Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Elements: by Angel Caso 3ºa
Uploaded by
Ángel Caso0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views9 pagesOriginal Title
COMPUTER ELEMENTS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views9 pagesComputer Elements: by Angel Caso 3ºa
Uploaded by
Ángel CasoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
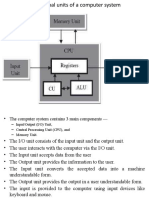
Computer elements
BY ANGEL CASO 3ºA
1.MICROPROCESSOR
It´s an integrated circuit made up of millions of tiny transistors working
together to process the instructions and data received from the
memory
•The clock rate sets the pace at which processes are completed. It
continously generates electrical impulses
•Today´s microprocessors can process 64 bits at a time
•A microprocessor´s power also depends on its cache memory and the
speed at which it comunicates with the RAM
2.Memory and units of storage
• RAM
1.The computer´s main memory is its RAM
2.When we run an app, its instrucstion and data are
copied to this memory so that the microprocessor can
use them
3.This is beacuse accessing the hard disk is very slow
4.Since RAM doesn´t retain information when the
computer is switched off, we must save our work
before closing the app. Otherwise we will loose our
work
2.Memory and units of storage
• Cache memory
1.RAM cannot work at the same speed as the
microprocessor, so a much faster memory
is isntalled between the RAM and the
microprocessor: the cache memory
2.The cache memory stores the data that the
microprocessor uses most often
2.Memory and units of storage
• ROM BIOS
1.When you turn on your computer, it automatically
checks the system. This initial check is carried out
using instructionsstored in a spoecial read-only
memory: nthe ROM BIOS
2.If everything is correct, the BIOS starts the
operating system in the main memory, so that this
system can take control of the computer
2.Memory and units of storage
3.Motherboard and connecting devices
• Inside the computer you´ll find a large board which we call
motherboard. All the other components of the computer are
connected to it.
• The communications between the different components of the
motherboard takes place through sets of copper wires called
buses
• The motherboard includes the following components:
1. Slots that can be used to expand or add new components
2. The IDE or ATA and SATA connectors connect the har disk, Cd
drive and DVD drive to the motherboard
3. The chipset is a number of integrated circuits designed to perform
related functions; they control the flow of bits to and from the
motherboard
4. Various input/ output ports
Connecting external devices
We can phisically connect devices to the computer in different ways:
•Usin´ an expansión slot on the motherboard, to connect a sound card or a graphics card
•By special connectors on the motherboard, for such devices as the hard disk, DVD drives and so
on
•Usin´ the external ports on the side or back of the computer, for example the USB port
Connecting external devices
• We also need to install a driver that aloows the device to
communicate with the operating system.
The operating system automatically installs drivers for most devices.
We can also install new devices by usin´ the software provided by the
device manufacturer. To do this , we need to use one of the following
tools:
1. Asistente para agregar hardware in Windows. Use this to add new
hardware
2. Informe sobre nuevos dispositivos, a report on new devices in Linux
• Operating systrems also have device managers that allow you view
and change device properties, update drivers or uninstall software:
1. Administrador de dispositivos in Windows
2. Gestor de dispositivos in Linux
You might also like
- Operating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandOperating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 PPTDocument34 pagesUnit 4 PPTಹರಿ ಶಂNo ratings yet
- It Workshop LAB MANUALDocument45 pagesIt Workshop LAB MANUALNanny BoppanaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computer SystemDocument61 pagesBasics of Computer Systemshahiddange05No ratings yet
- Information Technology Project ON: Parts of Comuter-CPUDocument26 pagesInformation Technology Project ON: Parts of Comuter-CPUshreyashk1010No ratings yet
- Lesson3 141205082141 Conversion Gate02Document25 pagesLesson3 141205082141 Conversion Gate02Archie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- Ce Workshop Lab ManualDocument140 pagesCe Workshop Lab Manualvamsi raviNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Device Management - Opr SysDocument8 pagesUnit 5 Device Management - Opr SysBibek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Computer-Based Information SystemDocument55 pagesComputer-Based Information Systemjeme2nd27210% (1)
- Information TechnologyDocument97 pagesInformation TechnologySia P.LNo ratings yet
- Computer System & Organization: Unit-IDocument58 pagesComputer System & Organization: Unit-I8D Audio TuneNo ratings yet
- The System UnitDocument53 pagesThe System Unitk3lvynNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics: Analytical Ability and Digital AwarenessDocument31 pagesComputer Basics: Analytical Ability and Digital AwarenessADITYA KUMAR0% (2)
- Unit 1: Computers, Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument65 pagesUnit 1: Computers, Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersHARSHITHA BHAVISETTINo ratings yet
- Gilas PC MaintenanceDocument97 pagesGilas PC MaintenanceEmmanuel Jimenez-Bacud, CSE-Professional,BA-MA Pol SciNo ratings yet
- Itws Dip LabmanualDocument79 pagesItws Dip Labmanualdh_kumarNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Troubleshooting ReportDocument8 pagesGroup 2 Troubleshooting ReportClarina Jane DosdosNo ratings yet
- A Computer System Consists of Mainly Four Basic UnitsDocument4 pagesA Computer System Consists of Mainly Four Basic UnitsMark GuguNo ratings yet
- Discovering Computers 2011: Living in A Digital WorldDocument52 pagesDiscovering Computers 2011: Living in A Digital WorldAqib KhakhiNo ratings yet
- منهاج مادة الحاسوب باللغة الانكليزيةDocument12 pagesمنهاج مادة الحاسوب باللغة الانكليزيةmuradNo ratings yet
- Installing and Configuring SystemsDocument47 pagesInstalling and Configuring SystemsDonna Fe De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Lect5 HardwareDocument22 pagesLect5 HardwareHgfdgNo ratings yet
- Functional UnitsDocument13 pagesFunctional UnitsAnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- On The Inside: Central Processing Unit (CPU)Document50 pagesOn The Inside: Central Processing Unit (CPU)vinay136384No ratings yet
- It 111 Components of ComputerDocument93 pagesIt 111 Components of Computeranime admirersNo ratings yet
- Co - SvewDocument82 pagesCo - SvewnbprNo ratings yet
- CHM All NotesDocument28 pagesCHM All Notesabhishek.kunduNo ratings yet
- Computer System, Devices and PeripheralsDocument26 pagesComputer System, Devices and PeripheralsNanette M. SansanoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document7 pagesAssignment 2deepali ghadiaNo ratings yet
- Manual Cws 1Document34 pagesManual Cws 1raramit2No ratings yet
- Computer Systems Architecture: Learning Outcome 01Document16 pagesComputer Systems Architecture: Learning Outcome 01Muhammedh ShadirNo ratings yet
- It Workshop LAB MANUALDocument145 pagesIt Workshop LAB MANUALAvinash TalapulaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 MOTHERBOARDDocument45 pagesPart 1 MOTHERBOARDOrlando FelixNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 System UnitDocument43 pagesTopic 2 System UnitAinnur SyamiraNo ratings yet
- It Workshop Lab ManualDocument144 pagesIt Workshop Lab Manualhanji17No ratings yet
- University of Salahaddin College of Engineering Software & Informatics DepDocument26 pagesUniversity of Salahaddin College of Engineering Software & Informatics DepZayto SaeedNo ratings yet
- Computer Science NotesDocument48 pagesComputer Science NotesaDEOlu AdesinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Embedded SystemsDocument50 pagesIntroduction To Embedded SystemsAmbika NaikNo ratings yet
- FundamentalDocument87 pagesFundamentalAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer System Overview: CH Balasubramanyam Pgt-Computer Science Velammal Bodhi Campus - PonneriDocument55 pagesComputer System Overview: CH Balasubramanyam Pgt-Computer Science Velammal Bodhi Campus - PonneriVelammal vNo ratings yet
- Components of The System UnitDocument33 pagesComponents of The System Unitapi-304500968No ratings yet
- ICT Lecture 02updatedDocument58 pagesICT Lecture 02updatedUzair Ali ZahidNo ratings yet
- ComputingDocument31 pagesComputingNurudeen Bamidele Faniyi (fbn)No ratings yet
- Triple Circuit Lines Presentation (Widescreen)Document29 pagesTriple Circuit Lines Presentation (Widescreen)Novel StarNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware FundamentalsDocument34 pagesComputer Hardware FundamentalsArmin Arguson100% (1)
- Hardware BasicsDocument200 pagesHardware BasicsSathish Kumar100% (1)
- MS Office and Computer ApplicationDocument12 pagesMS Office and Computer ApplicationAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Refers To The Physical Machine That Make Up The Computer Installation. These Are TheDocument5 pagesComputer Hardware Refers To The Physical Machine That Make Up The Computer Installation. These Are Thekariukipoly0% (1)
- Block Diagram of Digital Computer: Central Processing Unit (CPU) 1. 2. 3Document11 pagesBlock Diagram of Digital Computer: Central Processing Unit (CPU) 1. 2. 3desojolNo ratings yet
- Comp Mst...Document10 pagesComp Mst...Aashish SahiNo ratings yet
- Com Data ProcessingDocument27 pagesCom Data ProcessingHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- 202 Processing Computer Hardware (Printable)Document64 pages202 Processing Computer Hardware (Printable)Eilu DavidNo ratings yet
- 02 - Components of The System Unit PDFDocument59 pages02 - Components of The System Unit PDFJohn Michael ÜyNo ratings yet
- MS Office 2007 - NotesDocument89 pagesMS Office 2007 - NotesmanuNo ratings yet
- Hardware: Control UnitDocument8 pagesHardware: Control Unitigwe nnabuikeNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Computer System: Lecture OneDocument35 pagesAn Overview of The Computer System: Lecture OneSaabir Sheekh Muuse MoalimNo ratings yet
- Computer ApplicationDocument22 pagesComputer ApplicationRIMA CHATURVEDI100% (2)
- 2 - Computer Hardware ReviewDocument37 pages2 - Computer Hardware ReviewDimas setyaNo ratings yet
- Power Point Recu InfoDocument10 pagesPower Point Recu InfopauretuertoNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: by Elena Gomez and Angel Caso 3ADocument13 pagesIsaac Newton: by Elena Gomez and Angel Caso 3AÁngel CasoNo ratings yet
- Name: Ángel Caso de La Vega Class: 3º Group: A: Practical ActivitiesDocument16 pagesName: Ángel Caso de La Vega Class: 3º Group: A: Practical ActivitiesÁngel CasoNo ratings yet
- Perspective 1 Perspective 2 Perspective 3 Perspective 4Document1 pagePerspective 1 Perspective 2 Perspective 3 Perspective 4Ángel CasoNo ratings yet
- 3-IN-1 GLASS: by Angel Caso 3°ADocument8 pages3-IN-1 GLASS: by Angel Caso 3°AÁngel CasoNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Materials: by Angel Caso 3°ADocument8 pagesFerrous Materials: by Angel Caso 3°AÁngel CasoNo ratings yet
- Tópicos LiterariosDocument5 pagesTópicos LiterariosÁngel CasoNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Resueltos Sobre Energía y Ensayos de Tracción, Dureza y Resiliencia PDFDocument20 pagesEjercicios Resueltos Sobre Energía y Ensayos de Tracción, Dureza y Resiliencia PDFÁngel CasoNo ratings yet
- Google Digital Garage Module 7 Answers - Make Search Work For You Answers - Courses Answer - Quiz Answer, Exam Answer, Digital Garage AnswersDocument1 pageGoogle Digital Garage Module 7 Answers - Make Search Work For You Answers - Courses Answer - Quiz Answer, Exam Answer, Digital Garage Answersfrew abebeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 13 7Document14 pagesLecture Notes 13 7Aldrige LuisNo ratings yet
- NASSCOM-DSCI Cyber Security Advisory Group (CSAG) ReportDocument78 pagesNASSCOM-DSCI Cyber Security Advisory Group (CSAG) ReportrajeshNo ratings yet
- BrusDocument10 pagesBrusGloriany MiguelNo ratings yet
- Man L (En) S3 00 R1 0Document63 pagesMan L (En) S3 00 R1 0Dexter PoliNo ratings yet
- Cisco Unified Border Element (Cube) GuideDocument1,166 pagesCisco Unified Border Element (Cube) GuideDilip Kumar100% (1)
- Speech Recognition Seminar ReportDocument32 pagesSpeech Recognition Seminar ReportSuraj Gaikwad86% (96)
- Replika: Building An Emotional Conversation With Deep LearningDocument26 pagesReplika: Building An Emotional Conversation With Deep LearningKartikeya Shorya100% (3)
- PPL Lab Assignment CodeDocument30 pagesPPL Lab Assignment CodesunNo ratings yet
- SYEN 3330 Digital Systems: Chapters 4 - Part3: Verilog - Part 1Document17 pagesSYEN 3330 Digital Systems: Chapters 4 - Part3: Verilog - Part 1anjanappaNo ratings yet
- Gemini T: RGB Glass-Wing Mid-TowerDocument2 pagesGemini T: RGB Glass-Wing Mid-TowerMariano GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biometric Fingerprint Based Access Control and Library Management SystemDocument3 pagesBiometric Fingerprint Based Access Control and Library Management SystemPrajwal PrakashNo ratings yet
- 1 FordFulkersonDocument60 pages1 FordFulkersonIsrat Jahan Rain BorshaNo ratings yet
- Packt - Hands On - Ensemble.learning - With.python.2019Document424 pagesPackt - Hands On - Ensemble.learning - With.python.2019yohoyonNo ratings yet
- PL-100 Exam - Free Actual Q&as, Page 1 - ExamTopicsDocument635 pagesPL-100 Exam - Free Actual Q&as, Page 1 - ExamTopics333surimaNo ratings yet
- DP-203 - Data Engineering On Microsoft Azure 2021-1Document42 pagesDP-203 - Data Engineering On Microsoft Azure 2021-1Aayoshi Dutta100% (2)
- Multimedia Audio and VideosDocument41 pagesMultimedia Audio and Videoskolakim75No ratings yet
- Cse320 Srs Awasthi FinalDocument21 pagesCse320 Srs Awasthi Finalaggressiveboy.sharmaNo ratings yet
- Crash 2024 01 13 03 17 44 522Document10 pagesCrash 2024 01 13 03 17 44 522ar7374057No ratings yet
- Enclosure - Drystar 5302 Axys - Print Drum ModuleDocument7 pagesEnclosure - Drystar 5302 Axys - Print Drum ModuleHoracio Efrain Rios TrocheNo ratings yet
- 2016 Nielsen Social Media ReportDocument29 pages2016 Nielsen Social Media ReportJill JillNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument5 pagesCase StudyMohd AfiqNo ratings yet
- Measurement Techniques - Lesson02Document43 pagesMeasurement Techniques - Lesson02Umut ŞENNo ratings yet
- Log 06 28 00Document9 pagesLog 06 28 00Kapten JenggotNo ratings yet
- Smartwalk Installation Manual v2 5 SmartlinkDocument16 pagesSmartwalk Installation Manual v2 5 SmartlinkJuniorNo ratings yet
- Aws Saa McqsDocument24 pagesAws Saa McqsHarleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Oct. For RefundDocument5 pagesOct. For RefundJoevan VillaflorNo ratings yet
- SBI PO Mains 2016: Reasoning AbilityDocument25 pagesSBI PO Mains 2016: Reasoning AbilityMALOTH BABU RAONo ratings yet
- 0019 Microsoft Powerpoint 2003 PDFDocument69 pages0019 Microsoft Powerpoint 2003 PDFEjaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- 320bl EXCABADORADocument6 pages320bl EXCABADORARembertoNo ratings yet