Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Batch Fermentation in Batch Fermentation, The Sterile Growth Medium Is Inoculated With The Appropriate
Uploaded by
ShanmugapriyaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Batch Fermentation in Batch Fermentation, The Sterile Growth Medium Is Inoculated With The Appropriate
Uploaded by
ShanmugapriyaCopyright:
Available Formats
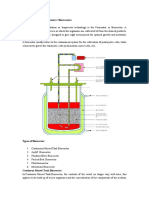
Batch fermentation
In batch fermentation, the sterile growth medium is inoculated with the appropriate
microorganisms, and the fermentation proceeds without the addition of fresh growth medium.
(1) The composition of culture medium, the concentration of microorganisms, the internal
chemical composition of the microorganisms and the amount of metabolite are all change
during fermentation. (2) All 6 phases of bacterial growth cycle are observed.
Fed-Batch fermentation
In fed-batch fermentation, fresh growth medium is added continuously during fermentation,
and no growth medium is removed until the end of the process.(1) The continuous addition of
medium prolongs both the log and stationary phases, thereby increasing the biomass and the
amount of metabolites. (2) However, microorganisms in stationary phase often produce
proteolytic enzymes (proteases) to degrade proteins. (3) A fed-batch fermentation strategy can
increase the yield from 25% to more than 1,000% compared with batch fermentation.
III. Continuous fermentation
In continuous fermentation, fresh growth medium is added continuously during fermentation,
but there is also continuous removal of an equal volume of medium containing suspended
microorganisms.(1) A steady-state condition of the total number of cells and the total volume in
the bioreactor is maintained. (2) A single reaction can be maintained for a much longer period.
(3) However, potential drawbacks are loss recombinant plasmid constructs in some cells,
difficulty in maintenance of an industrial scale and variation from batch to batch.
the advantages of fed batch mode of fermentation.
• production of high cell densities due to extension of working time (particularly important in the production of
growth-associated products)
• controlled conditions in the provision of substrates during the fermentation, particularly regarding the
concentration of specific substrates as for ex. the carbon source
• control over the production of by-products or catabolite repression effects due to limited provision of substrates
solely required for product formation
Define fluidized bed reactor
• A fluidized bed reactor (FBR) is a type of reactor device that can be used to carry out a variety of multiphase
chemical reactions.
• Advantages of fluidized bed reactor
• 1. Good mixing
• 2. Good uniformity of temperature
• 3. Catalyst can be continuously regenerated with the use of an auxiliary loop
• Disadvantages of fluidized bed reactor
• 1. Bed-fluid mechanics not well known
• 2. Severe agitation can result in catalyst destruction and dust formation
• 3. Uncertain scale-up
27. Define Recycle stream
A process stream that returns material from downstream of a process unit back to the process unit.
28. Define bypass stream
It is a stream that skips one or more stages of the process and goes directly to another down stream stage.
29. Define Purge Stream
Purge stream is a bled off to remove an accumulation of inerts or unwanted material that might otherwise buildup in the
recycle stream.
PACKED BED REACTOR
A packed bed is a hollow tube, pipe, or other vessel that is filled with a packing material. The packing can be randomly filled
with small objects like Raschig rings or else it can be a specifically designed structured packing. Packed beds may also contain
catalyst particles or adsorbents such as zeolite pellets, granular activated carbon, etc. The purpose of a packed bed is
typically to improve contact between two phases in a chemical or similar process. Packed beds can be used in a chemical
reactor, a distillation process, or a scrubber, but packed beds have also been used to store heat in chemical plants. In this
case, hot gases are allowed to escape through a vessel that is packed with a refractory material until the packing is hot. Air or
other cool gas is then fed back to the plant through the hot bed, thereby pre-heating the air or gas feed.
Advantages of packed bed reactor
1. High conversion per unit mass of catalyst 2. Low operating cost 3. Continuous operation
Disadvantages of packed bed reactor
1. Undesired thermal gradients may exist 2. Poor temperature control 3. Channeling may occur 4. Unit may be difficult to
service and clean
You might also like
- Fermentation Process: Key Components and Types of BioreactorsDocument114 pagesFermentation Process: Key Components and Types of BioreactorsyoganandaNo ratings yet
- Process Validation ProtocolDocument31 pagesProcess Validation ProtocolMangesh Parulekar93% (14)
- Types of Fermenters & Types of BioreactorsDocument24 pagesTypes of Fermenters & Types of BioreactorsMoaz Fiaz80% (5)
- Best Practice For Pilot Plant LayoutDocument10 pagesBest Practice For Pilot Plant LayoutRashesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Fermentors and BioreactorsDocument16 pagesDifferent Types of Fermentors and BioreactorsJaison JeevanandamNo ratings yet
- Batch and Semi-batch Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandBatch and Semi-batch Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Bioreactor and SterilizationDocument22 pagesBioreactor and SterilizationMuhd Shukri100% (2)
- Types of Chemical ReactorsDocument7 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactorsLyka BalmesNo ratings yet
- Fermentation Industries ReportDocument13 pagesFermentation Industries Reportamoeba_iitkgpNo ratings yet
- Ethyl Benzene Plant DesignDocument31 pagesEthyl Benzene Plant DesignRohit Kakkar100% (13)
- Fermenter DesignDocument31 pagesFermenter DesignV0% (1)
- Catalyst in Basic OleochemicalDocument10 pagesCatalyst in Basic OleochemicalwinwinNo ratings yet
- Techno-Economic Feasibility Report On Production of Methyl Ester Sulfonate From Palm OilDocument352 pagesTechno-Economic Feasibility Report On Production of Methyl Ester Sulfonate From Palm OilvpsrpuchNo ratings yet
- Selective Hydrogenation of Methyl Acetylene and Propadiene in An IndustrialDocument7 pagesSelective Hydrogenation of Methyl Acetylene and Propadiene in An IndustrialAdrian Fernandez BelloNo ratings yet
- 1.1 INTRO ProcessDocument43 pages1.1 INTRO ProcessEreenNo ratings yet
- Fermentation SystemsDocument40 pagesFermentation SystemsLolly AntillonNo ratings yet
- Zain Ahmed Siddiqee Ce - E07 - 103Document17 pagesZain Ahmed Siddiqee Ce - E07 - 103zainsiddiqee80% (10)
- TOPIC 5 - Types of BioreactorDocument35 pagesTOPIC 5 - Types of BioreactorfadhilahmadNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic Fixed-Bed Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandAdiabatic Fixed-Bed Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Design of Cumene Producing PlantDocument57 pagesDesign of Cumene Producing PlantAylin Uçar88% (17)
- Batch Reactor Design and PerformanceDocument16 pagesBatch Reactor Design and Performancechisom100% (1)
- Bioreactor: ECH 3201 Biochemical EngineeringDocument26 pagesBioreactor: ECH 3201 Biochemical EngineeringWazif ZakwanNo ratings yet
- Bioreactor 2020 PPT PDFDocument76 pagesBioreactor 2020 PPT PDFAbrar Ali Sitab100% (3)
- 2A BioreactorDocument18 pages2A Bioreactortehreem iftikharNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document32 pagesLecture 6Neywa RasliNo ratings yet
- Bioreactor types for products of microbial, plant and Animal originDocument45 pagesBioreactor types for products of microbial, plant and Animal origint.a.m.cooldarkboyNo ratings yet
- Batch ReactorDocument3 pagesBatch ReactorNicole Ann KimmayongNo ratings yet
- Bubble Column Fermenter/BioreactorDocument9 pagesBubble Column Fermenter/BioreactorLouellaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Product Manufactured by Using BioreactorDocument29 pagesIndustrial Product Manufactured by Using BioreactorVishwanath Hebbi0% (1)
- Ferment orDocument9 pagesFerment ortripsNo ratings yet
- Bioreactor (Introduction) Lec 1-2Document26 pagesBioreactor (Introduction) Lec 1-2mahi mridulaNo ratings yet
- BioreactorsDocument32 pagesBioreactorskhadeeja vjfndnNo ratings yet
- InBt121 Module 2Document127 pagesInBt121 Module 2Dylene EstremosNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-2Document27 pagesUnit 5-2tejasribalsuNo ratings yet
- Reactors1 33Document2 pagesReactors1 33Mourad kharbachNo ratings yet
- I. Batch Reactor: Ancheta, Nicole Ann KDocument4 pagesI. Batch Reactor: Ancheta, Nicole Ann KNicole Ann KimmayongNo ratings yet
- Reactors1 31Document2 pagesReactors1 31Mourad kharbachNo ratings yet
- Chemical Product and Process Design: Dr. Aprilina Purbasari, ST, MTDocument32 pagesChemical Product and Process Design: Dr. Aprilina Purbasari, ST, MTnurfadilla raufNo ratings yet
- Bioreactors LatestDocument34 pagesBioreactors LatestSyeda KazmiNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Bioreactor Design 1Document31 pages2.5 Bioreactor Design 1Astra BeckettNo ratings yet
- KULIAH TEKNOLOGI BIOKIMA 10 NOVEMBER 2012Document51 pagesKULIAH TEKNOLOGI BIOKIMA 10 NOVEMBER 2012soni_abdullahNo ratings yet
- BIOREACTOR DESIGNDocument9 pagesBIOREACTOR DESIGNVignesh KNo ratings yet
- Fermentors Types and Design 2015Document23 pagesFermentors Types and Design 2015NJOKU VERONICA CHIZOBANo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Unit-2Document17 pagesRenewable Energy Unit-2Sachin ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Fermentation: TechnologyDocument7 pagesFermentation: TechnologyfestagjakovaNo ratings yet
- Module-2 NotesDocument41 pagesModule-2 NotessanemsinoritaNo ratings yet
- Types of Reactor2Document4 pagesTypes of Reactor2Aleem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Visual Encyclopedia of Chemical Engineering Bioreactors: FermentersDocument13 pagesVisual Encyclopedia of Chemical Engineering Bioreactors: FermentersVanNo ratings yet
- Introduction & FundamentalDocument4 pagesIntroduction & FundamentalsugieebakiNo ratings yet
- 6aerobic Fludised Bed BioreactorDocument5 pages6aerobic Fludised Bed Bioreactorsneha raphelNo ratings yet
- Fermentation TechnologyDocument14 pagesFermentation TechnologyUmarNo ratings yet
- Satynarayana ExtractionDocument16 pagesSatynarayana ExtractionBalaji Prasanna KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of ReactorsDocument16 pagesTypes of Reactorsmunding21No ratings yet
- Figure 1: Labelled Diagram of Batch Stirred-Tank ReactorDocument4 pagesFigure 1: Labelled Diagram of Batch Stirred-Tank Reactorfareeha saeedNo ratings yet
- Solid State Fermentation: With Bioreactor DesignsDocument25 pagesSolid State Fermentation: With Bioreactor DesignsHarshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Waste in ReactorsDocument4 pagesWaste in ReactorsjamesNo ratings yet
- Stirrer Batch ReactorDocument4 pagesStirrer Batch ReactorCik Tiem NgagimanNo ratings yet
- Bio EnergyDocument9 pagesBio EnergySanjayvadamudulaNo ratings yet
- Study and Improvement in Operations of Chemical Plant: Guide: Shri. Mahesh DhawalikarDocument68 pagesStudy and Improvement in Operations of Chemical Plant: Guide: Shri. Mahesh DhawalikarPrathamesh NaikNo ratings yet
- Types of Bioreactors for FermentationDocument4 pagesTypes of Bioreactors for FermentationRamya TeddyNo ratings yet
- BioreactorDocument3 pagesBioreactorSTAFF JINNAH COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Sistem Bioreaktor2Document35 pagesSistem Bioreaktor2Faraliza Hassan ShokriNo ratings yet
- Biogas DigestersDocument4 pagesBiogas DigestersAnoop ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Biotransformation 111201084539 Phpapp02Document46 pagesBiotransformation 111201084539 Phpapp02thakur1989No ratings yet
- ADVANCED CHEMICAL REACTION FLUIDIZED BED BIOREACTORDocument16 pagesADVANCED CHEMICAL REACTION FLUIDIZED BED BIOREACTORFarisRazzakNo ratings yet
- Bioreactor Design and Operation ReportDocument15 pagesBioreactor Design and Operation ReportAtif MehfoozNo ratings yet
- Types of FermenterDocument24 pagesTypes of FermenterANJALI100% (2)
- What Is Real-Time PCR?Document34 pagesWhat Is Real-Time PCR?ShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Resveratrol Enhances Mitomycin C Effects in Colorectal Cancer CellsDocument8 pagesResveratrol Enhances Mitomycin C Effects in Colorectal Cancer CellsShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Advances in Membrane Slurry Reactors For HeterogenDocument7 pagesAdvances in Membrane Slurry Reactors For HeterogenShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Ghasem I An 2020Document11 pagesGhasem I An 2020ShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Bubble Column Reactor: Presented byDocument19 pagesPresentation On Bubble Column Reactor: Presented byShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- DNA Manipulation TechniquesDocument39 pagesDNA Manipulation TechniquesShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Abstract Design Circle Bubble PowerPoint Templates WidescreenDocument3 pagesAbstract Design Circle Bubble PowerPoint Templates WidescreenShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Bokeh Blue Background PowerPoint Templates WidescreenDocument3 pagesBokeh Blue Background PowerPoint Templates WidescreenandrianikinoyNo ratings yet
- Waves of Red PowerPoint Templates WidescreenDocument3 pagesWaves of Red PowerPoint Templates WidescreenShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Polymers: The Use of Natural Polymers in Tissue Engineering: A Focus On Electrospun Extracellular Matrix AnaloguesDocument32 pagesPolymers: The Use of Natural Polymers in Tissue Engineering: A Focus On Electrospun Extracellular Matrix AnaloguesShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Linker, AdaptorsDocument25 pagesLinker, AdaptorsShanmugapriya100% (1)
- GE6757 - Total Quality Management PDFDocument40 pagesGE6757 - Total Quality Management PDFSathish Kumar BaskarNo ratings yet
- Superconducting Magnetic Energy Storage: Presented By-Tanvir Ahmed ToshonDocument20 pagesSuperconducting Magnetic Energy Storage: Presented By-Tanvir Ahmed ToshonAdil KhanNo ratings yet
- Lead Acid, Lithium Iron, Fuel CellDocument48 pagesLead Acid, Lithium Iron, Fuel CellShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument17 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of ReactorsDocument39 pages4 Types of ReactorsShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Collagen: Applications of A Natural Polymer in Regenerative MedicineDocument15 pagesCollagen: Applications of A Natural Polymer in Regenerative MedicineShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Insight and Entrepreneurship: The 5 C's of Insight DevelopmentDocument10 pagesInsight and Entrepreneurship: The 5 C's of Insight DevelopmentShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Polymers: Recent Advances in Natural Gum-Based Biomaterials For Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: A ReviewDocument38 pagesPolymers: Recent Advances in Natural Gum-Based Biomaterials For Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: A ReviewShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Lec 6Document12 pagesLec 6ShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- BT Biotechnology: Section 1: Engineering MathematicsDocument3 pagesBT Biotechnology: Section 1: Engineering MathematicsNishant ShadeNo ratings yet
- New Gold Nanoparticle Probes For Target Identification of Bioactive Small MoleculesDocument3 pagesNew Gold Nanoparticle Probes For Target Identification of Bioactive Small MoleculesShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Lec 25Document15 pagesLec 25ShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Lec 23Document15 pagesLec 23ShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Lec21 IBEDocument9 pagesLec21 IBEShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Lec 29Document13 pagesLec 29ShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Lec 24Document16 pagesLec 24ShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Lec 28Document12 pagesLec 28ShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Lec 26Document8 pagesLec 26ShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Lec 27Document13 pagesLec 27ShanmugapriyaNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL ENGINEERING PROBLEMSDocument5 pagesCHEMICAL ENGINEERING PROBLEMSAbu Bakr Abdul MajeedNo ratings yet
- EnnnDocument9 pagesEnnnSajid AliNo ratings yet
- PIC, PID Control 2Document8 pagesPIC, PID Control 2Ermias NigussieNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Oxidation Into Nitrous Oxide Over Mn-Bi-Al Catalyst I Pokrovskaya Et Al Chem Eng J 2003 PDFDocument8 pagesAmmonia Oxidation Into Nitrous Oxide Over Mn-Bi-Al Catalyst I Pokrovskaya Et Al Chem Eng J 2003 PDFjuan davidNo ratings yet
- Final Thesis BabarDocument107 pagesFinal Thesis BabarAram Nasih Muhammad0% (1)
- Industri Klor AlkaliDocument20 pagesIndustri Klor AlkaliYovitaAyuningtyasNo ratings yet
- FTPDocument5 pagesFTPSurendar Vejayan100% (1)
- Semi-Batch Reactor Design EquationsDocument22 pagesSemi-Batch Reactor Design EquationsMelgi159100% (1)
- Empirical Modeling of Urea Synthesis Chemical EquilibriaDocument4 pagesEmpirical Modeling of Urea Synthesis Chemical EquilibriaRungrawin NgamkhumNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow ReactorDocument12 pagesPlug Flow Reactorindustries pétrochimiquesNo ratings yet
- CPE603 GuideDocument6 pagesCPE603 GuideainmnrhNo ratings yet
- Green Methanol Production Process From Indirect CO2Document57 pagesGreen Methanol Production Process From Indirect CO2Melinda FischerNo ratings yet
- Ravindran A TH 1986Document18 pagesRavindran A TH 1986YovaAndelaSariNo ratings yet
- Bioprocess Engineering QuestionsDocument13 pagesBioprocess Engineering QuestionsPalanisamy Selvamani100% (1)
- Engineering Softwares Used in The Food Engineering EducationDocument13 pagesEngineering Softwares Used in The Food Engineering Educationlhphong021191No ratings yet
- Lectcture 3 Addtinal Materials On StressDocument113 pagesLectcture 3 Addtinal Materials On StressNegese TeklearegayNo ratings yet
- CSTR SeriesDocument3 pagesCSTR SeriesAbdoul RahimNo ratings yet
- Reactor Design (I) : Chemical IdentityDocument5 pagesReactor Design (I) : Chemical Identityنزار الدهاميNo ratings yet
- Heuristic Design of Reaction/Separation ProcessesDocument8 pagesHeuristic Design of Reaction/Separation ProcessesAndrea VittoNo ratings yet
- Pre GATE 2018 2nd Test Question PaperDocument20 pagesPre GATE 2018 2nd Test Question PaperPANKAJ AGRAHARINo ratings yet
- Adiabatic Reactor 2Document11 pagesAdiabatic Reactor 2luis manuel peñalver maldonadoNo ratings yet
- AM Technology: Flow ReactorsDocument4 pagesAM Technology: Flow ReactorsShrinivas JahagirdarNo ratings yet
- L9-Tubular Flow ReactorDocument20 pagesL9-Tubular Flow ReactorCik Tiem Ngagiman82% (11)