Professional Documents
Culture Documents
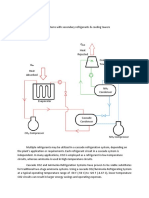
Boiling Points Are Used in A Series of Single Stage Units. The Condenser
Boiling Points Are Used in A Series of Single Stage Units. The Condenser
Uploaded by
Nikhil Singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views7 pagesOriginal Title
cascade-ref-system.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views7 pagesBoiling Points Are Used in A Series of Single Stage Units. The Condenser
Boiling Points Are Used in A Series of Single Stage Units. The Condenser
Uploaded by
Nikhil SinghCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
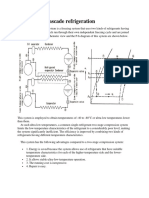
Cascade Refrigeration System:
In a cascade system a series of refrigerants with progressively lower
boiling points are used in a series of single stage units. The condenser
of lower stage system is coupled to the evaporator of the next higher
stage system and so on. The component where heat of condensation
of lower stage refrigerant is supplied for vaporization of next level
refrigerant is called as cascade condenser.
This system employs two different refrigerants operating in two individual
cycles. They are thermally coupled in the cascade condenser. The
refrigerants selected should have suitable pressure-temperature
characteristics. An example of refrigerant combination is the use of
carbon dioxide (NBP = -78.400C) in low temperature cascade and
ammonia (NBP = -33.33 oC) in high temperature cascade. It is possible to
use more than two cascade stages, and it is also possible to combine
multi-stage systems with cascade systems.
Applications of cascade systems:
i. Liquefaction of petroleum vapours
ii. Liquefaction of industrial gases
iii. Manufacturing of dry ice
iv. Deep freezing etc
two-stage cascade refrigeration system
Optimum cascade temperature:
For a two-stage cascade system working on Carnot cycle, the optimum
cascade temperature at which the COP will be maximum, Tcc,opt is given by:
where Te and Tc are the evaporator temperature of low temperature cascade
and condenser temperature of high temperature cascade, respectively.
You might also like
- Low Temperature RefrigerationDocument9 pagesLow Temperature Refrigerationguadalupe_cortes_21100% (2)
- Thermodynamic Analysis of A 2-Stage Cascade VCR CycleDocument27 pagesThermodynamic Analysis of A 2-Stage Cascade VCR CycleAkshat RNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Capter 11 (Refrigeration Cycle)Document7 pagesLecture 5 Capter 11 (Refrigeration Cycle)Yato SenkaiNo ratings yet
- Ii. Iii. Iv.: Cascade SystemsDocument6 pagesIi. Iii. Iv.: Cascade SystemsBaravan A. İsmailNo ratings yet
- Ultralow-Temperature Refrigeration: Related Commercial ResourcesDocument11 pagesUltralow-Temperature Refrigeration: Related Commercial ResourcesBurning TrainNo ratings yet
- Andreza, Lemuel V. Activity 8 PDFDocument4 pagesAndreza, Lemuel V. Activity 8 PDFlemuel andrezaNo ratings yet
- IJREI_Thermal modelling of three stage vapour compression cascade refrigeration system using entropy generation principle for reducing global warming and ozone depletion using ecofriendly refrigerants for semen preservationDocument7 pagesIJREI_Thermal modelling of three stage vapour compression cascade refrigeration system using entropy generation principle for reducing global warming and ozone depletion using ecofriendly refrigerants for semen preservationIjrei JournalNo ratings yet
- 18.multistage Systems and Cascade SystemsDocument9 pages18.multistage Systems and Cascade SystemsericNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Ultra Low Temperature Refrigeration SystemsDocument35 pagesChapter 5. Ultra Low Temperature Refrigeration SystemsHosnii QamarNo ratings yet
- Cascade Refrigeration System (Report)Document8 pagesCascade Refrigeration System (Report)THE PUBGTV100% (1)
- Experimental Investigation On Cascade Refrigeration System With and Without Phase Change MaterialDocument8 pagesExperimental Investigation On Cascade Refrigeration System With and Without Phase Change MaterialijsretNo ratings yet
- Study of Refrigeration SystemsDocument28 pagesStudy of Refrigeration SystemsAkhil ShettyNo ratings yet
- Report On Cascade Refrigeration SystemsDocument11 pagesReport On Cascade Refrigeration SystemsJashandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Episode 3 MultipressuresystemsDocument75 pagesEpisode 3 MultipressuresystemsANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Ashrae R02 39siDocument12 pagesAshrae R02 39siMikechal AwacayNo ratings yet
- AJES Vol.6 No.1 January June 2017 pp.18 22Document5 pagesAJES Vol.6 No.1 January June 2017 pp.18 22Design isotechplNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration (Multipressure & Cascade Systems)Document19 pagesRefrigeration (Multipressure & Cascade Systems)Kevin JoeNo ratings yet
- Cascade RefrigerationDocument1 pageCascade RefrigerationRAVI BARTIANo ratings yet
- 9729محاضره1مقرر تبريد وتكييفDocument6 pages9729محاضره1مقرر تبريد وتكييفeslam AtitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Chap 9Document35 pagesChapter - Chap 9SimphiweNo ratings yet
- Rac Solution Set ADocument7 pagesRac Solution Set AMuhammad AkhtarNo ratings yet
- A 2-Stage Cascade Refrigeration CycleDocument8 pagesA 2-Stage Cascade Refrigeration CycleSaeikh Z. HassanNo ratings yet
- 20 2020-03-27 Refrigerant Cycle ATEEDocument3 pages20 2020-03-27 Refrigerant Cycle ATEEعبير ابوصالحهNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument19 pagesRefrigerationDDCMNo ratings yet
- CascadeDocument9 pagesCascadeChandel ManujNo ratings yet
- Jten 2016 2 6.1210Document12 pagesJten 2016 2 6.1210danish5aliNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration System PDFDocument39 pagesRefrigeration System PDFSiti Hajar Shamsul Kamar86% (7)
- Thermodynamic Performance Analysis of Cascade Refrigeration System - A ReviewDocument5 pagesThermodynamic Performance Analysis of Cascade Refrigeration System - A ReviewOnofreNo ratings yet
- Project Repoert Test Rig OrgDocument66 pagesProject Repoert Test Rig OrgSandeep 21No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Capter 11 (Refrigeration Cycle)Document9 pagesLecture 4 Capter 11 (Refrigeration Cycle)Yato SenkaiNo ratings yet
- 04TRK Sistem MultistageDocument28 pages04TRK Sistem MultistageAga Fir IkbarNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemDocument18 pagesVapor Compression Refrigeration SystemKen GodNo ratings yet
- Cascade Refrigeration With Inverse Brayton CycleDocument21 pagesCascade Refrigeration With Inverse Brayton CycleShubham Raj RajNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 13 - Multi Stage Refrigeration Cycle - LanjutanDocument8 pagesPertemuan 13 - Multi Stage Refrigeration Cycle - LanjutanAde FandiNo ratings yet
- Ans 1 (A) P-V DiagramDocument4 pagesAns 1 (A) P-V DiagramPardeep8056No ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Liquefaction: Instructor: Engr. Caressa Marie Frial-De JesusDocument22 pagesRefrigeration and Liquefaction: Instructor: Engr. Caressa Marie Frial-De JesusEmmanuel PlazaNo ratings yet
- Multi-Pressure SystemDocument10 pagesMulti-Pressure SystemCassie E. ZernaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 RefrigerationDocument23 pagesChapter 11 Refrigerationmuru0105No ratings yet
- NOTES 5 - RefrigerationDocument20 pagesNOTES 5 - RefrigerationMakoya_malumeNo ratings yet
- Reindl PDFDocument6 pagesReindl PDFstuntmanzNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Liquids RecoveryDocument19 pagesNatural Gas Liquids RecoveryermiasNo ratings yet
- Multi StageDocument36 pagesMulti StageBfhf HdhgNo ratings yet
- The University of The South Pacific: School of Engineering and PhysicsDocument4 pagesThe University of The South Pacific: School of Engineering and PhysicsRoshiv SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rac CH 2.1Document54 pagesRac CH 2.1Gemechu DelesaNo ratings yet
- Tobias, Jade C. Bsme 3A: Assignment # 5Document10 pagesTobias, Jade C. Bsme 3A: Assignment # 5Jade Tobias100% (1)
- 351 Chap1 Refrigeration Intro 2014Document24 pages351 Chap1 Refrigeration Intro 2014Faiz AmeeriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 RefrigerationDocument65 pagesLecture 6 RefrigerationRamon Gerald AsiloNo ratings yet
- Black Book VCCDocument50 pagesBlack Book VCCRahul Pawar100% (2)
- Hybrid Refrigeration SynopsisDocument12 pagesHybrid Refrigeration SynopsisZia Muhammad HaiderNo ratings yet
- Design and Control of A Cryogenic Multi-Stage Compression Refrigeration ProcessDocument8 pagesDesign and Control of A Cryogenic Multi-Stage Compression Refrigeration ProcessGezu AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Liquids RecoveryDocument17 pagesNatural Gas Liquids Recoveryabdur rehmanNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration ME 201Document13 pagesRefrigeration ME 201pathan_440No ratings yet
- Vipin New PaperDocument8 pagesVipin New PaperSalemNo ratings yet
- Cascade SystemsDocument5 pagesCascade SystemsMark De LeonNo ratings yet
- Automatic Purgers in Refrigeration Systems PDFDocument7 pagesAutomatic Purgers in Refrigeration Systems PDFrofasiNo ratings yet
- 4 - II. Innovative - Cascade, multi-VCRSDocument28 pages4 - II. Innovative - Cascade, multi-VCRSSumran ShahidNo ratings yet
- Value Analysis of Advanced Heat Rejection Systems For Geothermal Power PlantsDocument4 pagesValue Analysis of Advanced Heat Rejection Systems For Geothermal Power PlantsYanan CamarazaNo ratings yet
- Cascade Refrigeration System Lab ManualDocument7 pagesCascade Refrigeration System Lab ManualAshish VermaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Nanofabrication TechnologiesDocument26 pagesApplications of Nanofabrication TechnologiesNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Micro-And Nanofabrication Methods in Nanotechnological Medical and Pharmaceutical DevicesDocument13 pagesMicro-And Nanofabrication Methods in Nanotechnological Medical and Pharmaceutical DevicesNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of 5 NM Linewidth and 14 NM Pitch Features by Nanoimprint LithographyDocument4 pagesFabrication of 5 NM Linewidth and 14 NM Pitch Features by Nanoimprint LithographyNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 MultistageVCRSDocument17 pagesUnit 2 MultistageVCRSNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- VarsDocument16 pagesVarsNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Multiple Evap SystemDocument13 pagesMultiple Evap SystemNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Blow Moulding: Assignment 2 (Ms Ii)Document12 pagesBlow Moulding: Assignment 2 (Ms Ii)Nikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- CryogenicsDocument11 pagesCryogenicsNikhil SinghNo ratings yet