Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Standard Method
Standard Method
Uploaded by
Salwa Kamilia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views19 pagesA municipal water company was having issues analyzing iron levels in water samples using atomic absorption spectrometry. To investigate, a series of iron standards with concentrations ranging from 0 to 10 ppm were prepared and their absorbances measured. The absorbance of an undiluted water sample was also measured. Using the calibration curve generated from the iron standards, the concentration of iron in the original undiluted water sample was calculated to be 21.25 ppm.
Original Description:
Original Title
Standard Method.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA municipal water company was having issues analyzing iron levels in water samples using atomic absorption spectrometry. To investigate, a series of iron standards with concentrations ranging from 0 to 10 ppm were prepared and their absorbances measured. The absorbance of an undiluted water sample was also measured. Using the calibration curve generated from the iron standards, the concentration of iron in the original undiluted water sample was calculated to be 21.25 ppm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views19 pagesStandard Method
Standard Method
Uploaded by
Salwa KamiliaA municipal water company was having issues analyzing iron levels in water samples using atomic absorption spectrometry. To investigate, a series of iron standards with concentrations ranging from 0 to 10 ppm were prepared and their absorbances measured. The absorbance of an undiluted water sample was also measured. Using the calibration curve generated from the iron standards, the concentration of iron in the original undiluted water sample was calculated to be 21.25 ppm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
External Standard
Single Eksternal Standard
Multiple-point External Standard
A municipal water company was having problems with its
water analysis. The problem lay in the AAS determination of
Fe at 248.3 nm. The absorbance of the water, after 5 fold
dilution was 0.646 at 248.3 nm. On a proper investigation of
the above problem a series of iron standards were prepared
by taking various volumes of a 0.0593 mg Fe per mL and
diluting up to 100 mL. Calculate the ppm in the water
sample. The absorbance of the solutions were as follows:
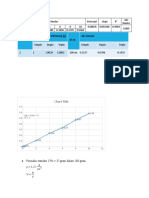
Volume larutan Absorbansi
stok Fe standar
(mL)
0 0,000
1 0,113
3 0,334
5 0,530
7 0,672
10 0,813
Answer
Y = 0,1402x + 0,0501
C
Vol (ppm Absorbance 0,646 Concentration 4,25
(mL) ) Abs Diluting 5x 4,25 x 5 = 21,25 ppm
0 0 0
1 0,593 0,113
3 1,779 0,334
5 2,965 0,53
7 4,151 0,672
10 5,93 0,813
Standard Addition
• Standard addition is a method to
determine the amount of analyte in an
unknown.
– In standard addition, known quantities of
analyte are added to an unknown.
– We determine the analyte concentration from
the increase in signal.
• Standard addition is often used when
the sample is unknown, trace or
complex.
Single Standard Addition
It also possible to make standard addition directly to the
sample after measuring Ssamp. In this case, the final
volume after the standard addition is Vo + Vs
Multiple-point Standard Addition
Single:
The signal is plotted versus the
volume of the added standard
Single:
The signal is plotted versus the
concentration of the added standard
answer
Internal Standard
You might also like
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- UVDocument11 pagesUVShaun Loo100% (3)
- Determination of Riboflavin in Soft Drinks by Fluorescence SpectrophotometryDocument9 pagesDetermination of Riboflavin in Soft Drinks by Fluorescence SpectrophotometryNur IzzatieNo ratings yet
- Practical 1: Determination of Reducing Sugar Using The Dinitrosalicylic (DNS) Colourimetric MethodDocument8 pagesPractical 1: Determination of Reducing Sugar Using The Dinitrosalicylic (DNS) Colourimetric MethodNurSyazaHaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Uv-Visible Determination of An Unknown Concentration of Kmno Solution A. Pre-Laboratory QuestionsDocument4 pagesExperiment 2: Uv-Visible Determination of An Unknown Concentration of Kmno Solution A. Pre-Laboratory QuestionsMuhd Mirza HizamiNo ratings yet
- Materi - 1 - SpectrosDocument49 pagesMateri - 1 - SpectrosSalwa KamiliaNo ratings yet
- Concentration of SolutionsDocument32 pagesConcentration of SolutionsRaja Mohan Gopalakrishnan100% (2)
- Chm580 Experiment 2Document8 pagesChm580 Experiment 2ohhi100% (1)
- UV VisDocument50 pagesUV VisSalwa Kamilia83% (6)
- LR-Practical 2 (AAS Ashing)Document12 pagesLR-Practical 2 (AAS Ashing)najwaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report (Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy)Document8 pagesLab Report (Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy)Shirley Cheong67% (6)
- Problem Set 1Document3 pagesProblem Set 1Lu JunqueiraNo ratings yet
- Molvigcourtney Labreport8Document7 pagesMolvigcourtney Labreport8api-405393737No ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Che 314Document11 pagesExperiment 3 Che 314Seele TlhagaNo ratings yet
- CHM260 Basic Instrumental Analysis Laboratory Summary WrittenDocument12 pagesCHM260 Basic Instrumental Analysis Laboratory Summary WrittenCassyNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 AasDocument16 pagesExp 4 AasDaniel IsmailNo ratings yet
- CHM 260 Lab Report Exp 4Document7 pagesCHM 260 Lab Report Exp 4Warina 01No ratings yet
- Uv Vis Spectroscopy Lab Report of The Detection of Analytes From Environmental Samples Using UvDocument13 pagesUv Vis Spectroscopy Lab Report of The Detection of Analytes From Environmental Samples Using UvSaba Naseer100% (1)
- Bab 4 Hasil Dan PembahasanDocument3 pagesBab 4 Hasil Dan PembahasanM SyafNo ratings yet
- Uv Spectro PracDocument11 pagesUv Spectro PracLungeloNo ratings yet
- KRIBIOLISA Anti-Trastuzumab ELISA Validation - Ver 1 0 Validation FileDocument3 pagesKRIBIOLISA Anti-Trastuzumab ELISA Validation - Ver 1 0 Validation FileKRISHGEN BIOSYSTEMSNo ratings yet
- Concentration vs. Absorbance: 1. Standard CurveDocument2 pagesConcentration vs. Absorbance: 1. Standard CurveHee MinNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy: John Kristoffer M. Japzon Ronell Q. LeeDocument36 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy: John Kristoffer M. Japzon Ronell Q. LeeIbrahim BouniNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Science (Hons) Applied ChemistryDocument20 pagesBachelor of Science (Hons) Applied Chemistryfaiqah hasbullah100% (1)
- Chem 133 Exer 7 Full ReportDocument7 pagesChem 133 Exer 7 Full ReportCharlez UmerezNo ratings yet
- Kurva Kalibrasi (Soal AAS) : JawabanDocument5 pagesKurva Kalibrasi (Soal AAS) : JawabanDoni DermawanNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - CalibrationDocument24 pagesChap 1 - CalibrationSENG LEE LIMNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Anion Analysis by Ion ChromatographyDocument6 pagesExperiment 3 Anion Analysis by Ion ChromatographyYuying FengNo ratings yet
- Kassandra Duran, Jose Encabo, Ryan Enriquez, Marion Agatha Esguerra, Raemee Hanna Facon Group 5 2B Medical Technology Biochemistry LaboratoryDocument5 pagesKassandra Duran, Jose Encabo, Ryan Enriquez, Marion Agatha Esguerra, Raemee Hanna Facon Group 5 2B Medical Technology Biochemistry LaboratoryRyan Karlo Cruz EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 CH317 2020 Fall Statistics Part4 GGclasssDocument21 pagesLecture1 CH317 2020 Fall Statistics Part4 GGclasssshanicejames7867No ratings yet
- Foster Cole 101230199 Malaïka Zarrouki 2021-01-29Document7 pagesFoster Cole 101230199 Malaïka Zarrouki 2021-01-29Cole FosterNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 10 CHM3100Document8 pagesLab Report Experiment 10 CHM3100Nurin BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Applied Sciences: Spectrochemical Methods of Analysis (CHM 580)Document9 pagesFaculty of Applied Sciences: Spectrochemical Methods of Analysis (CHM 580)Husna Insyirah Bt SamadNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry (Chm421) : Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesAnalytical Chemistry (Chm421) : Laboratory ReportNajmi NasirNo ratings yet
- pw1 PDFDocument10 pagespw1 PDFUlvi AgayevNo ratings yet
- pw1 PDFDocument10 pagespw1 PDFUlvi AgayevNo ratings yet
- Determining The Levels of Iron (Fe) by The Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometric MethodDocument9 pagesDetermining The Levels of Iron (Fe) by The Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometric MethodveronikaNo ratings yet
- Kelompok Bobot Sampel Ditimbang (G) Di Ad Abs SampelDocument4 pagesKelompok Bobot Sampel Ditimbang (G) Di Ad Abs SampelJilan QfNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument13 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectrosatikah100% (1)
- Lab 4 Report FinalDocument7 pagesLab 4 Report FinalSanjida IslamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 (Answers)Document14 pagesTutorial 2 (Answers)sudhanshu shekharNo ratings yet
- KELOMPOK 8 - 4B - Analisis FormalinDocument11 pagesKELOMPOK 8 - 4B - Analisis FormalinLidya Evangelista TampubolonNo ratings yet
- Analyzing The Statistical Error of Physical Chemistry Experimental DataDocument7 pagesAnalyzing The Statistical Error of Physical Chemistry Experimental DataNurin BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Analysis Tests With Answer KeyDocument5 pagesVolumetric Analysis Tests With Answer KeyHermanNo ratings yet
- USP Calcium CarbonateDocument2 pagesUSP Calcium CarbonateAnnastasia PiyogoNo ratings yet
- 01.ex Name Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron.Document4 pages01.ex Name Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron.Md Sohel RanaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Beer Lambert'S Law Experiment: Determing The Concentration of Unknown Asa SolutionsDocument5 pagesLab Report Beer Lambert'S Law Experiment: Determing The Concentration of Unknown Asa Solutionsumair saleemNo ratings yet
- AntacidDocument5 pagesAntacidÖznur DuranNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Spectrochemical Analysis: BE132P Instrumentation in Biological Engineering 1Document7 pagesExercise 1: Spectrochemical Analysis: BE132P Instrumentation in Biological Engineering 1Bernadette Virola CuevasNo ratings yet
- Zinc Acetate Oral SolutionDocument1 pageZinc Acetate Oral SolutionKasidit SornchaiNo ratings yet
- Aas - 2Document25 pagesAas - 2Ahmed FauziNo ratings yet
- Determination of Nitrate in Wastewater Using Sodium SalicylateDocument13 pagesDetermination of Nitrate in Wastewater Using Sodium SalicylateJuan ManuelNo ratings yet
- Prelab QuestionsDocument9 pagesPrelab QuestionsLexNo ratings yet
- Method For Testing Trace Heavy Metal Concentration in Industrial Wastewater by GF AADocument6 pagesMethod For Testing Trace Heavy Metal Concentration in Industrial Wastewater by GF AADaniel Camilo CarreñoNo ratings yet
- Al-Quds UniversityDocument7 pagesAl-Quds UniversityShahd Abu SnenehNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Determination of Lead in Anchovies by Cold Vapour Generation Atomic Absorption SpectrometryDocument31 pagesExperiment 3: Determination of Lead in Anchovies by Cold Vapour Generation Atomic Absorption SpectrometrymanurihimalshaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry 7aDocument9 pagesAnalytical Chemistry 7aGarfield SmithNo ratings yet
- Water Photometric Analysis PDFDocument40 pagesWater Photometric Analysis PDFعادل الحمدي0% (1)
- Supervisor: Saleh Suleiman Chem426 Name: Lina Abukwik ID Number:1171067Document9 pagesSupervisor: Saleh Suleiman Chem426 Name: Lina Abukwik ID Number:1171067lina kwikNo ratings yet
- Chapter UV-VIS - ProblemDocument1 pageChapter UV-VIS - ProblemNguyễn Hoàng QuânNo ratings yet
- Method Validation For Analysis of Nickel IN Water/Waste Water Samples Using AasDocument10 pagesMethod Validation For Analysis of Nickel IN Water/Waste Water Samples Using AasnarendraNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis of UV-Vis SpectrosDocument15 pagesQuantitative Analysis of UV-Vis SpectrosSalwa KamiliaNo ratings yet
- Materi - 2 - Atomic AbsorptionDocument51 pagesMateri - 2 - Atomic AbsorptionSalwa KamiliaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis of UV-Vis SpectrosDocument15 pagesQuantitative Analysis of UV-Vis SpectrosSalwa KamiliaNo ratings yet
- Materi - 2 - Atomic AbsorptionDocument51 pagesMateri - 2 - Atomic AbsorptionSalwa KamiliaNo ratings yet