100% found this document useful (1 vote)
337 views39 pagesUnderstanding Transactional Analysis
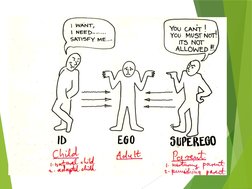
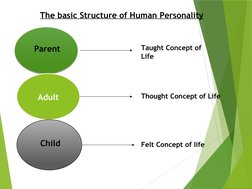
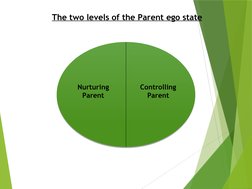
Transactional analysis is a method for understanding communication between people based on the idea that individuals operate from three ego states - parent, adult, and child. Developed by Eric Berne, it analyzes interactions or "transactions" between these ego states that can be complementary, crossed, or ulterior. Understanding which ego state a person is using allows for better communication and relationships.
Uploaded by
shivangi singhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
337 views39 pagesUnderstanding Transactional Analysis
Transactional analysis is a method for understanding communication between people based on the idea that individuals operate from three ego states - parent, adult, and child. Developed by Eric Berne, it analyzes interactions or "transactions" between these ego states that can be complementary, crossed, or ulterior. Understanding which ego state a person is using allows for better communication and relationships.
Uploaded by
shivangi singhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd