Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PPT 1 - Intro To Database System
Uploaded by
Ed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views41 pagesThis document provides an introduction to database systems and concepts over two chapters. It discusses the file-based approach versus the database approach, highlighting advantages like data independence with databases. The three-level ANSI SPARC architecture separates the conceptual, external and internal levels. Common data models include object-based and record-based for the conceptual level. Conceptual modeling involves constructing a model of enterprise information independently of implementation details.
Original Description:
Original Title
20201112141009_PPT 1 - Intro to Database System (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an introduction to database systems and concepts over two chapters. It discusses the file-based approach versus the database approach, highlighting advantages like data independence with databases. The three-level ANSI SPARC architecture separates the conceptual, external and internal levels. Common data models include object-based and record-based for the conceptual level. Conceptual modeling involves constructing a model of enterprise information independently of implementation details.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views41 pagesPPT 1 - Intro To Database System
Uploaded by
EdThis document provides an introduction to database systems and concepts over two chapters. It discusses the file-based approach versus the database approach, highlighting advantages like data independence with databases. The three-level ANSI SPARC architecture separates the conceptual, external and internal levels. Common data models include object-based and record-based for the conceptual level. Conceptual modeling involves constructing a model of enterprise information independently of implementation details.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 41
Introduction to Database System
Week 1 - Introduction to Database & Environment
Database System A Practical Approach to Design, Implemetation, and Management
Connolly, T., & Begg, C.
Chapter 1 & 2
Learning Outcome
At the end of this semester, the student should
be able to:
• Interpret business problems that can be
accommodated by database system
Sub Topics
• Introduction
• File-based Approach
• Database Approach
• Advantage and Disadvantage of DBMS
• Three Level ANSI SPARC architecture
• Data Models dan Conceptual Modelling
INTRODUCTION
Introduction
• The database is now such an integral part of our day-
to-day life that often we are not aware that we are
using one.
• A database application is simply a program that
interacts with the database at some point in its
execution.
• The use of a more inclusive database system as a
collection of application programs that interact with
the database together with the DBMS and the
database itself.
Introduction
• Database is the most important development
in the field of software engineering.
• Currently the database system is the
framework underlying the information system
and change the way the organization operates.
• Database technology has become an exciting
field to work on, such as algorithms for file
storage, file access, and query optimization.
Database Application
• Purchases from the supermarket
• Purchases using your credit card
• Booking a vacation with a travel agent
• Using the local library
• Taking out insurance
• Renting a DVD
• Using the Internet
• Studying at College
FILE-BASED APPROACH
Definition
• File-based systems were an early attempt to
computerize the manual filing system
that we are all familiar with.
• File-based system is A collection of
application programs that perform services
for the end-users, such as the production of
reports. Each program defines and manages
its own data.
Case Example
• The Sales Department is responsible for the
selling and renting of properties. For example,
whenever a client who wishes to offer his or her
property as a rental
approaches the Sales Department must complete
a particular form ( we show you in next slide) .
Example (cont)
Step 1
Source : Connoly & Begg (2015)
Example (cont)
Step 2
• With the assistance of the DP Department, the
Sales Department creates an information
system to handle the renting of property. The
system consists of three files containing
property, owner, and client details, as
illustrated in Figure in next slide. For simplicity,
we omit details relating to members of staff,
branch offices, and business owners.
Example (cont)
Figure for step 2
Source : Connoly & Begg (2015)
Example (cont)
Step 3
• Whenever a client agrees to
rent a property, a form with
the client and property
details is filled in by one of
the sales staff, as shown in
Figure 1.3. This form is
passed to the Contracts
Department, which
allocates a lease number
and completes the payment
and rental period details.
Source : Connoly & Begg (2015)
Example (cont)
Step 4
• Again, with the assistance of
the DP Department, the
Contracts Department creates
an information system to
handle lease agreements. The
system consists of three files
that store lease, property, and
client details, and that contain
similar data to that held by
the Sales Department, as
illustrated in Figure beside.
Source : Connoly & Begg (2015)
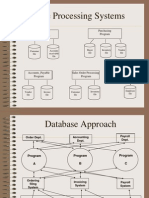
Example (cont)
Step 5
• File based processing of each department.
Source : Connoly & Begg (2015)
Limitation
• Separation and isolation of data
• Duplication of data
• Data dependence
• Incompatible file formats
• Fixed queries/proliferation of application
programs
DATABASE APPROACH
The Database
• Database is a shared collection of logically
related data and its description, designed to
meet the information needs of an
organization.
• A database is also defined as a self-describing
collection of integrated records.
Database Approach
• The approach taken with database systems, where
the definition of data is separated from the
application programs, is similar to the approach
taken in modern software development, where an
internal definition of an object and a separate
external definition are provided.
• One advantage of this approach, known as data
abstraction.
Definitions of Database
• Another expression in the definition of a
database that we should explain is
“logically related.” When we analyze the
information needs of an organization,
we attempt to identify entities, attributes, and
relationships.
Example
For example, Figure in next slide will shows an Entity–
Relationship (ER) diagram for part of the DreamHome case
study. It consists of :
•Six entities (the rectangles): Branch, Staff,
PropertyForRent, Client, PrivateOwner, and Lease;
•Seven relationships (the names adjacent to the lines): Has,
Offers, Oversees, Views, Owns, LeasedBy, and Holds;
•Six attributes, one for each entity: branchNo, staffNo,
propertyNo, clientNo, ownerNo, and leaseNo.
ERD
Source : Connoly & Begg (2015)
The DBMS
• DBMS is a software system that enables users to define,
create, maintain, and
control access to the database.
• DBMS facilities :
Allows DDL ( Data Definition Language)
Allows DML (Data Manipulation Language)
It provided controlled access to the database
Illustration of Database
Approach
Sumber: Conolly (2015)
Source : Connoly & Begg (2015)
(Database) Application
Program
• Application program is A computer program
that interacts with the database by issuing an
appropriate request (typically an SQL
statement) to the DBMS.
• Users interact with the database through a
number of application programs that are
used to create and maintain the database
and to generate information.
• We can identify five major components in the DBMS
environment: hardware, software, data, procedures,
and people
Components
of the DBMS
Environment
Source : Connoly & Begg (2015)
Database Application
Program (Now)
Source : Connoly & Begg (2015)
ADVANTAGE AND DISADVANTAGE
OF DBMS
Advantages
Source : Connoly & Begg (2015)
Disadvantages
• Complexity
• Size
• Cost of DBMSs
• Additional hardware costs
• Cost of conversion
• Performance
• Greater impact of a failure
THREE LEVEL
ANSI SPARC ARCHITECTURE
3 Level Architechture
Source : Connoly & Begg (2015)
Its consist of :
• External level, The users’ view of the database. This
level describes that part of the database that is
relevant to each user.
• Conceptual level, The community view of the
database. This level describes what data is stored in
the database and the relationships among the data.
• Internal level, The physical representation of the
database on the computer. This level describes how
the data is stored in the database.
Data Independence
Source : Connoly & Begg (2015)
DATA MODELS AND
CONCEPTUAL MODELLING
Data Models
• An integrated collection of concepts for describing
and manipulating data, relationships between data,
and constraints on the data in an organization.
• A data models can be thought of as comprising 3
components:
- a structural part
- a manipulative part
- a set of integrity constraints
Data Model (cont)
• There have been many data models
proposed in the literature. They fall into
three broad categories: object-based,
record-based, and physical data models. The
first two are used to describe data at the
conceptual and external levels, the third is
used to describe data at the internal level
Conceptual Modelling
Conceptual modeling or conceptual database
design is the process of constructing a model
of the information use in an enterprise that is
independent of implementation details, such
as the target DBMS, application programs,
programming languages, or any other physical
considerations.
Reference
Connolly, T., & Begg, C. (2015). Database
System A Practical Approach to Design,
Implementation, and Management 6th Edition.
Pearson
Thank You
You might also like
- ISYS6508 Database System: Week 1 Introduction To Database & EnvironmentDocument28 pagesISYS6508 Database System: Week 1 Introduction To Database & EnvironmentRapik HardiantoNo ratings yet
- ISYS6307 Data & Information Management: Database Development LifecycleDocument37 pagesISYS6307 Data & Information Management: Database Development LifecycleRahma RaniNo ratings yet
- 1 8 Database and Data ModellingDocument6 pages1 8 Database and Data ModellingnelisappawandiwaNo ratings yet
- cs3270 Lecture1 170313023931Document38 pagescs3270 Lecture1 170313023931Joshua MarquezNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Database Systems: Lesson 1: Introduction To DatabasesDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Database Systems: Lesson 1: Introduction To DatabasesNilupulee WasanaNo ratings yet
- C02 Data - Models WEEK 2 PDFDocument57 pagesC02 Data - Models WEEK 2 PDFAinil HawaNo ratings yet
- AMD - Lecture 01Document47 pagesAMD - Lecture 01My DataNo ratings yet
- Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument30 pagesDatabase System Concepts and ArchitectureAyush RathoreNo ratings yet
- Mit Database NotesDocument703 pagesMit Database NotesGrant DuncanNo ratings yet
- CORE CV Template 3Document4 pagesCORE CV Template 3anwarNo ratings yet
- CS6302 Notes PDFDocument126 pagesCS6302 Notes PDFrewop sriNo ratings yet
- FinalProject DescriptionDocument5 pagesFinalProject DescriptionBhanu ReddyNo ratings yet
- Database SlidesDocument23 pagesDatabase SlidesBilal AnwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 IntroductionDocument41 pagesChapter 01 IntroductionHIWALE PRAGATINo ratings yet
- Unit I - Introduction To DatabaseDocument31 pagesUnit I - Introduction To DatabaseGaurav Patni100% (1)
- DBMS C1P1Document49 pagesDBMS C1P1Amit SinghNo ratings yet
- DBDM 16 Marks All 5 UnitsDocument74 pagesDBDM 16 Marks All 5 Unitsathirayan85No ratings yet
- Advantages of DBMS ApproachDocument7 pagesAdvantages of DBMS ApproachAgee SujathaNo ratings yet
- DBMS1 7Document531 pagesDBMS1 7savoir001No ratings yet
- Class 1 - E in ERDDocument33 pagesClass 1 - E in ERDKarthik sivanesanNo ratings yet
- BSC CsIt Complete RDBMS NotesDocument86 pagesBSC CsIt Complete RDBMS NotesNilesh GoteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document27 pagesChapter 3yoantanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Part-1 and 2Document58 pagesUnit 3 Part-1 and 2G.K.HarishNo ratings yet
- Advanced Database Systems: Module TitleDocument17 pagesAdvanced Database Systems: Module TitleMclab MedcollegeNo ratings yet
- DBMS NotesDocument34 pagesDBMS NotesAkash PalNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemsDocument20 pagesAccounting Information Systemsمحمود احمدNo ratings yet
- I Certify That The Work Submitted For This Assignment Is My Own and Research Sources Are Fully AcknowledgedDocument17 pagesI Certify That The Work Submitted For This Assignment Is My Own and Research Sources Are Fully AcknowledgedLê Văn PhươngNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Database Systems - PPTX (Repaired)Document238 pagesFundamentals of Database Systems - PPTX (Repaired)Capt. NuhaminNo ratings yet
- OODBMS - ConceptsDocument9 pagesOODBMS - Conceptssmartbilal5338No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To DatabasesDocument35 pages1 Introduction To DatabasesBricious Mulimbi100% (1)
- File Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramDocument29 pagesFile Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Dbms Notes For Anna UniversityDocument132 pagesDbms Notes For Anna UniversityJaisakthiRaman Murugan67% (3)
- Notes To The Textbook: Implementation, and Management by Thomas M. Connolly & Carrolyn E. Begg, Published byDocument8 pagesNotes To The Textbook: Implementation, and Management by Thomas M. Connolly & Carrolyn E. Begg, Published byImran QadirNo ratings yet
- Cours Database SystemDocument151 pagesCours Database SystemCapt. NuhaminNo ratings yet
- CS6302Document126 pagesCS6302brm1shubhaNo ratings yet
- Dbms Notes: Unit 1Document14 pagesDbms Notes: Unit 1AmoghaVarsha Atith Gowda MuralidharaNo ratings yet
- Computing Essentials: DatabasesDocument49 pagesComputing Essentials: Databasessadam hussainNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument70 pagesDBMSGitte DnyaneshwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - ObjectivesDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - ObjectivessohussainNo ratings yet
- Database System Concepts Before The Advent of Database SystemsDocument13 pagesDatabase System Concepts Before The Advent of Database Systemsanon-147072No ratings yet
- Accounting Information Systems 14e Romney Chapter 4Document41 pagesAccounting Information Systems 14e Romney Chapter 4ESLAM ABOU EL YAZEED EL GEHINYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Data Resource ManagementDocument6 pagesChapter 5 Data Resource ManagementAmanda Wijaya100% (1)
- Database Chapter 01Document59 pagesDatabase Chapter 01rockers91100% (1)
- Mcs 023Document261 pagesMcs 023Pavin ChandraNo ratings yet
- Unit I and II of DBMSDocument25 pagesUnit I and II of DBMSMINERVA JHANo ratings yet
- Dbms ConceptsDocument13 pagesDbms ConceptsShobhit DeoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management SYSTEMDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Database Management SYSTEMsikandertamoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Fundamental ConceptsDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Fundamental ConceptsNonso EnemuohNo ratings yet
- DBMS Complete PDFDocument94 pagesDBMS Complete PDFFatima FayyazNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems: George Klington. ADocument18 pagesDatabase Management Systems: George Klington. AklingtonNo ratings yet
- Unit01 - Database System Concept & Data ModelingDocument34 pagesUnit01 - Database System Concept & Data ModelingWomen's Polytechnic ChandannagarNo ratings yet
- Pengantar: Intro To DatabaseDocument33 pagesPengantar: Intro To DatabaseDayu DiahNo ratings yet
- DBMS Class 10Document24 pagesDBMS Class 10ericmsc84% (38)
- Ques What Is DBMS - Explain The Basic Architecture of DBMS ?Document34 pagesQues What Is DBMS - Explain The Basic Architecture of DBMS ?Ashu JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document39 pagesChapter 10Salma MalikNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Second EditionFrom EverandCloud Computing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Getting Started with Oracle Data Integrator 11g: A Hands-On TutorialFrom EverandGetting Started with Oracle Data Integrator 11g: A Hands-On TutorialRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Java/J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandJava/J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- RF Applications DevelopmentDocument4 pagesRF Applications DevelopmentMr GrachNo ratings yet
- Process Simulate Training DAYS4 5 Version 12.1.3Document83 pagesProcess Simulate Training DAYS4 5 Version 12.1.3BOULAL MEDNo ratings yet
- AWS General Version 1.0Document342 pagesAWS General Version 1.0gopuggNo ratings yet
- DCI Travel Plan SRS v1.2Document52 pagesDCI Travel Plan SRS v1.2Aman Kumar ShawNo ratings yet
- Device Protection With Microsoft Endpoint Manager and Microsoft Defender For Endpoint - Module 08 - Exploit Guard and Application GuardDocument67 pagesDevice Protection With Microsoft Endpoint Manager and Microsoft Defender For Endpoint - Module 08 - Exploit Guard and Application GuardLuke WhitemanNo ratings yet
- CD Unit-3 Part-2Document21 pagesCD Unit-3 Part-2dartionjpNo ratings yet
- BAB 6 USING INFORMATION Technology, Eleventh EditionDocument64 pagesBAB 6 USING INFORMATION Technology, Eleventh EditionCitra Rezki RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Cuckoo KVM ResearchDocument9 pagesCuckoo KVM ResearchNadzyaNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification RFMS V2.1.0 13.10.2017Document37 pagesTechnical Specification RFMS V2.1.0 13.10.2017László KovácsNo ratings yet
- Ain Dumps 2023-May-02Document13 pagesAin Dumps 2023-May-02Emad MasandehNo ratings yet
- 2019 - 2020 Ef 451 Assignment 1Document7 pages2019 - 2020 Ef 451 Assignment 1Cephas Mpandika KalemboNo ratings yet
- Huawei - What About BTS Network Architecture at RAN LayersDocument8 pagesHuawei - What About BTS Network Architecture at RAN Layerssameh sheblNo ratings yet
- Sap S4 Hana: Finance ModuleDocument85 pagesSap S4 Hana: Finance Moduleabbas salahNo ratings yet
- WinspiroPRO Revision HistoryDocument33 pagesWinspiroPRO Revision HistoryАзбука МорзеNo ratings yet
- Cisco Urwb fm1000 Gateway UsermanualDocument138 pagesCisco Urwb fm1000 Gateway UsermanualJuan PerezNo ratings yet
- Continuous Delivery Patterns and Anti-PatternsDocument9 pagesContinuous Delivery Patterns and Anti-Patternsalx yedekNo ratings yet
- Ics 3Document8 pagesIcs 3Ruturaj PatilNo ratings yet
- 2018 HYPACK User Manual 04Document216 pages2018 HYPACK User Manual 04Maika LyNo ratings yet
- Sharp Dojo Content GuidelineDocument64 pagesSharp Dojo Content GuidelineCSNo ratings yet
- Fortios v7.0.7 Release NotesDocument37 pagesFortios v7.0.7 Release NotesLabra DorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Application Software True/FalseDocument14 pagesChapter 6: Application Software True/FalsesarahNo ratings yet
- H12-221 - V2.5-Enu V8.02Document164 pagesH12-221 - V2.5-Enu V8.02fish100% (1)
- Visa Confirmed L3 Test Tools - 092322Document5 pagesVisa Confirmed L3 Test Tools - 092322Vadsalasack VorlavongsorNo ratings yet
- 07WS PAS Install PSMDocument71 pages07WS PAS Install PSMMarcel FriesenNo ratings yet
- DX DiagDocument40 pagesDX DiagVictor CañasNo ratings yet
- Expert C++ Become A Proficient Programmer by Learning Coding Best Practices With C++17 and C++20s Latest Features by Vardan Grigoryan Shunguang WuDocument591 pagesExpert C++ Become A Proficient Programmer by Learning Coding Best Practices With C++17 and C++20s Latest Features by Vardan Grigoryan Shunguang Wupluisfer0100% (5)
- Ecatgui EngDocument5 pagesEcatgui EngNAGOIA BRNo ratings yet
- Cisco Devices For Microsoft Teams Rooms - CM 5551Document2 pagesCisco Devices For Microsoft Teams Rooms - CM 5551nthangloiNo ratings yet
- Arduino Basic Connection PDFDocument39 pagesArduino Basic Connection PDFsabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Systems Development: Fourth Edition by Wilkinson, Cerullo, Raval, and Wong-On-WingDocument39 pagesChapter 14: Systems Development: Fourth Edition by Wilkinson, Cerullo, Raval, and Wong-On-WingRidoni Fardeni HarahapNo ratings yet