Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter Three Financial Institutions in The Financial System
Uploaded by
Mikias Degwale0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views9 pagesFinance
Original Title
Chapter three 2012
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFinance
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views9 pagesChapter Three Financial Institutions in The Financial System
Uploaded by
Mikias DegwaleFinance
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Chapter Three
Financial Institutions in the
Financial System
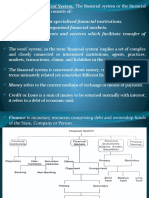
Introduction
•Business entities include nonfinancial and financial
enterprises.
•Nonfinancial enterprises manufacture products (e.g., cars,
steel, computers) and/or provide nonfinancial services
(e.g., transportation, utilities, computer programming).
•On the other hand, financial enterprises, more popularly
referred to as financial institutions, provide services
related to one or more of the following:
Cont’d
A.Transforming financial assets acquired through the market
from depositors to borrowers.
B.Exchanging of financial assets on behalf of customers.
C.Exchanging of financial assets for their own accounts.
D.Assisting in the creation of financial assets for their
customers, and then selling those financial assets to other
market participants.
E.Providing investment advice to other market participants.
F. Managing the portfolios of other market participants.
Cont’d
•Financial intermediaries / institutions may be
classified in a variety of ways.
•One of the most important distinctions is
between Depository and Non-Depository
Intermediaries.
•Below is their basic distinction:
Cont’d
1. Depository Intermediaries
They are the most commonly recognized intermediaries
because most people use their services on a daily basis.
Depository institutions issue a variety of checking or
savings accounts and time deposits and they use the
funds to make consumer, business and mortgage loans.
In other words, they accept deposits from individuals
and firms and use these funds to participate in the debt
market, making loans or purchasing other debt
instruments.
Cont’d
There are several types of depository intermediaries:
commercial banks and nonbank thrift institutions
(near banking institutions) or simply “thrifts” that
comprises saving institutions and credit unions.
Saving institutions include: savings and loan
associations and mutual savings banks.
Mutual savings banks are similar to S&Ls except that
they have more diversified uses of funds.
Cont’d
Whereas commercial banks concentrate on commercial
(business) loans, savings institutions concentrate on
residential mortgage loans.
Credit unions differ from commercial banks and savings
institutions in that they (1) are nonprofit and (2) restrict
their business to credit union members, who share a
common bond (such as a common employer or union).
In addition to accepting deposits, these institutions make
loans and provide other financial services.
Depository institutions are highly regulated because of
the important role that they play in the financial system.
Cont’d
2. Non-Depository Intermediaries
It includes contractual institutions (like insurance companies
and pension funds) and investment institutions (like
investment companies or mutual funds, finance companies,
and real estate investment trusts).
Contractual institutions attract funds by offering legal
contracts to the public in order to protect the savers against
potential risks. (like insurance companies and pension funds)
Investment institutions sell shares to the public and invest the
proceeds in stocks, bonds, and other securities. (like
investment companies or mutual funds, finance companies,
and real estate investment trusts).
Group Assignment (20%-2&3)
1. Discuss about depository and non-depository
financial institutions in Ethiopia
2. Discuss about the following non-depository
financial institutions
A. Investment companies or mutual funds
B. Finance companies and
C. Real estate investment trusts
3. Discuss about the current opportunities and
challenges of the Ethiopian financial institutions.
You might also like
- Case StudyDocument3 pagesCase StudyJUVY ALEJANDRO100% (2)
- The Roles of Financial Market and Financial InstitutionsDocument4 pagesThe Roles of Financial Market and Financial InstitutionstssuvroNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument115 pagesFinancial InstitutionsSantosh Gannamraju100% (1)
- MAES London Pricing Sheet Lets Make It HereDocument3 pagesMAES London Pricing Sheet Lets Make It HereNimesh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Three Financial MarketsDocument55 pagesChapter Two Three Financial MarketsDùķe HPNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Overview of Financial InstitutionsDocument12 pagesOverview of Financial InstitutionsLoui CanamaNo ratings yet
- Fim Chapter TwoDocument8 pagesFim Chapter Twotarekegn gezahegnNo ratings yet
- Industry - Fundamental AnalysisDocument13 pagesIndustry - Fundamental AnalysisJerin JoyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2powerpointDocument33 pagesCHAPTER 2powerpointMintayto TebekaNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionssDocument30 pagesFinancial Markets and InstitutionssEntityHOPENo ratings yet
- Money Banking Chapter 5Document12 pagesMoney Banking Chapter 5ebsa ahmedNo ratings yet
- FIM Group Assignmen FinalDocument9 pagesFIM Group Assignmen FinalEndeg KelkayNo ratings yet
- Engaging Activity Unit 4 Financial InstitutionDocument2 pagesEngaging Activity Unit 4 Financial InstitutionMary Justine ManaloNo ratings yet
- MfI Chapter 1Document32 pagesMfI Chapter 1Jiru AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Chapter2. Financial Inst&capital ArketsDocument12 pagesChapter2. Financial Inst&capital Arketsnewaybeyene5No ratings yet
- Business Finance Q3 Module 5.Document13 pagesBusiness Finance Q3 Module 5.alishareixdxdNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions in The Financial SystemDocument15 pagesFinancial Institutions in The Financial SystemNigussie Berhanu100% (1)
- Financial Institution Chapter TwoDocument14 pagesFinancial Institution Chapter TwoKalkayeNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Introduction To Financial InstitutionsDocument35 pagesCh. 1 Introduction To Financial Institutionsteshome dagne100% (2)
- Chapter Four and Five FIMDocument22 pagesChapter Four and Five FIMsamuel kebedeNo ratings yet
- Group 4 PresentationDocument6 pagesGroup 4 PresentationeranyigiNo ratings yet
- Fim 4Document33 pagesFim 4akshat srivastavaNo ratings yet
- PROJECT - Financial Industry Sector - ARUNIMA VISWANATH - 21HR30B12Document15 pagesPROJECT - Financial Industry Sector - ARUNIMA VISWANATH - 21HR30B12ARUNIMA VISWANATHNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionDocument3 pagesFinancial InstitutionMuhammad Saleem Sattar100% (1)
- IntroductionDocument10 pagesIntroductionHala EdwanNo ratings yet
- Atakelt Hailu (PHD), Assistant ProfessorDocument49 pagesAtakelt Hailu (PHD), Assistant Professoryemisrach fikiruNo ratings yet
- Banking Law - Mid-Term ExaminationDocument8 pagesBanking Law - Mid-Term ExaminationM.Zaigham RazaNo ratings yet
- Management of Financial Institutions - OfficeDocument69 pagesManagement of Financial Institutions - OfficeAsad KhanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - Financial Institutions, Intermediaries and Asset ManagementDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Financial Institutions, Intermediaries and Asset ManagementReggie AlisNo ratings yet
- Unit ThreeDocument22 pagesUnit ThreeEYOB AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document9 pagesLecture 1Jelani GreerNo ratings yet
- Investment ManagementDocument21 pagesInvestment ManagementAmarinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Indian Financial SystemDocument73 pagesUnit 1 - Indian Financial SystemHasrat AliNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Note 1-CMMDocument11 pagesSupplementary Note 1-CMMJenina Rose SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Role of Financial Institutes in FinanciaDocument18 pagesRole of Financial Institutes in FinanciaI Gusti Ayu Astrid SNo ratings yet
- FMI CH - 3 Admas AhmedDocument10 pagesFMI CH - 3 Admas AhmedRahel SolomonNo ratings yet
- 248 Chapter 2 SummaryDocument13 pages248 Chapter 2 SummaryAhmed KHALILNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument4 pagesFinancial InstitutionsTrifan_DumitruNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL SYSTEM Role in Economic DevelopmentDocument4 pagesFINANCIAL SYSTEM Role in Economic Developmentrevathi alekhya80% (10)
- Unit 1Document16 pagesUnit 1Shivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionDocument3 pagesFinancial InstitutionroilesatheaNo ratings yet
- FM&SDocument18 pagesFM&SVinay Gowda D MNo ratings yet
- Fin Ins Chapter 1Document34 pagesFin Ins Chapter 1Mehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1Youssef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Financial Intermediaries: Financial Institution Bank Bank Deposits Loans Assets LiabilitiesDocument3 pagesFinancial Intermediaries: Financial Institution Bank Bank Deposits Loans Assets LiabilitiesRishikaysh KaakandikarNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions & MarketsDocument7 pagesFinancial Institutions & MarketsVishal SinghNo ratings yet
- C - T 3. D N - D F I: Hapter Hree Eposit Taking and ON Eposit Taking Inancial NstitutionsDocument15 pagesC - T 3. D N - D F I: Hapter Hree Eposit Taking and ON Eposit Taking Inancial Nstitutionsyared haftuNo ratings yet
- Financial Institution AssignmentDocument7 pagesFinancial Institution AssignmentMOHIT JINo ratings yet
- Financial Hand Out 22-2Document13 pagesFinancial Hand Out 22-2Hace AdisNo ratings yet
- Debre Markos Universty College of Post-Graduate Studies Department of Accounting and FinanceDocument14 pagesDebre Markos Universty College of Post-Graduate Studies Department of Accounting and FinanceMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- 1 Financial SystemDocument72 pages1 Financial Systemsaha apurvaNo ratings yet
- FMI Class - Chap 2Document29 pagesFMI Class - Chap 2ruman mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Bfi PPT - 0129 To 0213Document43 pagesBfi PPT - 0129 To 0213Andrei Cruz AriateNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Financial System, Its Components: Unit 1Document16 pagesAn Introduction To Financial System, Its Components: Unit 1bhavyaNo ratings yet
- Finalcil Market - Bba Unit One &twoDocument79 pagesFinalcil Market - Bba Unit One &twoBhagawat PaudelNo ratings yet
- BFI 317 Lesson 1 An Overview of Banks and The Financial - Services SectorDocument16 pagesBFI 317 Lesson 1 An Overview of Banks and The Financial - Services Sectorjusper wendoNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Introduction To Financial InstitutionsDocument45 pagesCh. 1 Introduction To Financial InstitutionsSofoniyas GashawNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument115 pagesFinancial Institutionsmukesh sahooNo ratings yet
- International Trade Finance: A NOVICE'S GUIDE TO GLOBAL COMMERCEFrom EverandInternational Trade Finance: A NOVICE'S GUIDE TO GLOBAL COMMERCENo ratings yet
- Financial Markets Fundamentals: Why, how and what Products are traded on Financial Markets. Understand the Emotions that drive TradingFrom EverandFinancial Markets Fundamentals: Why, how and what Products are traded on Financial Markets. Understand the Emotions that drive TradingNo ratings yet
- Bank Fundamentals: An Introduction to the World of Finance and BankingFrom EverandBank Fundamentals: An Introduction to the World of Finance and BankingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Levels of Economic Integration: Global LandscapeDocument2 pagesLevels of Economic Integration: Global LandscapeMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two-Foundation of Individual Behavior and Learning in An OrganizationDocument16 pagesChapter Two-Foundation of Individual Behavior and Learning in An OrganizationMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two-Foundation of Individual Behavior and Learning in An OrganizationDocument14 pagesChapter Two-Foundation of Individual Behavior and Learning in An OrganizationMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document13 pagesCH 01Mikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Foundation of Group Behavior: 1.1. Defining and Classifying Team And/or GroupDocument15 pagesChapter Three Foundation of Group Behavior: 1.1. Defining and Classifying Team And/or GroupMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Foundation of Group Behavior: 1.1. Defining and Classifying Team And/or GroupDocument17 pagesChapter Three Foundation of Group Behavior: 1.1. Defining and Classifying Team And/or GroupMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Levels of Economic Integration: Global LandscapeDocument2 pagesLevels of Economic Integration: Global LandscapeMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven-Organizational Culture and DiversityDocument7 pagesChapter Seven-Organizational Culture and DiversityMikias Degwale100% (1)
- 1.1. What Is Stress?: Chapter Six-Stress ManagementDocument6 pages1.1. What Is Stress?: Chapter Six-Stress ManagementMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Voluntary RegistrationDocument3 pagesVoluntary RegistrationMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight - Power and Politics in An OrganizationDocument4 pagesChapter Eight - Power and Politics in An OrganizationMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Part One: Business ValuationDocument57 pagesChapter Five Part One: Business ValuationMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document13 pagesCH 01Mikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument2 pagesSolutionMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Registering For VATDocument1 pageRegistering For VATMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Investment/Project Appraisal - Capital BudgetingDocument40 pagesChapter Four: Investment/Project Appraisal - Capital BudgetingMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: Risk Management in Financial InstitutionsDocument22 pagesChapter Six: Risk Management in Financial InstitutionsMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and Market: (ACFN, 2 Credit Hour)Document25 pagesFinancial Institutions and Market: (ACFN, 2 Credit Hour)Mikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Interest Rate Determination and Bond ValuationDocument38 pagesChapter Five: Interest Rate Determination and Bond ValuationMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Financing Decisions / Capital StructureDocument72 pagesChapter Two: Financing Decisions / Capital StructureMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Dividend Decision/PolicyDocument38 pagesChapter Three: Dividend Decision/PolicyMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Advanced Corporate Finance (ACFN - 551) (Credit Hours: 3) : Departmet of Accounting and FinanceDocument85 pagesAdvanced Corporate Finance (ACFN - 551) (Credit Hours: 3) : Departmet of Accounting and FinanceMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Regulation of Financial Markets and Institutions and Financial InnovationDocument22 pagesChapter Five Regulation of Financial Markets and Institutions and Financial InnovationMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Raw Materials InventoryDocument4 pagesRaw Materials InventoryMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Debre Markos Universty College of Post-Graduate Studies Department of Accounting and FinanceDocument14 pagesDebre Markos Universty College of Post-Graduate Studies Department of Accounting and FinanceMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument7 pagesFinancial InstitutionsMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Financial Markets in The Financial SystemDocument66 pagesChapter Four Financial Markets in The Financial SystemMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Will Automation Take Away All Our JobsDocument7 pagesWill Automation Take Away All Our JobsBilal AminNo ratings yet
- Wage and Tax Statement: OMB No. 1545-0008 Visit The IRS Website atDocument3 pagesWage and Tax Statement: OMB No. 1545-0008 Visit The IRS Website atcofi kenteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Solutions Economics 19th EditionDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Solutions Economics 19th EditionFarhana Foysal SatataNo ratings yet
- Tourism Planning and Their Planning ImplicationsDocument11 pagesTourism Planning and Their Planning ImplicationsPatricia Mae Ramos BisenioNo ratings yet
- Chase Bank Statement TemplateDocument1 pageChase Bank Statement Templategmbeverywhere21No ratings yet
- Risk Evaluation FormDocument8 pagesRisk Evaluation FormJhon F SinagaNo ratings yet
- Asst. Prof. Rishi Dev ALS AUMDocument9 pagesAsst. Prof. Rishi Dev ALS AUMjoy parimalaNo ratings yet
- CH 11 QuizDocument4 pagesCH 11 QuizprowersappraiserNo ratings yet
- Minutes: 1 Quorum and Declarations of InterestDocument9 pagesMinutes: 1 Quorum and Declarations of InterestleseNo ratings yet
- How Will You Measure Your LifeDocument19 pagesHow Will You Measure Your LifeSpencerNo ratings yet
- Rupsa Dhar - 22PGDM197 - FIN1106Document5 pagesRupsa Dhar - 22PGDM197 - FIN1106Rupsa DharNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Project Report For MbaDocument84 pagesSummer Internship Project Report For MbaAkhil KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Savills LawsuitDocument18 pagesSavills LawsuitRobert GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Returns and Risks From InvestingDocument18 pagesThe Returns and Risks From InvestingAli Akand AsifNo ratings yet
- Taxation (United Kingdom) : Tuesday 12 June 2012Document12 pagesTaxation (United Kingdom) : Tuesday 12 June 2012Iftekhar IfteNo ratings yet
- Myndtree NewDocument9 pagesMyndtree NewlohithNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis - SlidesDocument53 pagesRatio Analysis - SlidesLysss EpssssNo ratings yet
- Wage InequalityDocument10 pagesWage Inequalityapi-339790662No ratings yet
- HP Magazine 2017 Spreads Web - AwDocument13 pagesHP Magazine 2017 Spreads Web - AwFernando RomoNo ratings yet
- Portakabin Edition 16 Lesson Resource Ansoffs MatrixDocument2 pagesPortakabin Edition 16 Lesson Resource Ansoffs MatrixAwantha MaharagamaNo ratings yet
- Chap 13 DWDocument45 pagesChap 13 DWMehrab IslamNo ratings yet
- Philippine Policy Towards Regional Cooperation in Southeast AsiaDocument450 pagesPhilippine Policy Towards Regional Cooperation in Southeast AsiaMariano RentomesNo ratings yet
- 高盛IPO全套教程Document53 pages高盛IPO全套教程MaxilNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Company Profile: (CITATION Wik20 /L 1033) (CITATION Sta19 /L 1033)Document18 pagesChapter One: Company Profile: (CITATION Wik20 /L 1033) (CITATION Sta19 /L 1033)Baken D DhungyelNo ratings yet
- E-Portfolio Econ 1740Document3 pagesE-Portfolio Econ 1740api-240741436No ratings yet
- Introduction To MicroeconomicsDocument43 pagesIntroduction To MicroeconomicsVũ Thùy DươngNo ratings yet
- Cunard Line:: Managing Integrated Marketing CommunicationDocument5 pagesCunard Line:: Managing Integrated Marketing CommunicationShubham SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION of Customer SatisfactionDocument2 pagesINTRODUCTION of Customer SatisfactionSai SuriyaNo ratings yet