Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Session 5
Uploaded by
chandel08Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Session 5
Uploaded by
chandel08Copyright:
Available Formats
Emotions and Moods
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7-1
Myth of rationality –
emotions were the
antithesis of rationality
and should not be seen in
the workplace
Belief that emotions of any
kind are disruptive in the
workplace
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7-2
Affect
◦ A generic term that encompasses a broad range of
feelings that people experience
Emotion
◦ Intense feelings that are directed at someone or
something
◦ Short termed and action-oriented.
Mood
◦ Feelings that tend to be less intense and longer-
lasting than emotions and often lack a contextual
stimulus
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7-3
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7-4
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7-
5
Day of Week and Time of Day
◦ More positive interactions will likely occur mid-
day and later in the week
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7-6
An employee’s expression of
organizationally desired
emotions during
interpersonal transactions at
work
Emotional dissonance is
when an employee has to
project one emotion while
simultaneously feeling
another
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7-7
Felt Emotions:
◦ the individual’s actual emotions
Displayed Emotions:
◦ the learned emotions that the organization
requires workers to show and considers
appropriate in a given job
◦ Surface Acting is hiding one’s true emotions
◦ Deep Acting is trying to change one’s feelings
based on display rules
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7-8
Satish fully understands the loss of Ronita, but then, the show must go on. Ronita’s lack of
enthusiasm and indifference was very much visible. Initially, every member of her team was
supportive, but now after 11 months, many have started complaining about her lack of interest in
team’s progress, even few have started questioning her ability to lead a high performing team.
Before the accident, when she lost her kid , Ronita was the star performer of the Zenith technologies.
Everyone was appreciative of her leadership, that’s the reason Satish appointed her the team lead of a
very important project. This is so far the biggest assignment the company has bagged, and the future
of Zenith depends on it.
What should Satish do ?
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
7-9
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7-
10
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7-
11
Selection – Employers should consider EI a
factor in hiring for jobs that demand a high
degree of social interaction
Decision Making – Positive emotions can
increase problem-solving skills and help us
understand and analyze new information
Creativity – Positive moods and feedback may
increase creativity
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7-
12
Motivation – Promoting positive moods may
give a more motivated workforce
Leadership – Emotions help convey messages
more effectively
Negotiation – Emotions may impair negotiator
performance
Customer Service – Customers “catch”
emotions from employees, called emotional
contagion
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7-
13
Job Attitudes – Emotions at work get carried
home but rarely carry over to the next day
Deviant Workplace Behaviors – Those who feel
negative emotions are more likely to engage
in deviant behavior at work
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7-
14
Use humor to lighten the
moment
Give small tokens of
appreciation
Stay in a good mood
themselves – lead by
example
Higher positive people
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7-
15
Does the degree to which people experience
emotions vary across cultures?
Do people’s interpretations of emotions vary
across cultures?
Do the norms for are the expressions of
emotions differ across cultures?
“YES” to all of the above!
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7-
16
Understand the role of emotions and
moods to better explain and predict
behavior
Emotions and moods do affect
workplace performance
While managing emotions may be
possible, absolute control of worker
emotions is not
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7-
17
Positive emotions can increase problem-
solving skills
People with high EI may be more effective in
their jobs
Managers need to know the emotional
norms for each culture they do business
with
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7-
18
Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7-
19
You might also like
- The Power of Positive Body Language: Mastering Nonverbal Communication to Improve Your Personal and Professional Relationships: Communication, #3From EverandThe Power of Positive Body Language: Mastering Nonverbal Communication to Improve Your Personal and Professional Relationships: Communication, #3No ratings yet
- Essentials of Organizational Behavior, 10/e: Emotions and MoodsDocument23 pagesEssentials of Organizational Behavior, 10/e: Emotions and MoodsAguswan FurwendoNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Organizational Behavior, 10/e: Emotions and MoodsDocument23 pagesEssentials of Organizational Behavior, 10/e: Emotions and MoodsAnonymous mzuRnewGNo ratings yet
- هيونداي اكسنت 2021 سعر مناسب للمستخدم - موقع حراجDocument24 pagesهيونداي اكسنت 2021 سعر مناسب للمستخدم - موقع حراجadelalgNo ratings yet
- 17 Editions: Organizational BehaviorDocument17 pages17 Editions: Organizational Behaviorramsha razaNo ratings yet
- Emotions and Moods: © 2007 Prentice Hall Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument22 pagesEmotions and Moods: © 2007 Prentice Hall Inc. All Rights ReservedridaNo ratings yet
- Emotions and Moods: © 2007 Prentice Hall Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument22 pagesEmotions and Moods: © 2007 Prentice Hall Inc. All Rights ReservedZia UddinNo ratings yet
- OB - Topic3 - Emotions Moods Personality and ValuesDocument53 pagesOB - Topic3 - Emotions Moods Personality and ValuestiffanyNo ratings yet
- Emotions & MoodsDocument22 pagesEmotions & MoodsFadel GibranNo ratings yet
- Emotions and MoodsDocument47 pagesEmotions and MoodsShouvik ChangkakotiNo ratings yet
- Reference Material I 07-Oct-2021 Emotions and MoodsDocument18 pagesReference Material I 07-Oct-2021 Emotions and Moodsrishika chhibberNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Organizational Behavior, Global Edition 12e: Moods, Emotions and Organizational BehaviourDocument22 pagesEssentials of Organizational Behavior, Global Edition 12e: Moods, Emotions and Organizational BehaviourYashwa AyubNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Emotions and MoodsDocument18 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Emotions and MoodsTayyab AliNo ratings yet
- BA 320: Organizational Behavior and Business AdministrationDocument27 pagesBA 320: Organizational Behavior and Business AdministrationUyen LeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Emotions and MoodDocument16 pagesChapter 4 Emotions and Moodworktemp395No ratings yet
- Emotions and Moods: EightDocument22 pagesEmotions and Moods: EightmiindsurferNo ratings yet
- Attitudes and Job Satisfaction: ThreeDocument17 pagesAttitudes and Job Satisfaction: Threeakash NegiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Emotions and MoodsDocument21 pagesChapter 4: Emotions and MoodsHwasub SongNo ratings yet
- Selling Today Manning Reece Ahearne - Chapter 3Document24 pagesSelling Today Manning Reece Ahearne - Chapter 3Free CourseNo ratings yet
- Robbins Ob14 PPT 04Document9 pagesRobbins Ob14 PPT 04Mahja LinNo ratings yet
- Chapter FiveDocument30 pagesChapter FiveMohammad MujahidNo ratings yet
- Chapter4emotionsandmoods 150614154551 Lva1 App6892Document18 pagesChapter4emotionsandmoods 150614154551 Lva1 App6892Muhammad Faizan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior 15th Global EditionDocument30 pagesOrganizational Behavior 15th Global Editionchaudhary ahmadNo ratings yet
- 04 - Emotions MoodsDocument20 pages04 - Emotions MoodsRafly FataNo ratings yet
- Attitudes and Job Satisfaction: ThreeDocument17 pagesAttitudes and Job Satisfaction: Threeartha wibawaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - 2022Document19 pagesChapter 4 - 2022quanhle2005No ratings yet
- Introduction To Organizational BehaviorDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Organizational BehaviorbhatippNo ratings yet
- Employee Behavior and Motivation: Inc. Publishing As Prentice HallDocument42 pagesEmployee Behavior and Motivation: Inc. Publishing As Prentice HallAlfryda Nabila Permatasari AegyoNo ratings yet
- Emotion, Moods & Emotional Intelligence - 03Document31 pagesEmotion, Moods & Emotional Intelligence - 03ADITYA PRATAP SINGH CHAUHAN 211154No ratings yet
- Robbins EOB10 Basic PPT CH01Document18 pagesRobbins EOB10 Basic PPT CH01mpsukarnoNo ratings yet
- Cha.4, Lec.1 OB, Com - Eve.Document10 pagesCha.4, Lec.1 OB, Com - Eve.Logo KrdoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 OB Attitudes and Job SatisfactionDocument22 pagesChapter 3 OB Attitudes and Job SatisfactionNooraldeen AlmoayedNo ratings yet
- Impact of Emotions On Work Perfomance - FinalDocument19 pagesImpact of Emotions On Work Perfomance - FinalSanjog Devrukhkar100% (7)
- Organizational Behavior: Attitudes and Job SatisfactionDocument13 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Attitudes and Job Satisfactionsaba rajaNo ratings yet
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument14 pagesEmotional IntelligenceFarah BerradhiNo ratings yet
- Ch4 - Emotions and Moods UpdatedDocument29 pagesCh4 - Emotions and Moods Updatedecholllin242No ratings yet
- MBA UWS Emotional IntelligenceDocument28 pagesMBA UWS Emotional IntelligenceNirushini ThurairajNo ratings yet
- Chpater 3 Updated 2022 Emotion and ModesDocument18 pagesChpater 3 Updated 2022 Emotion and ModesMohamed JamaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Emotions and MoodsDocument18 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Emotions and MoodsAtif Ul IslamNo ratings yet
- Chap 6Document21 pagesChap 6Dr.Babita BhatiNo ratings yet
- 6 - B - Importance of Emotional IntelligenceDocument15 pages6 - B - Importance of Emotional Intelligenceswastiknandgaonkar33No ratings yet
- Individual Differences: Attitude: Chapter Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesIndividual Differences: Attitude: Chapter Learning ObjectivesHazem SaeedNo ratings yet
- Contrast The Three Components of An Attitude: Attitudes Are Evaluative Statements - EitherDocument14 pagesContrast The Three Components of An Attitude: Attitudes Are Evaluative Statements - EitherSiddharthNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth EditionDocument28 pagesEssentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth EditionAakanksha KatariaNo ratings yet
- Contrast The Three Components of An Attitude: Attitudes Are Evaluative Statements - EitherDocument14 pagesContrast The Three Components of An Attitude: Attitudes Are Evaluative Statements - EitherSiddharthNo ratings yet
- Attitudes and Job Satisfaction: ThreeDocument19 pagesAttitudes and Job Satisfaction: ThreeZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Chapter 2Document24 pagesModule 1 Chapter 2SHreyas SHettigar (HONEY)No ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Attitudes and Job SatisfactionDocument14 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Attitudes and Job Satisfactionnourhan hegazyNo ratings yet
- Chpater 2 - Updated 2022Document13 pagesChpater 2 - Updated 2022Mohamed JamaNo ratings yet
- Robbins Ob16 PPT 04Document30 pagesRobbins Ob16 PPT 04begmNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Emotions and MoodsDocument18 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Emotions and MoodsCool MomNo ratings yet
- EmotionsDocument27 pagesEmotionsMasya IlyanaNo ratings yet
- MAN201 - Class 2 - Attitudes + Job Satisfaction - Emotions + MoodsDocument11 pagesMAN201 - Class 2 - Attitudes + Job Satisfaction - Emotions + MoodsDuyen Anh TruongNo ratings yet
- OB Session 5 Emotions Moods and Stress ManagementDocument50 pagesOB Session 5 Emotions Moods and Stress ManagementD GhoshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document18 pagesChapter 4Anika Nouroze ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- MGT201 Week 3 Lecture 3Document21 pagesMGT201 Week 3 Lecture 3Jumana AishathNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Seventeenth EditionDocument27 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Seventeenth EditionAbraham0% (1)
- C-3 Attitudes and Job SatisfactionDocument18 pagesC-3 Attitudes and Job Satisfactionsufian pabelNo ratings yet
- An Effective Manager Will Always Hire The Smartest Person AvailableDocument21 pagesAn Effective Manager Will Always Hire The Smartest Person AvailableArun RaiNo ratings yet
- Report - Workplace Emotions Attitudes and StressDocument20 pagesReport - Workplace Emotions Attitudes and StressCrisvemar CadanoNo ratings yet
- Term VI ElectiveDocument121 pagesTerm VI Electivechandel08No ratings yet
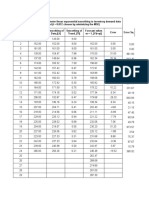
- Holts DataDocument3 pagesHolts Datachandel08No ratings yet
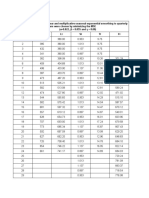
- Holts Winters MethodDocument3 pagesHolts Winters Methodchandel08No ratings yet
- Exercises On Dummy VariableDocument2 pagesExercises On Dummy Variablechandel08No ratings yet
- QDDocument1 pageQDchandel08No ratings yet
- Forecasting TechniquesDocument2 pagesForecasting Techniqueschandel08No ratings yet
- Case3-1 (Murphy)Document6 pagesCase3-1 (Murphy)chandel08No ratings yet
- IMC-TERI Case Related IMC Class ConceptsDocument5 pagesIMC-TERI Case Related IMC Class Conceptschandel08No ratings yet
- Imc-10.10.18 SPDocument18 pagesImc-10.10.18 SPchandel08No ratings yet
- FINAL & UPDATED-MK 612 IMC-Course Structure - September - December 2014Document8 pagesFINAL & UPDATED-MK 612 IMC-Course Structure - September - December 2014chandel08No ratings yet
- Cunard Lines-Case & Questions-Sept.'18Document5 pagesCunard Lines-Case & Questions-Sept.'18chandel08No ratings yet
- Getting The Most Out of Your Promotions and AdvtDocument4 pagesGetting The Most Out of Your Promotions and Advtchandel08No ratings yet
- Imc Case 1 - Psi India - 27.09. 14Document1 pageImc Case 1 - Psi India - 27.09. 14chandel08No ratings yet
- Case: Kay Sunderland - Session 2: Discussion QuestionsDocument2 pagesCase: Kay Sunderland - Session 2: Discussion Questionschandel08No ratings yet
- MOC-Role Play ExercisesDocument2 pagesMOC-Role Play Exerciseschandel08No ratings yet
- Pgdm-Sec C - 2015-16Document2 pagesPgdm-Sec C - 2015-16chandel08No ratings yet
- One To Two Max-1-2 Slides 1-2 Slides) (2 Slides) : 5 6 (10-12 Slides Only Brief and Concise)Document4 pagesOne To Two Max-1-2 Slides 1-2 Slides) (2 Slides) : 5 6 (10-12 Slides Only Brief and Concise)Sayan MitraNo ratings yet
- Section BDocument2 pagesSection Bchandel08No ratings yet
- MC II Project Work 2018Document1 pageMC II Project Work 2018chandel08No ratings yet
- Section A-PGDM-MC-II (Sept-Dec-2016) : Name Group NumberDocument2 pagesSection A-PGDM-MC-II (Sept-Dec-2016) : Name Group Numberchandel08No ratings yet
- HRM PGDM Groups MC IIDocument2 pagesHRM PGDM Groups MC IIchandel08No ratings yet
- PGDM B&FS 2015 16 (Groups)Document2 pagesPGDM B&FS 2015 16 (Groups)chandel08No ratings yet
- Questions - The Globalization of MarketsDocument1 pageQuestions - The Globalization of Marketschandel08No ratings yet
- PGDM Sec D 2015 16 (Groups)Document2 pagesPGDM Sec D 2015 16 (Groups)chandel08No ratings yet
- Cunard Lines-Case & Questions-Sept.'18Document5 pagesCunard Lines-Case & Questions-Sept.'18chandel08No ratings yet
- LM - Optimization - Sensitivity Analysis - Problem 1Document2 pagesLM - Optimization - Sensitivity Analysis - Problem 1chandel08No ratings yet
- Course Outline Logistics Modelling Term VI HarishRaoDocument5 pagesCourse Outline Logistics Modelling Term VI HarishRaochandel08No ratings yet
- Creative Brief - Group 2Document2 pagesCreative Brief - Group 2chandel08No ratings yet
- Answer 1Document3 pagesAnswer 1chandel08No ratings yet
- Sensitivity Problems - ExerciseDocument17 pagesSensitivity Problems - Exercisechandel08No ratings yet
- 15.910 Draft SyllabusDocument10 pages15.910 Draft SyllabusSaharNo ratings yet
- My New ResumeDocument1 pageMy New Resumeapi-412394530No ratings yet
- Mind Mapping BIOTEKDocument1 pageMind Mapping BIOTEKAdrian Muhammad RonalNo ratings yet
- MC 33199Document12 pagesMC 33199Abbode HoraniNo ratings yet
- Capitol Medical Center, Inc. v. NLRCDocument14 pagesCapitol Medical Center, Inc. v. NLRCFidel Rico NiniNo ratings yet
- Wiring DiagramsDocument69 pagesWiring DiagramsMahdiNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Policy Outcomes For Urban Resiliency in Informal Settlements Since Independence in Dhaka, Bangladesh: A ReviewDocument14 pagesEvaluating The Policy Outcomes For Urban Resiliency in Informal Settlements Since Independence in Dhaka, Bangladesh: A ReviewJaber AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Basics Stats Ti NspireDocument7 pagesBasics Stats Ti NspirePanagiotis SotiropoulosNo ratings yet
- ReleaseNoteRSViewME 5 10 02Document12 pagesReleaseNoteRSViewME 5 10 02Jose Luis Chavez LunaNo ratings yet
- Tavera Vs Valdez 1 Phil 468Document2 pagesTavera Vs Valdez 1 Phil 468John AmbasNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Performance of Container Terminals T PDFDocument10 pagesEvaluation of Performance of Container Terminals T PDFjohnNo ratings yet
- Web Server ProjectDocument16 pagesWeb Server Projectمعتز العجيليNo ratings yet
- Study For 33KV Sub-Marine Cable Crossings PDFDocument80 pagesStudy For 33KV Sub-Marine Cable Crossings PDFOGBONNAYA MARTINSNo ratings yet
- Berger Paints - Ar-19-20 PDFDocument302 pagesBerger Paints - Ar-19-20 PDFSahil Garg100% (1)
- French Revolution EssayDocument2 pagesFrench Revolution Essayapi-346293409No ratings yet
- Innova M3 New: 3. InstallationDocument8 pagesInnova M3 New: 3. InstallationAndreea DanielaNo ratings yet
- Project Guidelines (Issued by CBSE) : CA. (DR.) G.S. GrewalDocument51 pagesProject Guidelines (Issued by CBSE) : CA. (DR.) G.S. GrewalShruti Yadav0% (1)
- Group Tour Operators in Pune - Best Tours and Travels in PuneDocument10 pagesGroup Tour Operators in Pune - Best Tours and Travels in PuneGargi ToursNo ratings yet
- Tourism: The Business of Hospitality and TravelDocument33 pagesTourism: The Business of Hospitality and TravelNajla Nabila AurelliaNo ratings yet
- Stress and Strain - Axial LoadingDocument18 pagesStress and Strain - Axial LoadingClackfuik12No ratings yet
- PCU CalculationDocument2 pagesPCU CalculationMidhun Joseph0% (1)
- Transportation Problem VAMDocument16 pagesTransportation Problem VAMLia AmmuNo ratings yet
- Easy Pictionary Words: Angel Eyeball PizzaDocument3 pagesEasy Pictionary Words: Angel Eyeball Pizzakathy158No ratings yet
- Imp121 1isDocument6 pagesImp121 1isErnesto AyzenbergNo ratings yet
- Release ACOS 4.1.4-GR1-P10 IssuesDocument241 pagesRelease ACOS 4.1.4-GR1-P10 IssuesdanielatellaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology in The Banking SectorDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technology in The Banking Sectorvaralakshmi aNo ratings yet
- Lozada V Bracewell DigestDocument3 pagesLozada V Bracewell DigestMickey OrtegaNo ratings yet
- User Custom PP Install74Document2 pagesUser Custom PP Install74Zixi FongNo ratings yet
- Bemts-I (A) : Air Uni IsbDocument11 pagesBemts-I (A) : Air Uni IsbUmair AzizNo ratings yet
- Second Division: Republic of The Philippines Court of Tax Appeals Quezon CityDocument8 pagesSecond Division: Republic of The Philippines Court of Tax Appeals Quezon CityCamille CastilloNo ratings yet