Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Airport Lighting
Uploaded by
Santosh Khanal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
71 views41 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
71 views41 pagesAirport Lighting
Uploaded by
Santosh KhanalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 41
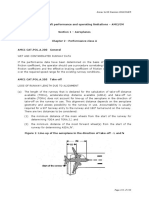
AIRPORT LIGHTING
FACTORS AFFECTING AIRPORT LIGHTING:
Airport classification
Amount of traffic
Availability of power
Nature of aircraft using the airport
Type of night operation plans
Type of landing surfaces provided
Weather condition, etc.
(contd.)
To achieve uniformity and to guide pilots for
unfamiliar airports, colours and general arrangement
of airport lights are standardized.
Airport lights are kept clean, well-maintained,
checked regularly for faulty bulbs and replacement.
Tough and laborious job, major airport contains
30,000 lights
Provision of emergency power supplies, which can
take over in seconds in case of any power failure.
ELEMENTS OF AIRPORT LIGHTING:
Airport beacon
Approach lighting
Apron and hangar lighting
Boundary lighting
Lighting of landing direction indicator
Lighting of wind direction indicator
Runway lighting
Taxiway lighting
Threshold lighting
1) AIRPORT BEACON:
Beacon- strong beam of light- used to indicate any
geographical location- situated slightly above the
horizontal- rotated to produce flashing light to an
observer.
It gives out white and green flashes in the horizontal
directions 180◦ apart. Flashes are visible for the pilot
from any direction of approach and it indicates the
approximate situation of an airport equipped for the
night operations.
Rotates at six revolutions per minute- mounted at top
of terminal building or hangar.
(contd.)
Obstruction not cleared yet- then separate tower is
provided for installation of rotating beacon.
Code beacon- indicates light provided sufficiently
high to clear all obstructions.
It consists of two 500 watts bulb with green colour
screen.
Continuously flashes a Morse code signal designating
the airport.
Airport Beacon Lighting:
APPROACH LIGHTING:
Before runway begins- sequence of high-intensity
lighting arrangement for a length of 900m.
Helps pilots to check if the aircraft is centered
correctly of not.
Gives way to touchdown zone lights from threshold of
the runway.
Normally mounted on pedestals-varying heights-to
accommodate any irregularities in ground- ensuring
the lights themselves are in level.
(contd.)
Arrangements adopted for approach lightings:
1) Calvert system
2) ICAO system
1) Calvert system:
Widely used in Europe and other parts of the world.
Developed by E.S.Calvert in Great Britain.
In this, there are six transverse rows of lights of
variable length placed at a c/c distance of 15om.
In this, the roll guidance is principally provided by the
transverse rows of lights.
2) ICAO system:
Known as centre-line configuration.
In this, there is only one crossbar 300m from the
threshold.
In this, the roll guidance is provided by bars 4.2m in
length, placed at 30m c/c on the extended centre-line
of the runway and a single crossbar 300m from the
threshold.
The 4.2m long bars consists of 5 closely spaced lights
to give the effect of continuous bar of light.
APRON AND HANGAR LIGHTING:
These areas for are flood lit for the convenience in
servicing and loading
Flood-lighting system: constitues a projector designed
to be arranged to illuminate a surface.
Mounted such a way that they do not cause glare in
the eyes of the pilots, passengers and service
personnel.
Recommendation: flood lights should be placed at a
height of not less than 12m above the pavement.
BOUNDARY LIGHTING:
Entire boundary of the airfield is provided with lights
at a c/c distance of about 90m with height of about
75cm from the ground.
If fence is provided along the boundary, then these
lights should be placed inside the fence at a distance of
about 3m.
For indicating hazardous approach, the boundary
lights are provided with red marker lights
LIGHTING OF LANDING DIRECTION
INDICATOR:
The landing direction indicator is illuminated with
suitable lighting arrangement so that the airport can
be used at night also.
LIGHTING OF WIND DIRECTION INDICATOR:
The wind direction indicator is illuminated by four
200 watts angle reflectors placed 1.8m above the top of
the cone for providing a continuous lighting at any
position of the cone.
This arrangement grants the use of wind direction
indicator at night and during bad weathers.
RUNWAY LIGHTING:
After crossing the threshold, the pilot must complete a
touchdown and roll out on the runway.
The planning of runway lighting is carried out in such
a way that the pilot gets enough information on
alignment, lateral displacement, roll and distance.
The lights are so arranged so that they form a visual
pattern which the pilot can interpret easily.
During night landings, flood lights were used in olden
days. But now runway edge lights are adopted.
(contd.)
Narrow gauge pattern- the most precise runway
alignment which is widely used.
It makes use of centre-line and touch down zone lights
for operations in very poor visibility.
Black hole effect: As the pilot crosses the threshold, and
continues to look along the centre-line, the principal
source of guidance, namely, the edge lights has moved
far to each side in the peripheral vision. As a result, the
central area appears black and the pilot is virtually flying
blind for the peripheral reference information.
(contd.)
This can be eliminated by adopting the narrow gauge
pattern of the runway lighting, the central portion gets
illuminated and the black hole effect is partly
eliminated.
The narrow gauge pattern forms a channel of light of
18m width up to 1140m from the threshold and beyond
this distance, the closely spaced lights are placed along
the centre-line of the runway extending up to the
other end of the runway.
(contd.)
All the lights provided on the runway are white in
colour and of flush type, i.e. they do not protrude
more than 1cm above the surface of pavement.
The runway edge lights are of elevated type and they
are white colour except for the last 400m if an
instrument runway facing the pilot which are of yellow
colour to indicte a caution zone.
TAXIWAY LIGHTING:
The pilots have to manoeuvre the aircrafts on a system
of taxiways to and from the terminal and hangar areas
either after landing or on the way to take off
The taxiway system is much complicated on large
airports and therefore it is necessary to provide
adequate lighting at night and at daytime when the
visibility is very poor.
Design considerations to be applied to the
visual aids for the taxiways:
For normal exits- centreline terminated at the edge of
the runway.
At taxiway intersections, the lights continue
across the intersection. They are placed at a
distance of 6m to 7.5m along the straight length
and 3m to 3.6m along the curves.
The complete route from the runway to the apron
should be easily identified.
The edge lights should not extend more than 75cm
above the pavement surface.
(contd.)
The exits from the runways should be so lighted that
the pilots are able to locate the exits 360m to 400m
ahead of the point of turn.
The intersection of taxiways and runways-taxiway
crossings should be clearly marked.
The lights on the tangent portion are placed not more
than 60m apart and the distance from the edge along
the curves and the intersections to facilitate easy
identification. The spacing varies from 6m for curve of
radius 4.5m to 60m for a curve of 300m.
(contd.)
There should be adequate guidance along the taxiway.
The taxiway edge lights are blue and the taxiway
centre lights are green.
The taxiway should be clearly identified so that they
are not confused with the runways.
THRESHOLD LIGHTING:
Identification of threshold- a major factor for decision
of the pilot to land or not to land
For this reason, the region near the threshold is given
with special lighting treatment.
At large airports: threshold is identified by a complete
line of green lights extending across the entire width
of the runway. They must be of semi-flash type, i.e.
protruding not more than 12cm above the surface.
(contd.)
At small airports, the threshold is identified by four
lights on each side of the threshold. They can be of
elevated type, i.e. protruding more than 12cm above
the surface.
The threshold lights in the direction if landing are
green and in the opposite direction, they are red to
indicated the end of the runway.
THANK YOU….
You might also like
- AtcDocument48 pagesAtcfrancis GodoyNo ratings yet
- Annexes 1 - 18Document26 pagesAnnexes 1 - 18MIKHAEL YERIKHONo ratings yet
- Important Components of An AirportDocument38 pagesImportant Components of An AirportRigil Kent RamosNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting CommunicationsDocument22 pagesAircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting CommunicationsMelissa Gonzalez TorresNo ratings yet
- ANNEX 16 - Environmental Protection (VolumeI)Document207 pagesANNEX 16 - Environmental Protection (VolumeI)Syahid MachedaNo ratings yet
- EAPPRI 1 2 RWY IncursionDocument90 pagesEAPPRI 1 2 RWY Incursioncsfekete1976No ratings yet
- IATA Cargo Handling Manual Implementation OverviewDocument35 pagesIATA Cargo Handling Manual Implementation OverviewMik AeilNo ratings yet
- OACI 10100Document44 pagesOACI 10100Pipiripi100% (1)
- Airport Operations Arrival/Departure Final PresentationDocument14 pagesAirport Operations Arrival/Departure Final PresentationSyeda Azka AliNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Runway LengthDocument43 pagesAircraft Runway LengthAgung TrianshariNo ratings yet
- V13 D03 1 PDFDocument45 pagesV13 D03 1 PDFFredy Camayo De La CruzNo ratings yet
- SI 8900-3.11, Check Pilot, Instructor and Supervisor Program PDFDocument39 pagesSI 8900-3.11, Check Pilot, Instructor and Supervisor Program PDFHerry HeryatnaNo ratings yet
- 2 DistancesDocument37 pages2 Distanceschhetribharat08No ratings yet
- ATSEP12 Aviation Law BookletDocument236 pagesATSEP12 Aviation Law BookletSiva Kumar100% (1)
- Airport Lighting Systems GuideDocument9 pagesAirport Lighting Systems GuideYosif ThiabNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Ground Handling ChecklistDocument2 pagesAircraft Ground Handling ChecklistFarell Ardyan100% (1)
- Icao Annex 14 - AerodromesDocument8 pagesIcao Annex 14 - AerodromesmrdnnmnNo ratings yet
- Physical Characteristics: Nov 23, 2021 ICAO Annex 14 Training Course 1Document74 pagesPhysical Characteristics: Nov 23, 2021 ICAO Annex 14 Training Course 1ho kong honNo ratings yet
- 3 ICAO Annex 14 Standards and Aerodrome Certification PDFDocument21 pages3 ICAO Annex 14 Standards and Aerodrome Certification PDFRorita CarolinaNo ratings yet
- Travel and Tourism Consultant DiplomaDocument7 pagesTravel and Tourism Consultant DiplomaAnushka SeebaluckNo ratings yet
- 009 BADA Aircraft Performance ModellingDocument68 pages009 BADA Aircraft Performance Modellingpsanford2No ratings yet
- Foca Guidance Material Information Om TMDocument364 pagesFoca Guidance Material Information Om TMd_zagorcaniNo ratings yet
- Air Traffic ControlDocument18 pagesAir Traffic ControlAshish Kumar SarangiNo ratings yet
- Airport Operations Manual: August 20, 2020Document73 pagesAirport Operations Manual: August 20, 2020hakan özcanNo ratings yet
- Bag tag identification and historyDocument11 pagesBag tag identification and historyAna Clara HortaNo ratings yet
- AIS to AIM Roadmap ExplainedDocument17 pagesAIS to AIM Roadmap ExplainedGIS SUL AIRPORTNo ratings yet
- IATA Airport Operations Diploma ProgrammeDocument4 pagesIATA Airport Operations Diploma ProgrammeRafael EichlerNo ratings yet
- CAP795 SMS Guidance To OrganisationsDocument24 pagesCAP795 SMS Guidance To OrganisationsAleš ŠtimecNo ratings yet
- Atm 1204-Chapter 2 (Aerodrome Control)Document64 pagesAtm 1204-Chapter 2 (Aerodrome Control)Anish KumarNo ratings yet
- Annex 17 - 9th Edition Amendment 12Document54 pagesAnnex 17 - 9th Edition Amendment 12junNo ratings yet
- Airport Parts 1B (GROUP 1)Document33 pagesAirport Parts 1B (GROUP 1)Benedict CarandangNo ratings yet
- Runway Lights and MarkingsDocument44 pagesRunway Lights and Markingscgsmile100% (4)
- Aerodrome MarkingsDocument3 pagesAerodrome MarkingslegopoonNo ratings yet
- Ipm P&G E11thDocument171 pagesIpm P&G E11thStefano WangNo ratings yet
- LOC Prevention Beyond The Control of Pilots PDFDocument36 pagesLOC Prevention Beyond The Control of Pilots PDFSergio Romero100% (1)
- Training: Innovative and Comprehensive Training Product SuiteDocument6 pagesTraining: Innovative and Comprehensive Training Product SuiteGourav DasNo ratings yet
- AOI 13 Airside Driving Training and Regulations of Airside Safety PDFDocument23 pagesAOI 13 Airside Driving Training and Regulations of Airside Safety PDFSatyendra PandeyNo ratings yet
- CANSO Standard of Excellence in Safety Management SystemsDocument44 pagesCANSO Standard of Excellence in Safety Management SystemsMirtha AngelesNo ratings yet
- Pilot RefDocument3 pagesPilot Refvikash_kumar_thakurNo ratings yet
- AIR TRAFFIC CONTROL (A Summary)Document11 pagesAIR TRAFFIC CONTROL (A Summary)Prinkesh BarodiyaNo ratings yet
- ATNS Aeronautical Information ManagementDocument8 pagesATNS Aeronautical Information ManagementDaba Cheikh WadeNo ratings yet
- Aviation Security Officer Job Description QJ10188Document3 pagesAviation Security Officer Job Description QJ10188Phyo ThantNo ratings yet
- Annex 14-Aerodromes FinalDocument71 pagesAnnex 14-Aerodromes FinalPorsche ChonthichaNo ratings yet
- AirportDocument18 pagesAirportRufaidaNo ratings yet
- BSP Dish Revision 23Document409 pagesBSP Dish Revision 23tediNo ratings yet
- Ahm TocDocument18 pagesAhm TocMik Aeil50% (2)
- FSF Runway Excursions ReportDocument235 pagesFSF Runway Excursions ReportGustavo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- IATA Meal CodesDocument1 pageIATA Meal CodesqueztalNo ratings yet
- Navigate Airside FacilitiesDocument55 pagesNavigate Airside FacilitiesSara Saad100% (1)
- 033 Objectives Flight Planning Monitoring PDFDocument24 pages033 Objectives Flight Planning Monitoring PDFSergey DNo ratings yet
- 8896-Met1Document41 pages8896-Met1lanhuong9No ratings yet
- Bird Strike Methodology PDFDocument22 pagesBird Strike Methodology PDFmjreddy036965No ratings yet
- Hand PDFDocument45 pagesHand PDFledelgado.tacv323350% (2)
- Lecture 7 - Global Positioning GpsDocument40 pagesLecture 7 - Global Positioning Gpszuliana100% (2)
- Runway LightingDocument47 pagesRunway LightingAr Varun Verma100% (1)
- Run Way LightingDocument16 pagesRun Way LightingMoudud Ul Islam AwanNo ratings yet
- Runway Lighting Requirements and Airport Lighting TypesDocument4 pagesRunway Lighting Requirements and Airport Lighting TypesfacedoneNo ratings yet
- Air Traffic Control and Airport Design UNIT 6Document44 pagesAir Traffic Control and Airport Design UNIT 6Prof L. OblisamyNo ratings yet
- Baggage Reconcilation ChartDocument9 pagesBaggage Reconcilation ChartSantosh KhanalNo ratings yet
- Amadeus PresentationDocument19 pagesAmadeus PresentationSantosh KhanalNo ratings yet
- All Aviation Abbreviations PDFDocument55 pagesAll Aviation Abbreviations PDFexpairtiseNo ratings yet
- Airimp IataDocument628 pagesAirimp IataSantosh KhanalNo ratings yet
- Apms - Asphalt Pavement Management SystemDocument20 pagesApms - Asphalt Pavement Management SystemBasukiNo ratings yet
- Design of Modern Airports - Seminar ReportDocument20 pagesDesign of Modern Airports - Seminar ReportAshish Anant50% (8)
- Aip LPPTDocument43 pagesAip LPPTJoão MartinhoNo ratings yet
- Flight Express: Cessna 210 CenturionDocument46 pagesFlight Express: Cessna 210 CenturionLucas KnightNo ratings yet
- VHHHDocument39 pagesVHHHKyleNo ratings yet
- A320 Characteristic Airport and Maintenance Planning PDFDocument429 pagesA320 Characteristic Airport and Maintenance Planning PDFJonathan NoriegaNo ratings yet
- NCAA Track and Field Rules 2014Document124 pagesNCAA Track and Field Rules 2014atpickerNo ratings yet
- Jeppview For Windows: General Information General InformationDocument6 pagesJeppview For Windows: General Information General InformationAfner Otniel100% (1)
- Loss of Runway Length Due To AlignmentDocument20 pagesLoss of Runway Length Due To Alignmentchhetribharat08No ratings yet
- NTSB Prelim Report On Gage Plane CrashDocument3 pagesNTSB Prelim Report On Gage Plane CrashOKCFOXNo ratings yet
- 2015 RoughnessDocument11 pages2015 Roughnessminhnv09No ratings yet
- FLIGHJT OPERATIONS Apostila-CompletaDocument104 pagesFLIGHJT OPERATIONS Apostila-CompletaTulioNo ratings yet
- Ground operations and safety rules for aircraftDocument91 pagesGround operations and safety rules for aircraftmuya78No ratings yet
- SignalsDocument11 pagesSignalsLlewellyn OliverNo ratings yet
- Apl-El Inewatt Airfield Lighting SolutionsDocument2 pagesApl-El Inewatt Airfield Lighting SolutionsRachid FRIDINo ratings yet
- Lebl ChartDocument100 pagesLebl ChartErlangga YudhaNo ratings yet
- GACAR Part 5 - SMSDocument37 pagesGACAR Part 5 - SMSweNo ratings yet
- Maintain aerodrome facilitiesDocument6 pagesMaintain aerodrome facilitiesZero RequiemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 Basco Batanes AirportDocument44 pagesChapter 1-3 Basco Batanes AirportLance Alviso100% (1)
- 3.2 Aerodrome Operator: Ref Recommendation Owner Implementation Date GuidanceDocument1 page3.2 Aerodrome Operator: Ref Recommendation Owner Implementation Date GuidanceCLIFFNo ratings yet
- 8 Optical Illusions Every Pilot Should Understand 3Document1 page8 Optical Illusions Every Pilot Should Understand 3rajivpatil11No ratings yet
- Doc9476 SMGCS PDFDocument89 pagesDoc9476 SMGCS PDFToni BaceanuNo ratings yet
- Ac121 2 8 (Rev 0) Level of Rescue and Fire Fighting Service Protection AvailableDocument7 pagesAc121 2 8 (Rev 0) Level of Rescue and Fire Fighting Service Protection AvailablepedatiNo ratings yet
- IOE MSc. Transportation: Old Questions of Second SemesterDocument8 pagesIOE MSc. Transportation: Old Questions of Second SemesterSwopnil KalikaNo ratings yet
- Pavement Types and FunctionsDocument13 pagesPavement Types and FunctionsRahul jichkarNo ratings yet
- Aerodrome Inspectors Workshop - FAADocument20 pagesAerodrome Inspectors Workshop - FAAVincent GrondinNo ratings yet
- Sae Technical Paper Series: Anita Teo, Kaushik Rajashekara, Jason Hill, and Brian SimmersDocument9 pagesSae Technical Paper Series: Anita Teo, Kaushik Rajashekara, Jason Hill, and Brian SimmersSteven SullivanNo ratings yet
- L-858 (Led)Document46 pagesL-858 (Led)Fabian FabNo ratings yet
- Vintage Airplane - Mar 1998Document36 pagesVintage Airplane - Mar 1998Aviation/Space History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Notice: Airport Noise Compatibility Program: Columbia Metropolitan Airport, SCDocument5 pagesNotice: Airport Noise Compatibility Program: Columbia Metropolitan Airport, SCJustia.comNo ratings yet