Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnostic Tests
Uploaded by
Charlz Zipagan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views10 pagesThis document discusses the assessment and management of patients with endocrine system problems. It outlines methods for taking a patient history including nutrition, family history, and current health problems. Physical assessment focuses on inspection of features affected by hormones and palpation of the thyroid and testes. Diagnostic assessments include laboratory tests of body fluids and hormones, imaging like X-rays and CT scans, and biopsies. The goal is a comprehensive evaluation to identify endocrine disorders and monitor treatment.
Original Description:
Original Title
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the assessment and management of patients with endocrine system problems. It outlines methods for taking a patient history including nutrition, family history, and current health problems. Physical assessment focuses on inspection of features affected by hormones and palpation of the thyroid and testes. Diagnostic assessments include laboratory tests of body fluids and hormones, imaging like X-rays and CT scans, and biopsies. The goal is a comprehensive evaluation to identify endocrine disorders and monitor treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views10 pagesDiagnostic Tests
Diagnostic Tests
Uploaded by
Charlz ZipaganThis document discusses the assessment and management of patients with endocrine system problems. It outlines methods for taking a patient history including nutrition, family history, and current health problems. Physical assessment focuses on inspection of features affected by hormones and palpation of the thyroid and testes. Diagnostic assessments include laboratory tests of body fluids and hormones, imaging like X-rays and CT scans, and biopsies. The goal is a comprehensive evaluation to identify endocrine disorders and monitor treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
MANAGEMENT OF
PATIENTS WITH
PROBLEMS OF ENDOCRINE
SYSTEM
CHARLES Z. ARIOLA JR., MSN., LPT, RN.
INSTRUCTOR I
ASSESSMENT
METHODS
PATIENT HISTORY
- use of systems approach
- identifying patients response to actual or perceived changes
- use of Gordon's Functional Health Patterns
1. Nutritional -Metabolic Pattern
2. Elimination Pattern
3. Sleep-Rest Pattern
4. Sexuallity-Reproductive Pattern
5. Activity-Exercise Pattern
ASSESSMENT
METHODS
NUTRITION HISTORY
- ask about history of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain
- ask for increase in fluid and food intake
- assess for dietary deficiencies
FAMILY HISTORY AND GENETIC RISK
- ask about any history of obesity, growth or development difficulties, DM,
infertility, or thyroid disorders.
ASSESSMENT
METHODS
CURRENT HEALTH PROBLEMS
- assess energy level changes such as ability to perform ADLs
- assess for elimination pattern such as urinary pattern
- assess sexual and reproductive functions
- assess for physical appearance changes
PHYSICAL
ASSESSMENT
INSPECTION
-an endocrine problem can change physical features because of its effect on
growth and development, regulation of sex hormone levels, fluids and
electrolyte balance and body's use of nutrients.
- use head to toe approach
- observe for patients general appearance, and assess height, weight, fat
distribution and muscle mass in relation to age.
- check the ler half of the neck for visible enlargement of the thyroid gland
- assess for skin colors (ex: vitiligo- patcy areas of pigment loss which often
occurs in face, neck and extremities
- inspect patient's fingernails for malformation, thickness or brittleness
- examine the extremities and the base of the spine for edema.
- check for abnormalities in chest size and symmetry
- inspect the breast for both men and women for size, symmetry,
pigmentation and discharge
- assess the patient's hair distribution
PHYSICAL
ASSESSMENT
PALPATION
- this is done in assessing thyroid gland and testes
- the thyroid gland is palpated for symmetry, size, general shape and the
presence of nodules or irregularities
AUSCULTATION
- auscultate the chest to assess for cardiac rate and rhythm
DIAGNOSTIC
ASSESSMENT
LABORATORY ASSESSMENT
- Use of body fluids such as saliva, blood urine
1. STIMULATION/SUPPRESSION TEST
- measurement of specific hormone levels
STIMULATION TESTING- a stimulus is provided to determine whether
the gland is capable of normal hormone production. Failure of hormones to
rise indicates HYPOFUNCTION
SUPPRESSION TESTING- used when hormones are high. failure of
suppression of hormone during testing indicates HYPERFUNCTION.
DIAGNOSTIC
ASSESSMENT
2. ASSAY
- measures the level of hormone in the blood or other body fluid.
3. URINE TESTS
- 24- hour urine collection reflects overall function of certain glands.
4. TEST FOR GLUCOSE
- tests for functions of the islet cells of the pancreas. the glycosylated
hemoglbin (HBA1c) reveals average blood glucose level for 2-3 months
DIAGNOSTIC
ASSESSMENT
6. IMAGING ASSESSMENT
- Anterior, posterior , or lateral skull X-rays
- MRI
- CT Scan
7. OTHER DIAGNOSTIC ASSESSMENT
- Needle Biopsy
You might also like
- The Herb Handbook - A Practical Guide To - Simone McGrathDocument128 pagesThe Herb Handbook - A Practical Guide To - Simone McGrathCristian Lungu100% (2)
- Vaccination Roulette: Experiences, Risks and AlternativesDocument336 pagesVaccination Roulette: Experiences, Risks and AlternativesMeryl Dorey100% (3)
- EXHIBIT 001 - NOTICE of Birthright and Right of SoilDocument3 pagesEXHIBIT 001 - NOTICE of Birthright and Right of Soilthenjhomebuyer100% (1)
- American Legion White Paper On Veteran SuicideDocument24 pagesAmerican Legion White Paper On Veteran SuicideJared KellerNo ratings yet
- PreeclampsiaDocument179 pagesPreeclampsiaJohn Wilbert Birung100% (3)
- 1 Gastrointestinal EmergenciesDocument142 pages1 Gastrointestinal EmergenciesRashida UmarNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeDocument47 pagesPolycystic Ovarian SyndromeAnonymous HgX3mN1o100% (1)
- Wounded AttachmentsDocument22 pagesWounded AttachmentsMichael van der VeldtNo ratings yet
- Healthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes: 100 Simple, Effective Ways to Prevent and Undo PrediabetesFrom EverandHealthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes: 100 Simple, Effective Ways to Prevent and Undo PrediabetesNo ratings yet
- Schools Division of Iloilo: Supreme Student Government (SSG) Progrms, Projects and Activities Monitoring FormDocument1 pageSchools Division of Iloilo: Supreme Student Government (SSG) Progrms, Projects and Activities Monitoring FormLIRA MAE DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Assessment Lecture 1Document28 pagesNutritional Assessment Lecture 1ESUFIYAN ALWSABINo ratings yet
- Cause and Prevention For Steam Turbine Blade Scaling FoulingDocument10 pagesCause and Prevention For Steam Turbine Blade Scaling FoulingSiva Kulanji100% (1)
- R 12 General Ledger White PaperDocument89 pagesR 12 General Ledger White PaperJihad Darwish100% (1)
- Assessment of Nutritional StatusDocument38 pagesAssessment of Nutritional Statusmichael jan de celis100% (3)
- AUB StartedDocument13 pagesAUB StartedIbrahim AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Endocrine NursingDocument16 pagesEndocrine NursingFreeNursingNotes100% (19)
- Intro To Medtech Clinical Chemistry ReviewerDocument11 pagesIntro To Medtech Clinical Chemistry Reviewerjesanndei100% (1)
- Assessment of The Endocrine SystemDocument29 pagesAssessment of The Endocrine SystemBintang Banyu Biru100% (1)
- Diagnosis of InfertilityDocument9 pagesDiagnosis of InfertilityRiena Rose Bayona100% (1)
- Nutritional Assessment: A. Yasmin Syauki Nutrition Department School of Medicine Hasanuddin UniversityDocument47 pagesNutritional Assessment: A. Yasmin Syauki Nutrition Department School of Medicine Hasanuddin UniversitylindaNo ratings yet
- Nurse Nutrition Study Guide Exam 3Document30 pagesNurse Nutrition Study Guide Exam 3Ek100% (1)
- Preventive Maintenance ChecklistDocument1 pagePreventive Maintenance ChecklistBelayneh AregaNo ratings yet
- The Human Needs Approach, A Basic Handbook For Nursing StudentsDocument23 pagesThe Human Needs Approach, A Basic Handbook For Nursing StudentsEcaroh Hew SmailliwNo ratings yet
- Charles Z. Ariola JR., MSN., LPT, Rn. Instructor IDocument10 pagesCharles Z. Ariola JR., MSN., LPT, Rn. Instructor ICharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders Assessment Methods 2Document27 pagesEndocrine Disorders Assessment Methods 2May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Assessment of Individuals: To Prepare A Nutrition Assessment, A Trained Health-Care Professional UsesDocument15 pagesNutritional Assessment of Individuals: To Prepare A Nutrition Assessment, A Trained Health-Care Professional Usesmedical studiesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway For Family Wellness Promotion in Elderly: Junayyah A. Sarip Jaeron Den D. TopinioDocument36 pagesClinical Pathway For Family Wellness Promotion in Elderly: Junayyah A. Sarip Jaeron Den D. TopinioJunayyah Abdullah SaripNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Module 4 5Document3 pagesNutrition Module 4 5Merald PerdigonNo ratings yet
- Nutritional AssessmentDocument38 pagesNutritional AssessmentCathrina BelardoNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Gizi Klinik Dasar 1Document59 pagesKuliah Gizi Klinik Dasar 1yuliaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument13 pagesLab Reportshivam9308306868No ratings yet
- Review of Systems: Nurs 02 - Health AssessmentDocument22 pagesReview of Systems: Nurs 02 - Health AssessmentteuuuuNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument29 pagesAbdominal Assessmentkent yeeNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument6 pagesReviewerKarl LintanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition AssessmentDocument32 pagesNutrition AssessmentJobelyn MalisaNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine DisordersDocument52 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine DisordersJerome RarogalNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeDocument36 pagesPolycystic Ovarian SyndromeRaras Mayang100% (1)
- Nutritional AssessmentDocument13 pagesNutritional Assessmenthazieldc10No ratings yet
- Week 2 Assessment of A Patient With A Gynaecological ProblemDocument37 pagesWeek 2 Assessment of A Patient With A Gynaecological ProblemMutai KiprotichNo ratings yet
- C. Nutrition AssessmentDocument4 pagesC. Nutrition AssessmentBryant joshua leonardoNo ratings yet
- Cpy 531 Lecture Notes 2Document9 pagesCpy 531 Lecture Notes 2onyibor joshuaNo ratings yet
- EndoDocument252 pagesEndoyuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Anorexia Nervosa PDFDocument6 pagesAnorexia Nervosa PDFmist73No ratings yet
- 7-Failure To ThriveDocument22 pages7-Failure To Thriveabdalmajeed alshammaryNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Institute of Post Graduate Medical Education and Research Puducherry - 605 006Document10 pagesJawaharlal Institute of Post Graduate Medical Education and Research Puducherry - 605 006Sam P DanielNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 and 5 - Introduction To Nutrition TherapyDocument46 pagesLecture 4 and 5 - Introduction To Nutrition TherapyAbdullah LateefNo ratings yet
- ISCP 4th Hari Kedua GoodDocument72 pagesISCP 4th Hari Kedua GoodMade SriNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Balance, Nutrition and Metabolism and EndocrineDocument12 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Balance, Nutrition and Metabolism and EndocrineLudwigJayBarayugaNo ratings yet
- Clinical MarasmusDocument27 pagesClinical MarasmusHANNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Endo, Meta, GI SyllabusDocument8 pagesNCM 103 Endo, Meta, GI Syllabusjongmartinez100% (1)
- Anorexia Nervosa: Dr. K.RavishankarDocument17 pagesAnorexia Nervosa: Dr. K.RavishankarChaitanya Kiran PullelaNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 Alterations in Nutri and GI Rev5Document100 pagesNCM 116 Alterations in Nutri and GI Rev5JxshxzsNo ratings yet
- USDA Grant Mattes 2016-2019Document5 pagesUSDA Grant Mattes 2016-2019The Nutrition CoalitionNo ratings yet
- 1 NuterationDocument36 pages1 Nuterationزينب القضيNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document32 pagesLec 3Hatdog Ka BaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Angesom K LectureDocument118 pagesDr. Angesom K LectureHenok Y KebedeNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Clients With Digestive Disorders (PBN)Document6 pagesAssessment of Clients With Digestive Disorders (PBN)abdulNo ratings yet
- 1 Assessment of Endocrine SystemDocument15 pages1 Assessment of Endocrine SystemHanen ZedanNo ratings yet
- Nurse ReviewDocument22 pagesNurse ReviewJane VerboNo ratings yet
- Transit of Pharmaceutical Forms The Small Intestine: Dosage ThroughDocument8 pagesTransit of Pharmaceutical Forms The Small Intestine: Dosage ThroughFarhan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Case HistoryDocument151 pagesCase HistoryASJADI SHEIKHNo ratings yet
- Anorexia Nervosa: Dr. K.RavishankarDocument21 pagesAnorexia Nervosa: Dr. K.RavishankarChaitanya Kiran PullelaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Care and AssessmentDocument27 pagesNutrition Care and AssessmentAfzal KhanNo ratings yet
- NCMB 314 - M2-Cu10Document10 pagesNCMB 314 - M2-Cu10Giselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 SyllabusDocument10 pagesNCM 103 SyllabuslouradelNo ratings yet
- Pengkajian Keperawatan Gawat Darurat Lanjut 2: Abdominal and Gastrointestinal EmergenciesDocument144 pagesPengkajian Keperawatan Gawat Darurat Lanjut 2: Abdominal and Gastrointestinal EmergenciesLuisHsanFigoNo ratings yet
- Different Types Phenotypes PCOS Role ManagementDocument60 pagesDifferent Types Phenotypes PCOS Role Managementcalvinjohn1690100% (1)
- Quiz 2Document5 pagesQuiz 2Charlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Assessment of AdlsDocument11 pagesAssessment of AdlsCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Document4 pagesIsabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Charlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document200 pagesLec 1Charlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Document8 pagesIsabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Charlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- First QuizDocument6 pagesFirst QuizCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Cardio MidtermDocument8 pagesCardio MidtermCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument51 pagesChest PhysiotherapyCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University City of Ilagan Campus: Care of The Clients With Endocrine and Metabolic DisorderDocument29 pagesIsabela State University City of Ilagan Campus: Care of The Clients With Endocrine and Metabolic DisorderCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Assessment & Functional PatternsDocument30 pagesMental Status Assessment & Functional PatternsCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Health History: Charles Z. Ariola JR., MSN, LPTDocument19 pagesHealth History: Charles Z. Ariola JR., MSN, LPTCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases of The Respiratory: Tuberculosis PneumoniaDocument37 pagesCommunicable Diseases of The Respiratory: Tuberculosis PneumoniaCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University City of Ilagan Campus: Care of The Clients With Endocrine and Metabolic DisorderDocument15 pagesIsabela State University City of Ilagan Campus: Care of The Clients With Endocrine and Metabolic DisorderCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Review of Nursing ProcessDocument83 pagesReview of Nursing ProcessCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria - Pertussis (REPORT)Document48 pagesDiphtheria - Pertussis (REPORT)Charlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Isabela State Unversity City of Ilagan Isabela College of Nursing NUR 312Document11 pagesIsabela State Unversity City of Ilagan Isabela College of Nursing NUR 312Charlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University City of Ilagan Campus: Care of The Clients With Endocrine and Metabolic DisorderDocument13 pagesIsabela State University City of Ilagan Campus: Care of The Clients With Endocrine and Metabolic DisorderCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University City of Ilagan CampusDocument16 pagesIsabela State University City of Ilagan CampusCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases of The Genitouriary System-Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument28 pagesCommunicable Diseases of The Genitouriary System-Sexually Transmitted DiseasesCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Pertussis: Is Highly Contagious Respiratory DiseaseDocument20 pagesPertussis: Is Highly Contagious Respiratory DiseaseCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases of The Circulatory System: Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF) MalariaDocument50 pagesCommunicable Diseases of The Circulatory System: Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF) MalariaCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
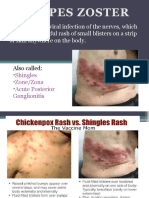
- Herpes ZosterDocument12 pagesHerpes ZosterCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument33 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- CHICKENPOXDocument32 pagesCHICKENPOXCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- DELL Precision 3460 SFF Spec SheetDocument3 pagesDELL Precision 3460 SFF Spec SheetfquispecNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship NotesDocument15 pagesEntity Relationship NotesChris HarrisNo ratings yet
- Lesson Skill Matrix: Software OrientationDocument10 pagesLesson Skill Matrix: Software OrientationMary Jane PagayNo ratings yet
- Scordo Writing ObjectivesDocument3 pagesScordo Writing ObjectivesSharmane SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Request: "Webdev - Webserver.Exe" Which Actually Takw Care of All Request and Response of An WebDocument59 pagesRequest: "Webdev - Webserver.Exe" Which Actually Takw Care of All Request and Response of An WebSeth JacksonNo ratings yet
- Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited: Ideal Institute of Technology, GhaziabadDocument16 pagesBharat Sanchar Nigam Limited: Ideal Institute of Technology, GhaziabadyrikkiNo ratings yet
- DDDocument3 pagesDDKundan karnNo ratings yet
- First Institutional Assembly Cluster 8 PersonnelDocument3 pagesFirst Institutional Assembly Cluster 8 PersonnelKenjie Gomez EneranNo ratings yet
- Al-Jawad, M. S., Et Al., 2016, Geological Model of Khasib Reservoir-Central Area-East Baghdad FieldDocument10 pagesAl-Jawad, M. S., Et Al., 2016, Geological Model of Khasib Reservoir-Central Area-East Baghdad Fieldwei zhouNo ratings yet
- SWI-Prolog-8 2 4Document680 pagesSWI-Prolog-8 2 4Steve LezamaNo ratings yet
- Hemotask2018 PDFDocument3 pagesHemotask2018 PDFPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Comparative Statement RevisedDocument7 pagesComparative Statement RevisedV SNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Review, March 28, 2013Document14 pagesPioneer Review, March 28, 2013surfnewmediaNo ratings yet
- Clinics in Chest MedicineDocument161 pagesClinics in Chest MedicineVeronica SimamoraNo ratings yet
- 21st CenturyLit Quarter2 Week1Document6 pages21st CenturyLit Quarter2 Week1SHAINE UNGABNo ratings yet
- Re-Visioning The Fascia As A Body-Wide Regulatory System: by Thomas MyersDocument4 pagesRe-Visioning The Fascia As A Body-Wide Regulatory System: by Thomas MyersAndrew LiebermannNo ratings yet
- Marriage Reg PDFDocument2 pagesMarriage Reg PDFamit jadhavNo ratings yet
- Visio-Recommendation Outcomes 1.00Document3 pagesVisio-Recommendation Outcomes 1.00raymondmonacoNo ratings yet
- Abakada Guro Party List v. ErmitaDocument3 pagesAbakada Guro Party List v. ErmitaMikee MacalaladNo ratings yet
- REGISTRARS OFFICE-MINUTES REPORT 2022 With Addtnl COPY RWFDocument4 pagesREGISTRARS OFFICE-MINUTES REPORT 2022 With Addtnl COPY RWFmarijoy pagalNo ratings yet
- The Green Marketing "Revolution" - Is It WorthDocument12 pagesThe Green Marketing "Revolution" - Is It WorthAndrew SmithNo ratings yet