 pagesIT 304 IT in The Global Economy: Dr. Harold D. Campbgirma824No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 (English 2020) - Poverty AlleviationDocument26 pagesChapter 13 (English 2020) - Poverty AlleviationM Tariqul Islam MishuNo ratings yet
- Poverty and Inequity in NigeriaDocument63 pagesPoverty and Inequity in NigeriaJustice OnuNo ratings yet
- Republic of Bangladesh: An Economic OverviewDocument15 pagesRepublic of Bangladesh: An Economic OverviewOsman Baig MirzaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Poverty in CubaDocument22 pagesMeasuring Poverty in CubaBMX2013No ratings yet
- Cambodia WDFDocument13 pagesCambodia WDFMR RAVEN REYNo ratings yet
- Cuba Has Managed To Feed Its People Well Even After The Collapse of Soviet CommunismDocument3 pagesCuba Has Managed To Feed Its People Well Even After The Collapse of Soviet CommunismDiego CastanedaNo ratings yet
- The State of Inequality - Un Zambia Signature Issue Paper 1 - June 2013Document28 pagesThe State of Inequality - Un Zambia Signature Issue Paper 1 - June 2013Ndime UsoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 RVSD EditedDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 RVSD EditedNearby ClassicNo ratings yet
- India Vs UsaDocument60 pagesIndia Vs Usasushma_sampath6197No ratings yet
- Cuba's Economy Over 25 YearsDocument2 pagesCuba's Economy Over 25 YearsCrisostomo IbarraNo ratings yet
- UAE's Transport and Logistics Cluster: An Opportunity to Diversify the EconomyDocument33 pagesUAE's Transport and Logistics Cluster: An Opportunity to Diversify the Economyisam mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Ec 001Document4 pagesEc 001thanhphong2001No ratings yet
- Booklet MDGs Indicators - English 2015Document48 pagesBooklet MDGs Indicators - English 2015Joanna Erlinda TaylanNo ratings yet
- Cuba Case Study - Economic EnvironmentDocument2 pagesCuba Case Study - Economic EnvironmentParth VagadiaNo ratings yet
- 1344 PovertyDocument49 pages1344 PovertyNassiwa JaneNo ratings yet
- Cuban Labor Rights and Economic ReformsDocument16 pagesCuban Labor Rights and Economic ReformsEdwin PorrasNo ratings yet
- Management of Mineral EconomyDocument7 pagesManagement of Mineral EconomyChola MukangaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Abstract For Uganda: 2009Document270 pagesStatistical Abstract For Uganda: 2009UwaziNo ratings yet
- Kuwait: Statistical Appendix: International Monetary Fund Washington, D.CDocument43 pagesKuwait: Statistical Appendix: International Monetary Fund Washington, D.Cswatigali4564No ratings yet
- CREA-Reporte Por CiudadesDocument5 pagesCREA-Reporte Por Ciudadespascal rosasNo ratings yet
- Angeles University Foundation College of Business and AccountancyDocument5 pagesAngeles University Foundation College of Business and AccountancyAndrew TorresNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Poverty Puzzle: Growth vs HeadcountDocument26 pagesPakistan Poverty Puzzle: Growth vs HeadcountHashim ZafarNo ratings yet
- Havana PDFDocument40 pagesHavana PDFΚωνσταντίνος ΓκάργκαςNo ratings yet
- Labor Force PakistanDocument21 pagesLabor Force PakistanHammad ShamsNo ratings yet
- Name of Data Series Label in Database Units of Series Data SourceDocument4 pagesName of Data Series Label in Database Units of Series Data SourceJoseph KalarickalNo ratings yet
- Grammer 2Document10 pagesGrammer 2rishabhmehta2008No ratings yet
- Presentation On Changes in RetailDocument13 pagesPresentation On Changes in RetailkartikharishNo ratings yet
- North America 1Document15 pagesNorth America 1bhaveshkpatel2003No ratings yet
- Economic GlobalizationDocument4 pagesEconomic GlobalizationHannah agustinNo ratings yet
- Population CountDocument5 pagesPopulation CountAlexander RiveraNo ratings yet
- A Pact For Mexico: A New Vision To Exploit Our PotentialDocument60 pagesA Pact For Mexico: A New Vision To Exploit Our Potentialapi-104233334No ratings yet
- Cuba 1Document3 pagesCuba 1Devika ShahNo ratings yet
- Retail in ColombiaDocument23 pagesRetail in ColombiaClarita RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Migration and Labor in Cocoa Production in West AfricaDocument23 pagesPresentation - Migration and Labor in Cocoa Production in West AfricaCharlotte LonitzNo ratings yet
- Ch-13 (English-2014) - Final - DraftDocument19 pagesCh-13 (English-2014) - Final - Draftshahid hossainNo ratings yet
- Budget Debate 2006-2007... Audley ShawDocument35 pagesBudget Debate 2006-2007... Audley ShawDaryl BaughNo ratings yet
- Poverty and Income InequalityDocument36 pagesPoverty and Income InequalityAlina ZaferNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Economic Review 2021 - Poverty AlleviationDocument21 pagesBangladesh Economic Review 2021 - Poverty AlleviationEnamul HuqNo ratings yet
- Knocked-Down Agriculture After De-Industrialization Another Destructive Influence of Neo-Liberalism M. ShafaeddinDocument19 pagesKnocked-Down Agriculture After De-Industrialization Another Destructive Influence of Neo-Liberalism M. ShafaeddinM.Shafaeddin3255No ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Sentence StructuresDocument2 pagesIELTS Writing Sentence StructuresfajrinNo ratings yet
- 5 LawDocument2 pages5 LawReveRieNo ratings yet
- 4 LawDocument2 pages4 LawReveRieNo ratings yet
- 3 LawDocument2 pages3 LawReveRieNo ratings yet
- 2 LawDocument2 pages2 LawReveRieNo ratings yet
- 1 LawDocument2 pages1 LawReveRieNo ratings yet
- StatsDocument5 pagesStatsReveRieNo ratings yet
- Results and DiscussionDocument12 pagesResults and DiscussionReveRieNo ratings yet
- Corazon Aquino's Speech Before The Joint Session of The United States CongreDocument25 pagesCorazon Aquino's Speech Before The Joint Session of The United States CongreReveRieNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 2 BSA 1Document1 pageAssignment No 2 BSA 1ReveRieNo ratings yet
- Corazon Aquino's Speech Before The Joint Session of The United States CongreDocument25 pagesCorazon Aquino's Speech Before The Joint Session of The United States CongreReveRieNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument1 pageReviewerReveRieNo ratings yet
- APC ManifestoDocument40 pagesAPC ManifestoDon EmekaNo ratings yet
- Vision IAS Abhyaas Test 1 English AnswersDocument34 pagesVision IAS Abhyaas Test 1 English Answerssantosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Module.1 Session 7, 8, 9 & 10Document109 pagesModule.1 Session 7, 8, 9 & 10Khushal ThakerNo ratings yet
- DEPARTMENT OF LABOR: Public Assistance During COVID-19 PandemicDocument4 pagesDEPARTMENT OF LABOR: Public Assistance During COVID-19 PandemicConnecticut House RepublicansNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 MoodleDocument36 pagesChapter 6 MoodleMichael TheodricNo ratings yet
- Disadvantages of Free TradeDocument10 pagesDisadvantages of Free TradeGraciela RealizaNo ratings yet
- Macro AssignmentDocument8 pagesMacro AssignmentAkingbade Olajumoke MabelNo ratings yet
- B 1Document25 pagesB 1Sabin SadafNo ratings yet
- Philadelphia Trumpet MagazineDocument40 pagesPhiladelphia Trumpet MagazinejoeNo ratings yet
- The Psychological Effects of UnemploymentDocument4 pagesThe Psychological Effects of UnemploymentHayaton IRNo ratings yet
- (Robert Lekachman (Eds.) ) Keynes' General Theory PDFDocument355 pages(Robert Lekachman (Eds.) ) Keynes' General Theory PDFAlvaro Andrés Perdomo100% (1)
- Bautista, Emmanuel D. IV-Newton: E.G. Science Not Conflict With ReligionDocument17 pagesBautista, Emmanuel D. IV-Newton: E.G. Science Not Conflict With ReligionJoemar FurigayNo ratings yet
- Positive and Normative EconomicsDocument2 pagesPositive and Normative EconomicsMawuena Susu100% (1)
- Download Diminishing Returns The New Politics Of Growth And Stagnation Mark Blyth full chapterDocument58 pagesDownload Diminishing Returns The New Politics Of Growth And Stagnation Mark Blyth full chapteralla.adams464100% (11)
- ONtalent Selected Articles From DeloitteReviewDocument168 pagesONtalent Selected Articles From DeloitteReviewDeloitte AnalyticsNo ratings yet
- Social Studies SBADocument7 pagesSocial Studies SBAAndreu Lloyd67% (3)
- Research Paper Eng105-SPN PDFDocument37 pagesResearch Paper Eng105-SPN PDFMd NayeemNo ratings yet
- Article On India of My Dreams - APDocument4 pagesArticle On India of My Dreams - APSkillzy SupportNo ratings yet
- STUDENT EMPLOYMENT EFFECT ON UNIVERSITY GRADUATES' WORK OUTLOOKDocument12 pagesSTUDENT EMPLOYMENT EFFECT ON UNIVERSITY GRADUATES' WORK OUTLOOKerumiqbalkhanNo ratings yet
- Colliers Research and Forecast Report 2019Document44 pagesColliers Research and Forecast Report 2019Hans LoonenNo ratings yet
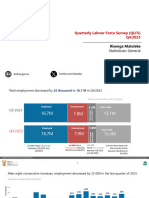
- Presentation QLFS Q4 2023Document26 pagesPresentation QLFS Q4 2023Krash KingNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics For Life Smart Choices For You Canadian 2Nd Edition Cohen Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesMicroeconomics For Life Smart Choices For You Canadian 2Nd Edition Cohen Test Bank Full Chapter PDFadrianavillanuevajzsifoacen100% (9)
- Career Road Map Guide For Engineers (Complete)Document149 pagesCareer Road Map Guide For Engineers (Complete)shoaib1985No ratings yet
- Dream Job Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesDream Job Cheat SheetMatthew KreilingNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Solution Manual For Macroeconomics 10th Edition AbelDocument17 pagesSolution Manual For Solution Manual For Macroeconomics 10th Edition AbelRoy Stookey100% (38)
- IB Economics Definitions PDFDocument21 pagesIB Economics Definitions PDFAnis BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- WEC02 01 Rms 20180815Document29 pagesWEC02 01 Rms 20180815XperiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 EssayDocument3 pagesChapter 8 EssayCasilda GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Eco 2Document5 pagesEco 2ZENITH EDUSTATIONNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument22 pagesCommunicationNatalie ThompsonNo ratings yet