Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Government Without Any Expectation of Direct Return in Benefit ". Ability To Pay. Taxed in The Same Way Without Any Discrimination
Uploaded by
yebegashet0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
153 views42 pagesThis document provides an overview of taxation. It defines what a tax is and lists objectives of taxation such as raising revenue and redistributing wealth. It discusses principles of taxation including equality, certainty, and productivity. It also describes proportional, progressive, regressive and digressive tax systems and how taxes can be shifted from one party to another.
Original Description:
Original Title
Ch-3(PFAT).pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of taxation. It defines what a tax is and lists objectives of taxation such as raising revenue and redistributing wealth. It discusses principles of taxation including equality, certainty, and productivity. It also describes proportional, progressive, regressive and digressive tax systems and how taxes can be shifted from one party to another.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
153 views42 pagesGovernment Without Any Expectation of Direct Return in Benefit ". Ability To Pay. Taxed in The Same Way Without Any Discrimination
Uploaded by
yebegashetThis document provides an overview of taxation. It defines what a tax is and lists objectives of taxation such as raising revenue and redistributing wealth. It discusses principles of taxation including equality, certainty, and productivity. It also describes proportional, progressive, regressive and digressive tax systems and how taxes can be shifted from one party to another.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 42
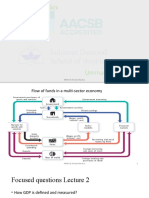
Chapter- 3
General overview of taxation
• A tax is “a compulsory charge imposed by the
Government without any expectation of direct return
in benefit ".
• The general public should be taxed according to their
ability to pay.
• The people in the same financial position should be
taxed in the same way without any discrimination.
• Taxes may be paid in cash or kind.
• A good tax system should not affect the ability and
willingness of the people to work, save and invest.
Cont...
• A sound tax system should contribute in the
economic development of a country.
• Hence, “Taxation should not be like killing the goose
that lays golden eggs".
General Characteristics of Tax:
1. Tax is a Compulsory Contribution:
• Any refusal in this regard leads to punishments.
2. Benefit is not the Basic Condition:
• For the payment of tax, there is no direct
return or quid proquo to the taxpayers.
Cont...
3. Personal Obligation:
• Tax imposes a personal obligation on the taxpayers.
4. Common Interest:
• It is used for the general and common benefit of the people as a whole.
5.Legal Collection
• It can be levied only by the government both central and state.
6.No Discrimination
• Tax is levied on all people without any discrimination.
7.Wide Scope
• Tax is levied not only on income but also on property and commodities.
8.Regular and periodical payment
Objectives of Taxation:
• Government levies and collects taxes for various objectives.
• These objectives may be specific or general.
Cont...
General Objectives:
• Government imposed taxes for three basic purposes viz., to
cover the cost of administration, maintaining law and order
in the country and for defence.
1. Raising Revenue:
• The basic purpose of taxation is raising revenue.
2. Removal of Inequalities in Income and Wealth:
• The welfare state aims at the removal of inequalities in
income and wealth.
3. Ensuring Economic Stability:
• Taxation affects the general level of consumption and
production.
Cont...
4. Reduction in Regional Imbalances
5. Capital Accumulation
6. Creation of Employment Opportunities
7. Preventing Harmful Consumption
8. Beneficial Diversion of Resources
9. Encouragement of Exports
10. Enhancement of Standard of Living
Cont...
Specific Objectives:
• To support the operation of that government itself.
• To influence the macro economic performance of the
economy.
• To carry out the functions of the government such as
national defence and providing government services.
• To redistribute resources between individuals or
classes in the population.
• To modify patterns of consumption or employment
within an economy.
Cont...
Principles of taxation:
• These principles are called as "Canons of Taxation".
• The following are the important canons of taxation.
I. Canons Advocated by Adam Smith
• Canon of Equality.
• Canon of Certainty.
• Canon of Convenience.
• Canon of Economy.
Cont...
II. Canons Advocated by Others:
• Canon of Productivity.
• Canon of Elasticity.
• Canon of Diversity.
• Canon of Simplicity.
• Canon of Expediency.
• Canon of Co-ordination.
• Canon of Neutrality.
Cont...
1. Canon of Equality:
• A good tax system should be based on the ability to
pay of the people on the basis of income and wealth
or on the basis of consumption i.e luxury or necessity.
• All people should bear the public expenditure in
proportion to their respective abilities.
• Tax burden should be more on the rich than on the
poor.
2. Canon of Certainty:
• It means the time, amount and method of payment
should all be clear and certain.
Cont...
• This removes all uncertainties in the payment of tax
and ensures smooth functioning of the tax
department and the tax payer can adjust his income
and expenditures accordingly.
3. Canon of Convenience:
• The tax should be levied and collected in such a way
that is convenient to taxpayer.
4. Canon of Economy:
• It states that the minimum possible amount should
be spent on tax collection.
• The maximum part of the collection should be
brought to the Government treasury.
Cont...
II. Canons Advocated by Others:
1. Canon of Productivity:
• The tax system should be productive enough.
• It should encourage productive activity by
encouraging the people to work, save and invest.
2. Canon of Elasticity:
• The taxes should be flexible.
3. Canon of Diversity:
• There should be diversity in the tax system of the
country as direct and indirect taxes.
Cont...
• It should not depend upon one or two types of taxes
alone.
4. Canon of Simplicity:
• Tax system should be simple, easy and understandable
to the common man.
5. Canon of Expediency:
• Tax should be levied after considering all favourable and
unfavourable factors from different angles such as
economical, political and social.
6. Canon of Co-ordination:
• There should be a proper co-ordination between
different taxes imposed by various authorities.
Cont...
7. Canon of Neutrality:
• This principle stresses that the tax system should not
have any adverse effect.
• It shouldn’t create any deflationary or inflationary
effects in the economy.
Cont...
PROPORTIONAL, PROGRESSIVE AND REGRESSIVE TAX
SYSTEMS
• The tax systems may be summarized as follows:
-Proportional Tax System.
-Progressive Tax System.
-Regressive Tax System.
-Digressive(mild) Tax System
1. Proportional(Flat) Tax System:
• A proportional tax, also called a flat tax is a system.
Cont...
• Taxes all entities in a class typically either citizens or
corporations at the same rate.
• Flat tax system may arguably have most of the
benefits of a progressive tax.
• Usually the flat tax is proposed to kick in at a certain
income level or...
• To exempt income below that level..
• Advocates of a flat tax claim that it will end unfair
discrimination.
Cont...
• Most political parties that advocate the introduction
of a flat tax are on the right of the political spectrum.
• Those who oppose a flat tax claim that it will benefit
the rich at the expense of the poor.
• . “The system in which the rates of taxation remains
constant as the tax base changes".
Limitations of Proportional Tax System:
• Inequitable Distribution
• Inadequate Resources
• Inelastic in Nature
Cont...
Proportional tax system has the following advantages:
• It is simple in nature.
• It is uniformly applicable.
• It will avoid mistakes and drawbacks of progressive
tax system.
Progressive(Graduated) Tax System:
• The term progressive refers to the way the rate
progresses from low to high.
Cont...
• People with more income pay a higher percentage of
it in taxes.
• Progressivity of the income tax means that marginal
tax rates are generally higher than average rates.
• “A system in which rates of taxation would increase
with the increase in income”
The advantages of progressive tax system include the
following:
• Equality in Sacrifice
• Reducing the Inequalities of Income and Wealth
Cont...
• Economy
• Elastic
• Stabilising the Economy
Limitations of Progressive Tax System:
• Ideal Progression is Impossible
• Progressive Taxation -a Graduated Robbery
• Disincentive to Work
• Discourages Savings and Investments
• Shifts the Total Economic Production of Society
Cont...
Regressive Tax System:
• It is the system in which the rate of tax declines with the
increase in the income or value of property.
• It places more burden on those with lower incomes.
• Many taxes other than the income tax tend to be
regressive in practice.
• "The tax rate decreases as the tax base increases".
• It violates the principles of equity and social justice.
• Even non-income taxes can regressive relative to income.
Cont...
DIGRESSIVE TAX SYSTEM
• Under this system, the rate of tax is mildly progressive up to
a certain limit and thereafter it may be fixed at a flat rate.
Tax rate(y)
Tax Base (x)
Cont...
IMPACT, SHIFTING AND INCIDENCE OF TAX:
1. Impact of a Tax/Tax Impact
• It refers to the immediate / initial burden of a Tax on
the person who pays it in the first instance.
• Impact of the Tax is always on the person who is
responsible by law to pay the Tax.
2. Incidence of a Tax/Tax Incidence
• It refers to the final or ultimate resting place of the
burden of the Tax payment.
• It is a place where the Tax is finally collected.
Cont...
• Tax incidence refers to the person who ultimately bears
the money burden of a tax.
3. Shifting of Tax/Tax shifting
• It refers to the process by which the money burden of
a Tax is transferred from one person to another
person.
• The process of passing on the tax burden to the buyer
of goods by the seller of goods.
• To sum up, three concepts are involved in the process
of taxing:
Cont...
• A tax may be imposed on a person(Impact of tax)
• The tax may be transferred by the first person to a
second person(Shifting of tax)
• The tax may be ultimately borne by the second
person(Incidence of tax)
Classification of Taxes
• The following are the common dimensions to classify
Tax:
a) Based on Impact and Incidence of Tax
b) Based on Tax bases
Cont...
c) Based on Tax Determinant
d) Based on Number of Taxes
e) Based on sources of Taxes
a) Based on Impact and Incidence of tax
• On the basis of impact (immediate burden) and
incidence (ultimate burden) of tax.
1. Direct Taxes
• Direct Taxes are those taxes whose impact
(immediate burden) and incidence (ultimate
burden) fall on the same person.
Cont...
• They can not be shifted(passed on) to others.
• Some examples are Employment income tax,
Business income tax, Rental income tax, Interest
income tax, Capital gain tax, property tax, agricultural
income tax, transfer taxes(estate tax, inheritance tax,
gift tax) etc.
• The following are advantages of direct taxes:
a) They reduce inequalities in income and wealth.
b) They are certain.
c) They are economical.
Cont...
d)They are elastic.
e) They are equitable.
f) They create civic consciousness.
• The following are weaknesses of Direct Taxes:
a)They can be easily evaded.
b)They are unpopular.
c)They are inconvenient.
d)Disincentive to work ,save, and invest.
e)Limited scope.
2. Indirect Taxes:
• They are those taxes whose impact (immediate burden) and
incidence (ultimate burden) fall on different persons.
Cont...
• Some examples are VAT, TOT ,etc.
• The following are advantages of Indirect Taxes:
a) They are convenient and popular.
b) They can not be evaded.
c) They can be elastic.
d) They lead to social welfare.
e) They have wide coverage.
f) They can be progressive.
Cont...
• The following are weaknesses of Indirect Taxes:
a) They are uncertain.
b) They promote inflation.
c) They result in high administrative costs.
d) They discourage savings.
e) They do not create civic consciousness.
b) Based on Tax Bases
1. Income Taxes
• They are Direct Taxes which are levied on income of
individuals and Businesses.
Cont...
2. Property Taxes
• They are also Direct Taxes which are levied on
property of persons or Businesses such as on wealth,
land, estate, and inheritance.
3. Commodity/Expenditure Taxes
• They are indirect Taxes which are levied on goods
and services.
• Some examples are value added tax, turnover tax,
excise tax, import duty, export duty.......
Cont...
c) Based on Tax Determinant
1. Specific Taxes
• They are Taxes which are levied on goods and services at a
fixed amount based on their weight, size, quantity, or other
measurements other than the value of goods and services.
• In this case value of the goods and services is irrelevant.
• The main advantage of this type of tax is that it is easy to
levy and more convenient.
2. Ad-valorem Taxes
The word Ad-valorem is derived from a Latin word to say
“According to the value”
Cont...
• Whatever is the weight or size of the unit of goods
,the tax determinant is the value of the goods.
d) Based on number of Taxes:
1. Single Tax
• It is a tax that occurs in a system in which the Taxes
are levied only on one object, that is, on one class
of people.
• In single tax, there is only one tax base.
2. Multiple Taxes
They are Taxes whose tax bases are diversified.
Cont...
• Multiple tax system consists of many kinds of
taxes(Both direct and indirect)
e) Based on sources of Transaction
1.Domestic Taxes
2. International Taxes
Effects of Taxation:
• Now-a-days, revenue rising is not the only purpose of
taxation.
1. Effects of Taxation on Production:
Cont...
Taxation can influence the production of a nation by influencing four
basic factors. They are as follows:
• Ability to work, save and invest.
• Willingness to work, save and invest.
• Diversion or allocation of resources between industries and places.
• On the size of the industries.
2. Effects of Taxation on Distribution:
The effects of taxation on the distribution of income and wealth
among the different sections of the society, depends upon two
important factors. They are as below:
• Nature of Taxation
• Kinds of Taxes.
Cont...
3. Effects of Taxation on Consumption:
• Taxes increases the price of the taxed goods relative to
the prices of untaxed or lower taxed goods.
• Taxation influences the consumption as well. Such
influences can be studied on the following grounds:
1. Influence the Allocation of Resource of Individuals:
2. Effects of Taxation on Consumption and Employment:
3. Effects of Taxation on Consumption during Inflation
and Depression:
4. Regulatory Effect of Taxation on Consumption:
Cont...
• There are two forms of tax evasion. They are as
follows:
1. Suppression of income
2. Inflation of expenditure.
• Examples for Tax Evasion:
• The following are the examples for tax evasion:
• A trader makes a sale for Birr.20, 000 and does not
account it, in his books under sales. He is evading tax.
Cont...
• An individual lends his money of Birr.50, 000 to
another person at 20% interest per annum and does
not include this income in his total income.
• Under-invoicing of sales and inflation of purchases.
• A manufacturing business employs 30 workers but
include 2 more additional namesake workers (not in
actual) in the muster roles.
Cont...
Causes of Tax Evasion:
The following are the important causes for Tax evasion:
• Multiplicity of Tax Laws
• Complicated Tax Laws
• High Rates of Taxation
• Inadequate Information as to Sources of Tax Revenue
• Investment in Real Property
• Ineffective Tax Enforcement
• Deterioration of Moral Standards
Cont...
Remedies for Tax Evasion:
1. Thorough Overhauling of Tax Laws:
• Tax evasion is loose drafting of tax laws which contain
several loop-holes and weak points.
2. Reduction in Tax Rates:
• The rate of tax should be reduced to a reasonable
level.
3. Replacement of Sales Tax & Excise Duties with VAT:
• As the crosschecking is possible in the case of VAT, it
is more effective.
Cont...
Tax Evasion Vs Tax Avoidance
• Tax evasion – not paying taxes legally.
• “Tax evasion implies the activities involving an element of
deceit, mis-representation of facts, falsification of accounts
including down right fraud”.
• Taxpayer with a view to violate civil and criminal provisions
of the tax laws.
• It is a crime in almost all countries and subjects the guilty
party to fines or even imprisonment.
• It may be said that the tax evasion is tax avoidance by illegal
means.
• Tax evasion is against the law and is an unsocial act.
Cont...
4. Tax on Agricultural Income:
• Tax evasions can be avoided by taxing the agricultural
income at normal rates.
5. Maintenance of Proper Accounts:
6. Introduction of Expenditure Tax:
7. Tightening of Tax Enforcement:
Tax Avoidance:
• Avoidance is within the ambit of law.
• Avoidance is the legal exploitation of the tax regime
to one's own advantage.
Cont...
• “Escaping from the tax liability by using the available
loop-holes of the tax laws”.
• Thus, tax avoidance means legal minimisation of tax
burden by the taxpayers.
You might also like
- Chapter Three: International Taxation IssuesDocument39 pagesChapter Three: International Taxation Issuesembiale ayaluNo ratings yet
- TAXATION001Document31 pagesTAXATION001Boqorka AmericaNo ratings yet
- What Is TaxDocument31 pagesWhat Is TaxVaibhav AhujaNo ratings yet
- Tax System: BY Arpita Pali Prachi Jaiswal Mansi MahaleDocument30 pagesTax System: BY Arpita Pali Prachi Jaiswal Mansi MahaleSiddharth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument54 pagesChapter Twoyechale tafereNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument28 pagesPresentationLaurence SamonteNo ratings yet
- A, Traditional Tax System Prior To 1941-In The Axumite Kingdom, There Was A Practice of TraditionalDocument7 pagesA, Traditional Tax System Prior To 1941-In The Axumite Kingdom, There Was A Practice of Traditionalliya100% (1)
- Auditing I Chapter 2Document63 pagesAuditing I Chapter 2Yitera Sisay100% (1)
- Chapter-Six Accounting For General, Special Revenue and Capital Project FundsDocument31 pagesChapter-Six Accounting For General, Special Revenue and Capital Project FundsMany Girma100% (1)
- UNIT-2 Public Revenue: An Overview of PRDocument67 pagesUNIT-2 Public Revenue: An Overview of PRmelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Taxation and Corporate Decision MakingDocument18 pagesChapter Four: Taxation and Corporate Decision Makingembiale ayalu100% (1)
- Fiscal Federalism and Power of TaxationDocument37 pagesFiscal Federalism and Power of TaxationWagner Adugna100% (1)
- Accounting For Indirect TaxesDocument40 pagesAccounting For Indirect TaxesSabaa if100% (1)
- Acct II Chapter 4 EdDocument2 pagesAcct II Chapter 4 Edmubarek oumerNo ratings yet
- Company Accounting - Powerpoint PresentationDocument29 pagesCompany Accounting - Powerpoint Presentationtammy_yau3199100% (1)
- Creating Value Through Required ReturnDocument74 pagesCreating Value Through Required Returnriz4winNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Accounting For Public SectorDocument10 pagesChapter One Accounting For Public SectorFasil MillionNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Coby Harmon University of California, Santa Barbara Westmont CollegeDocument38 pagesPrepared by Coby Harmon University of California, Santa Barbara Westmont Collegee s tNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Principles of Accounting and Financial Reporting For State and Local Governments (SLGS)Document55 pagesChapter Two: Principles of Accounting and Financial Reporting For State and Local Governments (SLGS)Bilisummaa GeetahuunNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Valuation of Financial Instruments & Cost of CapitalDocument68 pagesChapter Three: Valuation of Financial Instruments & Cost of CapitalAbrahamNo ratings yet
- Nefas Silk Poly Technic College: Learning GuideDocument43 pagesNefas Silk Poly Technic College: Learning GuideNigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- AfPS&CS Ch-01Document10 pagesAfPS&CS Ch-01Amelwork AlchoNo ratings yet
- MidTerm Lesson Part 1Document34 pagesMidTerm Lesson Part 1ARMAN WAYNE ANGELESNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTING: Concepts & ConventionsDocument34 pagesACCOUNTING: Concepts & Conventionsmehul100% (11)
- Unit6 2-ValuationofPreferredandCommonStockDocument77 pagesUnit6 2-ValuationofPreferredandCommonStockHay JirenyaaNo ratings yet
- B ADocument69 pagesB ATegegn Zeleke100% (1)
- Calculate Terminal Cash FlowDocument9 pagesCalculate Terminal Cash FlowKazzandraEngallaPaduaNo ratings yet
- Course: Advanced Auditing: Course Code: Credit HoursDocument32 pagesCourse: Advanced Auditing: Course Code: Credit HoursEyayaw AshagrieNo ratings yet
- Develop Understanding of TaxationDocument14 pagesDevelop Understanding of Taxationnatanme794No ratings yet
- AccountDocument37 pagesAccountGaurang MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assi 1234Document19 pagesRisk Assi 1234Yonatan100% (1)
- Nefas Silk Poly Technic College: Learning GuideDocument20 pagesNefas Silk Poly Technic College: Learning GuideNigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 6 - Responsibility AccountingDocument1 pageTOPIC 6 - Responsibility AccountingAnthony OtiatoNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Financial Statements ExplainedDocument77 pagesConsolidated Financial Statements ExplainedMisganaw DebasNo ratings yet
- Liablities Provision and Contingences Suger FactoryDocument49 pagesLiablities Provision and Contingences Suger FactorynatiNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Taxation PrinciplesDocument29 pagesIntroduction to Taxation PrinciplesJunel MamarilNo ratings yet
- Principles of AccountingDocument28 pagesPrinciples of Accountingعادل اعظمNo ratings yet
- Rules of Sustainable Development: Hartwick Solow London School Safe Minimum Standards Daly'S Operational PrinciplesDocument5 pagesRules of Sustainable Development: Hartwick Solow London School Safe Minimum Standards Daly'S Operational PrinciplesnikhilNo ratings yet
- Definition, Nature & Scope of WCDocument12 pagesDefinition, Nature & Scope of WCAshish Gautam0% (1)
- FGE Chapterr 1 PPTXDocument53 pagesFGE Chapterr 1 PPTXDEREJENo ratings yet
- Discuss Briefly The Historical Developments of That Contributed For The Development of Operations ManagementDocument7 pagesDiscuss Briefly The Historical Developments of That Contributed For The Development of Operations ManagementEyayaw AshagrieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PartnershipDocument76 pagesChapter 4 PartnershipAmsaluNo ratings yet
- Income Tax PresentationDocument22 pagesIncome Tax PresentationItchigo KorusakiNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Introduction To TaxationDocument14 pagesCh. 1 Introduction To TaxationYousef M. Aqel100% (1)
- IFRS Ethiopia D1S3 Presentation and Disclosure 3Document69 pagesIFRS Ethiopia D1S3 Presentation and Disclosure 3Yalem Alemayehu100% (1)
- 3.1 Employment Income Tax Edited March 2021Document22 pages3.1 Employment Income Tax Edited March 2021Bimmer MemerNo ratings yet
- Intro. To Income Tax FTDocument52 pagesIntro. To Income Tax FTJOANA GRACE ALLORINNo ratings yet
- Ias 12Document33 pagesIas 12samrawithagos2002No ratings yet
- MNE Tax Strategies and International TaxationDocument17 pagesMNE Tax Strategies and International TaxationyebegashetNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument220 pagesAccountingKrissa FriasNo ratings yet
- GNFP CH 3Document41 pagesGNFP CH 3Bilisummaa GeetahuunNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Elements of Cost and Classification of CostDocument25 pagesCh-2 Elements of Cost and Classification of CostEruNo ratings yet
- Activity Based CostingDocument30 pagesActivity Based Costinghardik1302No ratings yet
- Current Liabilities and Contingencies: HapterDocument58 pagesCurrent Liabilities and Contingencies: Haptergellie mare floresNo ratings yet
- Tax For CorpDocument28 pagesTax For CorpNiki DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Corporate Income Taxation-Special CorporationDocument24 pagesCorporate Income Taxation-Special CorporationXyla Marie EstorNo ratings yet
- Current LiabilitiesDocument111 pagesCurrent LiabilitiesMikaela LacabaNo ratings yet
- Capital StructureDocument41 pagesCapital StructureRAJASHRI SNo ratings yet
- Cash Management ProceduresDocument9 pagesCash Management ProceduresNigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Types of TaxationDocument61 pagesCharacteristics and Types of TaxationYoseph KassaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income Taxes Accounting For Income TaxesDocument41 pagesAccounting For Income Taxes Accounting For Income TaxesankitmogheNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document19 pagesCH 2yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Modul PAIIDocument199 pagesModul PAIIyebegashet100% (1)
- Chapter Three Payroll Accounting 3.1. Importance of Payroll AccountingDocument11 pagesChapter Three Payroll Accounting 3.1. Importance of Payroll Accountingyebegashet100% (2)
- CH 5Document11 pagesCH 5yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Out LinesDocument2 pagesOut LinesyebegashetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document62 pagesChapter 7yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document8 pagesChapter 6yebegashetNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document9 pagesCH 3yebegashet67% (3)
- Brief History of Income Taxes in EthiopiaDocument31 pagesBrief History of Income Taxes in Ethiopiayebegashet100% (2)
- Chapter 5Document7 pagesChapter 5yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Ambo University: College of Business and EconomicsDocument40 pagesAmbo University: College of Business and Economicsyebegashet50% (2)
- Chapter 6Document8 pagesChapter 6yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document7 pagesChapter 8yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document62 pagesChapter 7yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document7 pagesChapter 5yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Tax Types PDFDocument11 pagesTax Types PDFyebegashetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document31 pagesChapter 4yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document31 pagesChapter 4yebegashetNo ratings yet
- ch-4 Public DebtDocument30 pagesch-4 Public DebtyebegashetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document7 pagesChapter 8yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Slides On VAT 1Document36 pagesSlides On VAT 1yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Meaning and Scope of Public FinanceDocument21 pagesChapter 2-Meaning and Scope of Public FinanceyebegashetNo ratings yet
- Slides VAT 2Document24 pagesSlides VAT 2yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Slides On The Ethiopian Tax System2Document26 pagesSlides On The Ethiopian Tax System2yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Public Spending TheoriesDocument35 pagesPublic Spending TheoriesyebegashetNo ratings yet
- Government Without Any Expectation of Direct Return in Benefit ". Ability To Pay. Taxed in The Same Way Without Any DiscriminationDocument42 pagesGovernment Without Any Expectation of Direct Return in Benefit ". Ability To Pay. Taxed in The Same Way Without Any DiscriminationyebegashetNo ratings yet
- Slides On Taxes and Corporate Decision MakingDocument21 pagesSlides On Taxes and Corporate Decision Makingyebegashet100% (1)
- MNE Tax Strategies and International TaxationDocument17 pagesMNE Tax Strategies and International TaxationyebegashetNo ratings yet
- TAXATIONDocument22 pagesTAXATIONPardeep Singh SainiNo ratings yet
- 4 Microeconomics PDFDocument29 pages4 Microeconomics PDFSenthil Kumar KNo ratings yet
- Key formulas for measuring macroeconomic activity, inflation, unemployment, GDP, fiscal and monetary policyDocument1 pageKey formulas for measuring macroeconomic activity, inflation, unemployment, GDP, fiscal and monetary policyshindehokaiiNo ratings yet
- Bridge Course in EconomicsDocument17 pagesBridge Course in EconomicsProfessor Tarun DasNo ratings yet
- Concepts Statement 5 - As AmendedDocument18 pagesConcepts Statement 5 - As AmendedDian AngeleneNo ratings yet
- Economics NotesDocument47 pagesEconomics NotesChaitra HiremathNo ratings yet
- Minimum Wage 2014-2015Document3 pagesMinimum Wage 2014-2015Anand ChinnappanNo ratings yet
- Projected Income Statement of Ayala Land IncorporationDocument2 pagesProjected Income Statement of Ayala Land IncorporationErika May RamirezNo ratings yet
- Personal Income Tax Under The New Regime and Old RegimeDocument4 pagesPersonal Income Tax Under The New Regime and Old RegimeAiswarya BNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 Accounting Equation Without AnswerDocument5 pagesQuiz 3 Accounting Equation Without AnswerHello Kitty100% (1)
- Std. X Ch. 1 Development. Notes (21-22)Document9 pagesStd. X Ch. 1 Development. Notes (21-22)YASHVI MODINo ratings yet
- MacroEconomics GDP ConceptsDocument14 pagesMacroEconomics GDP Conceptssaif ur rehmanNo ratings yet
- Partnership Operations: Accounting Cycle of A PartnershipDocument13 pagesPartnership Operations: Accounting Cycle of A Partnershipred100% (1)
- Activity No. 2 (Moredo) : Problem 1Document3 pagesActivity No. 2 (Moredo) : Problem 1Eloisa Joy MoredoNo ratings yet
- Cepuros Foods Malaysia: Finding The Secret Sauce For Growth Student Spreadsheet SupplementDocument7 pagesCepuros Foods Malaysia: Finding The Secret Sauce For Growth Student Spreadsheet SupplementSaurabh MahajanNo ratings yet
- 5 - Tax Rules For Individuals Earning Income Both From Compensation and From Self-EditedDocument5 pages5 - Tax Rules For Individuals Earning Income Both From Compensation and From Self-EditedKiara Marie P. LAGUDANo ratings yet
- Municipal Fishery Lots and Revenues Subject to ExecutionDocument5 pagesMunicipal Fishery Lots and Revenues Subject to ExecutioncharmssatellNo ratings yet
- Valix 17 20 MCQ and Theory Emp Ben She PDFDocument48 pagesValix 17 20 MCQ and Theory Emp Ben She PDFMitchie FaustinoNo ratings yet
- Prac Aud 2Document5 pagesPrac Aud 2Maria Carmela Morauda0% (2)
- Tax Question PaperDocument20 pagesTax Question PaperSAMAR SINGH CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- Shaminah 1-3Document47 pagesShaminah 1-3mulabbi brianNo ratings yet
- CPD Budget Analysis FY2022Document116 pagesCPD Budget Analysis FY2022Sifat ShahreenNo ratings yet
- Income Statement For The Year Ended, December, 31, 2016: Pt. ZaliaDocument4 pagesIncome Statement For The Year Ended, December, 31, 2016: Pt. ZaliaNofi Nurlaila0% (1)
- Final Ems Gr. 7 Lesson Plans Term 2 Week 1 102Document20 pagesFinal Ems Gr. 7 Lesson Plans Term 2 Week 1 102Anonymous gPhRqg391% (11)
- HddaDocument4 pagesHddaNguyen Ngoc Huyen TrinhNo ratings yet
- Time Series Data On ASI 1998-99 To 2007-08Document975 pagesTime Series Data On ASI 1998-99 To 2007-08AnthriqueNo ratings yet
- PT Mulia Perdana's Financial StatementsDocument20 pagesPT Mulia Perdana's Financial StatementsMulia Ayu FadillahNo ratings yet
- Cta - Eb - CV - 01388 - D - 2017mar15 - Ass 2Document28 pagesCta - Eb - CV - 01388 - D - 2017mar15 - Ass 2Le SonneNo ratings yet
- Case 02 FedEx UPS 2016 F1773XDocument10 pagesCase 02 FedEx UPS 2016 F1773XJosie KomiNo ratings yet
- Demissie Damite - SNNPDocument155 pagesDemissie Damite - SNNPTesfahun tegegnNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Joint and By-Product Costing SystemDocument8 pagesUnit 7: Joint and By-Product Costing SystemCielo PulmaNo ratings yet