Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Critical Angle and Total Internal Reflection
Uploaded by
Emeille Dicks0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pagesThis document discusses critical angle and total internal reflection. It defines critical angle as the angle at which light rays starting reflecting back into a medium at the boundary with another medium. Total internal reflection occurs when light rays travel from a slower to a faster medium and the incident angle is greater than or equal to the critical angle. The document lists applications of total internal reflection such as fiber optics, periscopes, binoculars, and cameras.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses critical angle and total internal reflection. It defines critical angle as the angle at which light rays starting reflecting back into a medium at the boundary with another medium. Total internal reflection occurs when light rays travel from a slower to a faster medium and the incident angle is greater than or equal to the critical angle. The document lists applications of total internal reflection such as fiber optics, periscopes, binoculars, and cameras.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pagesCritical Angle and Total Internal Reflection
Uploaded by
Emeille DicksThis document discusses critical angle and total internal reflection. It defines critical angle as the angle at which light rays starting reflecting back into a medium at the boundary with another medium. Total internal reflection occurs when light rays travel from a slower to a faster medium and the incident angle is greater than or equal to the critical angle. The document lists applications of total internal reflection such as fiber optics, periscopes, binoculars, and cameras.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Grade 11
CRITICAL ANGLE AND TOTAL
INTERNAL REFLECTION
Objectives
▪ explain ‘critical angle’ and ‘total internal
reflection’;
▪ relate critical angles to total internal
reflection;
▪ draw diagrams illustrating applications of
total internal reflection
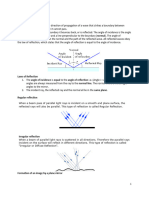
Demonstration
Questions
● At angle angle does the refraction in the block start
to change?
● How does the ray look after it reaches this angle?
Exercise
Explain how you think the material is able to
keep the light from spreading out of the
material at this angle
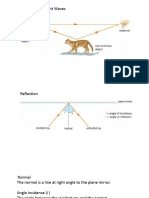
Critical Angle
Total Internal Reflection
▪ When light from one medium gets reflected
back into the medium at the boundary with
another medium
Critical Angle
▪ This is the angle which the light rays start to
reflect into the medium at the boundary with
another medium.
▪ Critical angle Formulae
� n = 1/sin c
■ n – refractive index
■ c – critical angle of the light ray
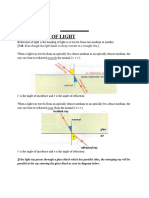
Conditions for Total
Internal Reflection
▪ The rays must be travelling from a slower
medium to a faster medium
▪ The incident angle must be greater than or
equal to the critical angle
Total Internal Reflection
in Industry
▪ Fibre Optics
▪ Periscopes
▪ Binoculars
▪ Cameras
Activity
▪ Highlight other areas which total internal
reflection is seen.
▪ Indicate how instruments which uses total
internal reflection can be improved.
You might also like
- Phy ADocument20 pagesPhy AShardul Singh 11 S1 DPSKNo ratings yet
- LightDocument23 pagesLightAmmar AdnanNo ratings yet
- WP4 Light WavesDocument16 pagesWP4 Light Waveswarona letangNo ratings yet
- Reflection & RefractionDocument50 pagesReflection & Refractionannette.geesiawan1No ratings yet
- Refraction of LightDocument6 pagesRefraction of LightlibertymarongaNo ratings yet
- Pusat Tuition Makrifat Chapter 6.2 F.4.PhyDocument6 pagesPusat Tuition Makrifat Chapter 6.2 F.4.PhyBazil BoliaNo ratings yet
- From The Physics ClassroomDocument7 pagesFrom The Physics ClassroomA.Benson0% (1)
- Total Internal ReflectionDocument24 pagesTotal Internal ReflectionasyiqqinNo ratings yet
- Light PUREDocument9 pagesLight PUREtalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- CH12 PPT 1Document49 pagesCH12 PPT 1kaungforgameNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Critical Angle and Refractive IndexDocument23 pagesRelationship Between Critical Angle and Refractive IndexNurul Syafiqah RoslanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Light PropagationDocument33 pagesChapter 2 Light PropagationM Hilman HakimNo ratings yet
- Light ReflectionandnrhehrDocument16 pagesLight ReflectionandnrhehrRaghav NegiNo ratings yet
- WP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2Document11 pagesWP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2matsweamogelang89No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Physics Les 7.5Document2 pagesGrade 7 Physics Les 7.5nomanabdullahkhan9No ratings yet
- Ray OpyicsDocument56 pagesRay OpyicsDhruv JainNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 658aaea043963Document14 pagesPHYSICS 658aaea043963Sumedha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Abhay Bharti PhysicsDocument14 pagesAbhay Bharti PhysicsRishi AnandNo ratings yet
- Total Internal ReflectionDocument18 pagesTotal Internal Reflectiontiwariakshay041No ratings yet
- 3.1 Light (1) (1) - 2Document10 pages3.1 Light (1) (1) - 2Dark VariantNo ratings yet
- Yogesh PhysicsDocument14 pagesYogesh PhysicsRishi AnandNo ratings yet
- CH12 PPT 1Document49 pagesCH12 PPT 1kaungforgameNo ratings yet
- 5.3 QUICK REVISION Total Internal ReflectionDocument51 pages5.3 QUICK REVISION Total Internal ReflectionAnna Latifah CammryNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 5: Light: Prepared By: Sharvinder SinghDocument28 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 5: Light: Prepared By: Sharvinder SinghSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics - Light: Notes and StuffsDocument42 pagesPhysics - Light: Notes and StuffsSijabuliso SibandaNo ratings yet
- Reflection of LightDocument8 pagesReflection of LightShivani ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Q4 Week 3 v2Document22 pagesPhysical Science Q4 Week 3 v2Balmon MonbalNo ratings yet
- Physical 3Document19 pagesPhysical 3Kirby SuarezNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Total Internal ReflectionDocument20 pagesPhysics Project On Total Internal Reflectiontyagihemant281No ratings yet
- 1 Reflection and RefractionDocument27 pages1 Reflection and RefractionAl John Paz FiedalanNo ratings yet
- Week 9 and 10-ODLDocument23 pagesWeek 9 and 10-ODLaymaNo ratings yet
- 53B LIGHT Refraction Total Internal ReflectionDocument20 pages53B LIGHT Refraction Total Internal ReflectionSiti Arbaiyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- 10 IlluminationDocument54 pages10 IlluminationYoo LeeNo ratings yet
- CDS Study Notes: Optics: LightDocument5 pagesCDS Study Notes: Optics: LightRANDOM VIDEOS 03No ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Physics ReflectionDocument15 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Physics ReflectionRaagul SaravanaKumarNo ratings yet
- Illumination FinalDocument26 pagesIllumination FinalAysha Akter UrmiNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project 2Document23 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project 2mallicksaad07No ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic, Nanded Micro Project Academic Year: 2020-2021Document12 pagesGovernment Polytechnic, Nanded Micro Project Academic Year: 2020-2021134 Bilolikar AdityaNo ratings yet
- RefractionDocument15 pagesRefractionStudent ResearchNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Geometric Optics PDFDocument36 pagesLecture 3 Geometric Optics PDFPuja KasmailenNo ratings yet
- Will All Light Be Refracted Lesser Than Critical Angle - Google SearchDocument1 pageWill All Light Be Refracted Lesser Than Critical Angle - Google SearchKuhendran RavandranNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectvvvDocument17 pagesPhysics ProjectvvvManish PatelNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument44 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightArman Akram100% (1)
- Notes: Introduction To Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument10 pagesNotes: Introduction To Light - Reflection & RefractionShardul SumantNo ratings yet
- 2 Reflection and RefractionDocument45 pages2 Reflection and RefractionAllyza Solomon100% (2)
- LightDocument6 pagesLightNishi ShahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedDocument40 pagesCHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedPriyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- Phy T1Document23 pagesPhy T1SivaSaiNo ratings yet
- Light NotesDocument8 pagesLight NotesSherazNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Answers: RememberingDocument21 pages7.1 Answers: RememberingDanny TNo ratings yet
- Reflection and RefractionDocument27 pagesReflection and RefractionEstelaBenegildoNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 1E Module 13 Light and OpticsDocument46 pagesPHYSICS 1E Module 13 Light and OpticsClaire G. MagluyanNo ratings yet
- What Is Reflection of Light?Document3 pagesWhat Is Reflection of Light?MD: Rabiul Awal ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Physics Project LWNKDocument16 pagesPhysics Project LWNKMeithaingam GonmeiNo ratings yet
- Light NotesDocument7 pagesLight NotesSadiqa ArooshNo ratings yet
- Physics Project - Thalha PDFDocument15 pagesPhysics Project - Thalha PDFThalha SNo ratings yet
- Archivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavDocument8 pagesArchivos PASCO - CA-6787 PDF Files - 3 Thermo., WavChess ManNo ratings yet
- Collimating a Newtonian Scientifically: Incorporating the Cave and Laser Telescope CollimatorsFrom EverandCollimating a Newtonian Scientifically: Incorporating the Cave and Laser Telescope CollimatorsNo ratings yet
- Data Representation: Grade 8Document16 pagesData Representation: Grade 8Emeille DicksNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light: Grade 11Document11 pagesReflection of Light: Grade 11Emeille DicksNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Science: Grade 8HDocument8 pagesEthics in Science: Grade 8HEmeille DicksNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Rays of LightDocument11 pagesReflection and Rays of LightEmeille DicksNo ratings yet
- Waves: Grade 11Document16 pagesWaves: Grade 11Emeille DicksNo ratings yet
- Pressure in Liquids: Grade 10Document10 pagesPressure in Liquids: Grade 10Emeille DicksNo ratings yet
- Refraction: Grade 11Document9 pagesRefraction: Grade 11Emeille DicksNo ratings yet
- Change in States: Grade 7Document14 pagesChange in States: Grade 7Emeille DicksNo ratings yet
- Temperature and The Environment: Grade 7Document13 pagesTemperature and The Environment: Grade 7Emeille DicksNo ratings yet
- Pressure: Grade 10Document7 pagesPressure: Grade 10Emeille DicksNo ratings yet
- Forms of Energy: Grade 10Document12 pagesForms of Energy: Grade 10Emeille DicksNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation and Power: Grade 10Document11 pagesEnergy Conservation and Power: Grade 10Emeille DicksNo ratings yet
- Rectification: Grade 11Document9 pagesRectification: Grade 11Emeille DicksNo ratings yet