Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Funniculars Shell Roof
Uploaded by
HIMA MiniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Funniculars Shell Roof
Uploaded by
HIMA MiniCopyright:
Available Formats
Profil
re s o u r c e s
Material and labour
requirement for Materials Unit Quantity
construction of
e
funicular roof Waste s tone pieces Quintal 3
of size 10’ x 12’ Bricks No. 300
Technolog
Number of Cement Bags 11
Funicular Sand Cft 31
Shells Aggregate 10/20mm Cft 50
in
Roof: 4 16mm reinf. Steel Kg 34
12mm reinf. s teel Kg 13
10mm reinf. Steel Kg 33
6mm G.I wire Kg 22 Funicular
Labour
y
Mason Man days 4 Shell Roof
Labour Man days 12
Bar benders Man days
2 conce p t
A Funicular Shell is a 3 dimensional catenary on a rectilinear base. The roofing
ap p li c a ti o n system consists of doubly curved shells made with materials of good
compressive strength such as waste stone pieces and brick tiles and supported
on reinforced
concrete edge beams. A series of these shells in variable geometric
configurations supported on a grid of concrete beams, identical to a coffer slab,
provides an attractive roof for small to medium spans.
com pone nts
Photographs courtesy:
Anangpur Building
Centre Edge Beam
This is a reinforced concrete beam which supports and distributes the horizontal thrust of the
funicular shell. The beam can be conventionally cast along with the funicular shell. As per the span,
know how the beam is designed for a coffer slab or a grid of beams. Alternatively, the beam can be partially
precast, in which case a pre-welded reinforcement cage is placed along the grid and cast half. The
cage is fabricated as a truss girder (see overleaf for details) which improves the load bearing
Jointly published by: capacity of beam considerably, while simultaneously reducing the beam section.
Funicular Shell
TARA Nirman Kendra Development Alternatives Building Materials & Technology The entire area to be roofed is divided into a grid depending on the size of the funicular shell
Village Ghittorni World Headquarters: Promotion Council required or the size / shape of moulds available. The rise to span ratio is 1:6, thus the optimal span
Mehrauli-Gurgaon Road B-32, TARA Crescent Ministry of Urban Affairs & Employment of the shell is 3 m though it can span up to 15 m. The mould is supported between the edge
New Delhi-110030 Qutub Institutional Area Govt. of India
India beams. Timber planks are used to bridge the gap between the edge of the mould and the edge
New Delhi-110016 Core 5-A, First Floor, India Habitat Centre
Phone: 91-11-26801521, Lodi Road, New Delhi-110003 beam. The shell comprises of the materials – bricks, stone waste – laid in the funicular profile
India
26800398 Web: www.devalt.org India topped with cement-sand mortar and concrete screed.
Phone: 91-11-24638096, 24638097,
Concrete In-fill
24636759
After the shells have been cast, the valley spaces which are formed between the shells can be filled
TARA with light-weight material like brick jelly lime concrete and finished flat. The infill will enable the
Nirman Development construction of an intermediate floor which can be used to build above.
Alternatives
Kendra
de ta ils adv anta ge s
Allows ample flexibility in design- funicular shells can take any shape – square, rectangular,
Funicular Shell triangular or trapezoidal
arrangement for a hall 6’9”
Uses locally available waste stone, normally available from stone cutting and polishing units
of B
size 20’ by 20’. ea For construction above the intermediate floor, the funicular roof provides greater flexibility for locating
Beam type A
m
ty
The roof has been divided pe walls since the load distribution is uniform because of arch action of the shell
B
into smaller spans with a Design of the funicular roof can be very well adapted to seismic design requirements
grid of beams (as shown in Beam type D 21’6”
Finishes like plaster and paint for the roof are not needed
the sketch). 3 shapes of
B e a m t yp e C
funicular shells have been 4’2”
Being a labour intensive technology, leads to employment generation and integrates craftsmanship
used in the roof Simple technology which can easily be adapted by semi-skilled labour with minimum supervision
Plan of the training hall, Beam type B The funicular roof is aesthetically much better than other roofs – various artistic patterns can be
indicating the grid made using brick and stone
of 4’
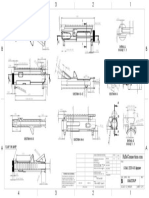
Edge Beams s p e ci fi c a ti o n s
21’ 6” Funicular Shell Profile : Doubly curved
For any desired plan shape & rise o f shell, ordinates on
various points can be calculated using formulae as per
IS 6332
5 No 12 mm 2 No 10 mm Clear span : 3’ t o 9’
Cross sections of This defines a range o f span f o r normal applications.
2 No 16 mm
Edge Bigger spans upto 40’ are also possible, subject t o
s t r uc t ur a l design
Beams Type A Type C
Shape : A variety o f shapes are possible-square, rectangular,
5 No 10 mm 3 No 16 mm
t r iangular t o suit the dimensions o f the f l o o r /
3 No 16 mm 4 No 16 mm Rise at centre roof
Triangulated
stiffeners to be : One sixth o f the clear
provided on Type B Type D span 6” t o 18” ( f o r 3’-9’
all Shell material
spans)
4 faces of the (for a masonry
beam shell) : Broken stone pieces o f 1”-2” thickness
Brick tiles (1.5”-2”) o f at least 50 kg/
Brick 3” thick Reinfo rcement
cm2 compressive strength
1.5” Thick cement Topping
concrete 1:2:4 : No reinforcement is needed in a
mortar masonry funicular shell
Edge Beam Reinforcement: A pre-welded beam wit h triangulated stiffeners on a l l
Section of : sides
Rich w it h 6 mm bars
cement-sand (as shown
mortar o f 1:2 in the figure).The beam is
Funicular (cast as
Pointing done in lime t o over
ratio be designed as per
the masonry span
shell
Shell surkhi mortar a
Steel beam Cross section : 9” x 9” (for a 9” thick masonry) can be commonly used
9’’x9’’ (1:3:8) grid of
Level to which beams)
beams are partially cast
Concrete : M 20 in-situ concrete f o r the beam as well as in the
before laying the mix valley between adjacent shells
funicular shell
cons tructi o n
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Winone Elevator Connection DiagramDocument40 pagesWinone Elevator Connection DiagramMuhammad Rashid75% (4)
- Jeppesen 021 - 03 - PowerplantDocument274 pagesJeppesen 021 - 03 - PowerplantSadcat97% (29)
- Eg Cost Effective PPT Centre For Development. StudiesDocument11 pagesEg Cost Effective PPT Centre For Development. StudiesHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Aec3414 Philosophy FinalDocument5 pagesAec3414 Philosophy Finalapi-532996380No ratings yet
- Ian Robb a.M.I.struct.E. (Auth.) - Steel Frame Design Examples-Macmillan Education UK (1961)Document216 pagesIan Robb a.M.I.struct.E. (Auth.) - Steel Frame Design Examples-Macmillan Education UK (1961)GT100% (1)
- Denso Mitsubishi L200 Common Rail PDFDocument53 pagesDenso Mitsubishi L200 Common Rail PDFAlex Renne Chambi100% (8)
- LA10 HistoryOfLandscapeArchitectureDocument15 pagesLA10 HistoryOfLandscapeArchitectureNor Suhaimi SamionNo ratings yet
- Thermal Comfort FactorsDocument8 pagesThermal Comfort FactorsHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- History of Landscape GardensDocument14 pagesHistory of Landscape GardensHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- ART01 - Art and Architecture - Student Notes PDFDocument21 pagesART01 - Art and Architecture - Student Notes PDFHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- A PrecastconstructionDocument26 pagesA PrecastconstructionHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Funniculars Shell RoofDocument2 pagesFunniculars Shell RoofHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Sino-Italian EcologicalDocument9 pagesSino-Italian EcologicalHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Cost Effective - PPT HamletDocument17 pagesCost Effective - PPT HamletHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- CONTEMPORARYDocument10 pagesCONTEMPORARYHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Sino-Italian EcologicalDocument9 pagesSino-Italian EcologicalHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- CONTEMPORARYDocument10 pagesCONTEMPORARYHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- bTYPES OF ELEVATORS - I PDFDocument18 pagesbTYPES OF ELEVATORS - I PDFHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Vertical Transportation in BuildingsDocument46 pagesVertical Transportation in BuildingsHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Energy Retrofit Godrej Bhavan CSDocument8 pagesEnergy Retrofit Godrej Bhavan CSVaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Contemp AssiDocument6 pagesContemp AssiHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Alibag House: by - Nari GandhiDocument10 pagesAlibag House: by - Nari GandhiHIMA Mini100% (2)
- Presented By: Sharon ShajiDocument45 pagesPresented By: Sharon ShajiHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Case Study 15.12.2016 PDFDocument20 pagesCase Study 15.12.2016 PDFHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Sharon ShajiDocument45 pagesPresented By: Sharon ShajiHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Energy EfficientDocument89 pagesEnergy EfficientHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Energy EfficientDocument89 pagesEnergy EfficientHIMA MiniNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient Solar Homes BuildingsDocument12 pagesEnergy Efficient Solar Homes BuildingsTaveshi PrakashNo ratings yet
- Exceptions and Limitation of Patent Rights and Its Enforcement in IndiaDocument8 pagesExceptions and Limitation of Patent Rights and Its Enforcement in IndiaVyas NikhilNo ratings yet
- What I Have Learned: MODULE 2: Stand On Issues Supported by Factual EvidencesDocument3 pagesWhat I Have Learned: MODULE 2: Stand On Issues Supported by Factual EvidencesJc Tan GallanoNo ratings yet
- NCh204 1977Document15 pagesNCh204 1977Cristian A. Rivera S.No ratings yet
- WESCAM MX-15-0503AA-SpecDocument2 pagesWESCAM MX-15-0503AA-SpecAIT FARIDNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - The V LanguageDocument4 pagesLesson Plan - The V LanguageLê Thị Ái NhiNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Social Security System MemberDocument1 pageRepublic of The Philippines Social Security System MemberreyNo ratings yet
- Getachew Final EditedDocument76 pagesGetachew Final EditedDesalegn DgaNo ratings yet
- Bootstrap 3 All Classes List Cheat Sheet Reference PDF (2020) PDFDocument21 pagesBootstrap 3 All Classes List Cheat Sheet Reference PDF (2020) PDFHoney ShineNo ratings yet
- Ascend P7: Huawei SchematicDocument51 pagesAscend P7: Huawei SchematicCarlos Andres EscamillaNo ratings yet
- FIS-Finishes Schedule - R1Document4 pagesFIS-Finishes Schedule - R1meghadurganNo ratings yet
- M16a3 Upper SpecsDocument1 pageM16a3 Upper SpecsMosinNo ratings yet
- 5 OPERATIVE Dentistry-Fifth year-FIFTH lect-16-4-2020-FAILURE OF RESTORATIONDocument24 pages5 OPERATIVE Dentistry-Fifth year-FIFTH lect-16-4-2020-FAILURE OF RESTORATIONIna YaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (Dsge) Modelling:Theory and PracticeDocument34 pagesDynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (Dsge) Modelling:Theory and PracticeRSNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided ManufacturingDocument3 pagesComputer Aided ManufacturingVivek PatelNo ratings yet
- CitiBank ApplicationDocument15 pagesCitiBank ApplicationJordan P HunterNo ratings yet
- Triangulation Research PaperDocument3 pagesTriangulation Research PaperCharmaine Montimor OrdonioNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations - Design, Construction and Testing Guide: What Is A Pile Foundation?Document3 pagesPile Foundations - Design, Construction and Testing Guide: What Is A Pile Foundation?Ashis MingalaNo ratings yet
- Learning Curves in Manufacturing IndustriesDocument3 pagesLearning Curves in Manufacturing Industriessubhash221103No ratings yet
- Learning Based Exposition-The Simple Present TenseDocument12 pagesLearning Based Exposition-The Simple Present Tenseyuri Berrocal YanceNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Examination Table: Order Number: 11.1047Document1 pageGynecological Examination Table: Order Number: 11.1047yosra MedicalNo ratings yet
- Java Io NotesDocument19 pagesJava Io Notesgupta_ssrkm2747No ratings yet
- Ethics 5Document3 pagesEthics 5MANINGO, EDRIAN JAY M.No ratings yet
- FC9170 02Document14 pagesFC9170 02ВладимирNo ratings yet
- Temporary Housing Kobe EarthquakeDocument18 pagesTemporary Housing Kobe EarthquakeMeenu100% (1)
- Ok - Las-Q2 Oral - Com W1Document5 pagesOk - Las-Q2 Oral - Com W1Ruben Rosendal De AsisNo ratings yet