Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Traditional Contracting: Dr. Rana Humayun Ihsan
Uploaded by
Khayar Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
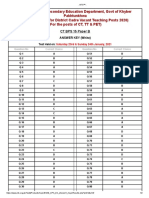
8 views15 pagesTraditional contracting follows a design-bid-build model with distinct roles. The owner hires a consultant to design the project and a main contractor to build it. The main contractor then hires subcontractors. The traditional project lifecycle includes conceptual design, schematic design, design development, construction, and testing/handover. Quality is ensured through principles like meeting requirements, customer satisfaction, and dispute resolution procedures defined in contract documents. The owner, consultant and contractor each have defined responsibilities to deliver the project on schedule and budget.
Original Description:
Contract lecture
Original Title
Traditional Contracting
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTraditional contracting follows a design-bid-build model with distinct roles. The owner hires a consultant to design the project and a main contractor to build it. The main contractor then hires subcontractors. The traditional project lifecycle includes conceptual design, schematic design, design development, construction, and testing/handover. Quality is ensured through principles like meeting requirements, customer satisfaction, and dispute resolution procedures defined in contract documents. The owner, consultant and contractor each have defined responsibilities to deliver the project on schedule and budget.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesTraditional Contracting: Dr. Rana Humayun Ihsan
Uploaded by
Khayar KhanTraditional contracting follows a design-bid-build model with distinct roles. The owner hires a consultant to design the project and a main contractor to build it. The main contractor then hires subcontractors. The traditional project lifecycle includes conceptual design, schematic design, design development, construction, and testing/handover. Quality is ensured through principles like meeting requirements, customer satisfaction, and dispute resolution procedures defined in contract documents. The owner, consultant and contractor each have defined responsibilities to deliver the project on schedule and budget.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Traditional Contracting
Dr. Rana Humayun Ihsan
Traditional Contracting
Design – bid – build:
Owner
Consultant (Architect/Engineers)
Main Contractor
Subcontractor
Subcontractor Electrical
Subcontractor Mechanical
Subcontractor (if any)
Traditional Contracting
Main groups in construction projects:
Owner—A person or an organization that initiates and sanctions a project. He or she
requests the need of the facility and is responsible for arranging the financial
resources for creation of the facility.
Designer (A/E)—This consists of architects or engineers or consultants. They are
the owner’s appointed group accountable to convert the owner’s conception and
needs into the specific facility with detailed directions through drawings and
specifications within the economic objectives. They are responsible for the design of
the project and in certain cases supervision of the construction process.
Contractor—A construction firm engaged by the owner to complete the specific
facility by providing the necessary staff, work force, materials, equipment, tool, and
other accessories to the satisfaction of the owner/end user in compliance with the
contract documents. The contractor is responsible for implementing the project
activities and to achieve owner’s objectives.
Traditional Contracting
Construction project life cycle:
1. Conceptual design
2. Schematic design
3. Design development
4. Construction
5. Testing, commissioning, and handover
Traditional Contracting
Construction project life cycle:
1. Conceptual design
Identification of need and objectives (TOR or terms of reference)
Identification of project team
Data collection
Identification of alternatives
Time schedule
Financial implications/resources
Development of concept design
Traditional Contracting
Construction project lifecycle:
Schematic design
General scope of works/basic design
Regulatory/authorities approval
Schedule
Budget
Contract terms and conditions
Traditional Contracting
Construction project lifecycle:
Design development
Regulatory/authorities approval
Contract documents and specifications
Detailed plan
Budget
Estimated cash flow
Contract documents
Bidding and tender documents
Traditional Contracting
Construction project lifecycle:
Construction
Mobilization
Execution of works
Planning and scheduling
Management of resources/procurement
Monitoring and control
Quality
Inspection
Traditional Contracting
Construction project lifecycle:
Testing, commissioning, and handover
Testing
Commissioning
Regulatory/authorities approval
As built drawings/records
Technical manuals and documents
Training of user’s personnel
Hand over facility to owner/end user
Move in plan
Substantial completion
Traditional Contracting
Principles of Quality in Construction Projects:
Meeting the customer’s need
Customer satisfaction
Fitness for use
Conforming to requirements
Degree of excellence at an acceptable price
Traditional Contracting
Principles of quality in construction projects:
Principle 1 Owner, consultant, and contractor are fully
responsible for application of the quality management system to
meet the defined scope of work in the contract documents
Principle 2 Consultant is responsible for providing owner’s
requirements explicitly and clearly defining in the contract
documents
Principle 3 Method of payments (work progress, material,
equipment, etc.) to be clearly defined in the contract documents.
Rate analysis of bill of quantities (BOQ) or bill of materials
(BOM) item to be agreed before signing of contract
Traditional Contracting
Principles of quality in construction projects:
Principle 4 Contract documents should include a clause to settle
the dispute arising during construction stage
Principle 5 Contractor should study all the documents during
tendering/bidding stage and submit his or her proposal taking
into consideration all the requirements specified in the contract
documents
Principle 6 Contractor shall follow an agreed upon quality
assurance and quality control plan; consultant shall be
responsible for overseeing the compliance with the contract
documents and specified standards
Traditional Contracting
Principles of quality in construction projects:
Principle 7 Contractor is responsible for providing all the
resources, manpower, material, equipment, and so on to build the
facility as per specifications
Principle 8 Contractor shall follow the submittal procedure
specified in the contract documents
Principle 9 Each member of project team should participate in
all the functional areas to continuously improve the quality of
the project
Traditional Contracting
Principles of quality in construction projects:
Principle 10 Contractor is responsible for constructing the
facility as specified and use the material, products, equipment,
and methods that satisfy the specified requirements
Principle 11 Contractor to build the facility as stipulated in the
contract documents, plan, specifications within the budget and
on schedule to meet owner’s objectives
Principle 12 Contractor should perform the works as per the
agreed upon construction program and handover the project as
per the contracted schedule
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Sample Needs StatementDocument66 pagesSample Needs StatementKhairuddin Ismail100% (6)
- 3-D WheelDocument24 pages3-D WheelKim Ciudadano29% (7)
- SAP SD by Manoj Tony Latest PDFDocument15 pagesSAP SD by Manoj Tony Latest PDFPavan TodkarNo ratings yet
- Payslip TemplateDocument7 pagesPayslip TemplateSusaine Sinohin100% (2)
- International Finance Homework SolutionDocument33 pagesInternational Finance Homework Solutionenporio7978% (9)
- Attachment D Scope of ServicesDocument12 pagesAttachment D Scope of ServicesMark Roger II HuberitNo ratings yet
- Parties of A Construction ProjectDocument8 pagesParties of A Construction ProjectT N Roland BourgeNo ratings yet
- Project Construction OverviewDocument28 pagesProject Construction OverviewLala TaoyNo ratings yet
- Contracts and Specifications: Contracts. Construction Contract Is A Formal Agreement For ConstructionDocument6 pagesContracts and Specifications: Contracts. Construction Contract Is A Formal Agreement For Constructionianiroy13No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument24 pagesIntroductionLynser AbanzadoNo ratings yet
- Professional Practice 2: UrdanetacityuniversityDocument4 pagesProfessional Practice 2: UrdanetacityuniversityaljonNo ratings yet
- ARD ProcessDocument7 pagesARD ProcessMARY FRANCHETTE JOY ADALINNo ratings yet
- Lecturer No.15, Development of Construction Project.Document9 pagesLecturer No.15, Development of Construction Project.wajidNo ratings yet
- Contracts - 1Document18 pagesContracts - 1Martin OsokaiseNo ratings yet
- Sample Draft Construction Supervision and Quality Control PlanDocument3 pagesSample Draft Construction Supervision and Quality Control Planነህምያ ጌታቸውNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument14 pagesREVIEWERJana MinNo ratings yet
- Proffessional - Practice 1Document34 pagesProffessional - Practice 1Ayu EmanaNo ratings yet
- Bim 2Document15 pagesBim 2Damilola AkinsanyaNo ratings yet
- c14 BSDDocument17 pagesc14 BSDCristian BlanaruNo ratings yet
- Design and ConstructionDocument26 pagesDesign and ConstructionnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Recommended Guideline For The Accord Policy On The Scope of PracticeDocument9 pagesRecommended Guideline For The Accord Policy On The Scope of PracticehalimbkNo ratings yet
- Duties & ResponsibilitiesDocument7 pagesDuties & ResponsibilitiesFreedom Love NabalNo ratings yet
- Uap Doc 205-208Document22 pagesUap Doc 205-208Abby AchaNo ratings yet
- Arch 492Document6 pagesArch 492Glyrah Marie Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Building ProcurementDocument27 pagesBuilding ProcurementLokuliyanaNNo ratings yet
- Phases of ConstructionDocument10 pagesPhases of ConstructionzaraNo ratings yet
- Assignment Ar ShahidaDocument46 pagesAssignment Ar Shahidasyaqirah_topNo ratings yet
- Professional Practise Letter To Client Regarding Contractor Etc 2021.03.03Document26 pagesProfessional Practise Letter To Client Regarding Contractor Etc 2021.03.03Ana GNo ratings yet
- Project Management Services For Building ProjectsDocument7 pagesProject Management Services For Building ProjectsAbdelmuneimNo ratings yet
- Project Management Ch1Document7 pagesProject Management Ch1ltai_laiNo ratings yet
- TESTSDocument10 pagesTESTSAbdullatif AllyNo ratings yet
- Procurement MethodsDocument11 pagesProcurement MethodsEVONNENo ratings yet
- The Comprehensive Guide To Construction Contract AdministrationDocument36 pagesThe Comprehensive Guide To Construction Contract AdministrationVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 CompleteDocument16 pagesAssignment 1 CompleteEvonYongNo ratings yet
- 4 Regular Design Services of The ArchitectDocument2 pages4 Regular Design Services of The ArchitectHaruno AknecsNo ratings yet
- CE Law 5 ContractDocument14 pagesCE Law 5 ContractMayvyyNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Services of An Architect 2.0Document16 pagesComprehensive Services of An Architect 2.0Mariel Paz MartinoNo ratings yet
- 4.1 ProcurementDocument48 pages4.1 ProcurementrobbsNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Specifications - EQS 2304 SpecificationsDocument16 pages1.0 Specifications - EQS 2304 SpecificationsCharles NdunguNo ratings yet
- Construction Process: by Syed Burhanuddin Hilmi Syed MohamadDocument61 pagesConstruction Process: by Syed Burhanuddin Hilmi Syed MohamadIzzati HamidNo ratings yet
- Project Cost Reduction and Value Engineering PDFDocument192 pagesProject Cost Reduction and Value Engineering PDFDEVA PRIYA ANIL 1861724No ratings yet
- Design MethodologyDocument3 pagesDesign MethodologyybrahimjNo ratings yet
- Pre-Design ServicesDocument5 pagesPre-Design ServicesKeziahjan ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Contruct SpecificationDocument23 pagesContruct SpecificationShayan AbagnaleNo ratings yet
- EPC ContractDocument82 pagesEPC ContractDanielNo ratings yet
- Construction Project Administration: Dr. Abubakar SharafatDocument31 pagesConstruction Project Administration: Dr. Abubakar Sharafatmalik awansNo ratings yet
- Ethics Assignment Correct FormatDocument4 pagesEthics Assignment Correct Formatdany rwagatareNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Review Questions SolutionDocument4 pagesLecture 2 Review Questions SolutionMALEK SKATERNo ratings yet
- BPM101 - Chap 2 - R2Document36 pagesBPM101 - Chap 2 - R2jin ke maNo ratings yet
- Roles and Functions of Parties Involved in A Construction ProjectDocument14 pagesRoles and Functions of Parties Involved in A Construction ProjectRanjith Ekanayake100% (1)
- Construction Practices: Engr. Ruderico M. Endriano JR, CeDocument11 pagesConstruction Practices: Engr. Ruderico M. Endriano JR, CeLynx101No ratings yet
- TOR For ConsultancyServicesDocument4 pagesTOR For ConsultancyServicesAnousack KittilathNo ratings yet
- Project Management 3Document3 pagesProject Management 3Geese GoNo ratings yet
- Regular Design Services of An ArchitectDocument5 pagesRegular Design Services of An ArchitectRej SwiftNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Architectural ServicesDocument10 pagesComprehensive Architectural ServicesDaNica Tomboc JavierNo ratings yet
- Part 1construction Methods and Project ManagementDocument82 pagesPart 1construction Methods and Project ManagementHonorio Joshua P.No ratings yet
- CH 6Document27 pagesCH 6selam tamruNo ratings yet
- Management of Construction Process and Project ProcurementDocument21 pagesManagement of Construction Process and Project ProcurementDanicaGanNo ratings yet
- Ec705 MSC - Civil Engineering (Construction) Ecm744 Construction Site and Safety ManagementDocument38 pagesEc705 MSC - Civil Engineering (Construction) Ecm744 Construction Site and Safety Managementhamedsan91No ratings yet
- Specifications and Quantities: Construction ProjectsDocument22 pagesSpecifications and Quantities: Construction ProjectsEnass YounisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction, Construction, Project Cycle, Preparing A Bid Package, Bidding Process and RequirementsDocument5 pagesLesson 1: Introduction, Construction, Project Cycle, Preparing A Bid Package, Bidding Process and RequirementsCRIZA JANE BUSTILLONo ratings yet
- Construction ManagemntDocument20 pagesConstruction ManagemntSaicharan Ayaluri100% (1)
- Mustafa PSTDocument1 pageMustafa PSTKhayar KhanNo ratings yet
- CT B WhiteDocument2 pagesCT B WhiteKhayar KhanNo ratings yet
- CT B GreenDocument2 pagesCT B GreenKhayar KhanNo ratings yet
- CT B WhiteDocument2 pagesCT B WhiteKhayar KhanNo ratings yet
- DC Summary NewDocument1 pageDC Summary NewKhayar KhanNo ratings yet
- MustafattDocument1 pageMustafattKhayar KhanNo ratings yet
- CBC2Document14 pagesCBC2Khayar KhanNo ratings yet
- Adp CH.2Document11 pagesAdp CH.2RK HassanNo ratings yet
- Logistics Management Plan FormatDocument10 pagesLogistics Management Plan FormatAnna BelleNo ratings yet
- Packaging and Purchase DecisionsDocument19 pagesPackaging and Purchase Decisionsgirish_gupta509575No ratings yet
- Module 21 Professional Responsi Ilities: MU EADocument1 pageModule 21 Professional Responsi Ilities: MU EAHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Full Download Foundations of Strategy 2nd Edition Grant Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Foundations of Strategy 2nd Edition Grant Test Bank PDF Full Chapterpellucidutter.uka6lr100% (18)
- IBIS WORLD INDUSTRY REPORT: Sandwich & Sub Store FranchisesDocument33 pagesIBIS WORLD INDUSTRY REPORT: Sandwich & Sub Store FranchisesFortuneNo ratings yet
- BALA - PRASANNA - KUMAR - SCM Fuc - ResumeDocument3 pagesBALA - PRASANNA - KUMAR - SCM Fuc - Resumesaurabh chaturvediNo ratings yet
- 1 Decision Making: Based On XATDocument16 pages1 Decision Making: Based On XATGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- B440 Management Representation LetterDocument2 pagesB440 Management Representation LetterTuấn Phạm Nguyễn ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Waleed QureshiDocument2 pagesWaleed QureshiWaleed Bin KhaliqNo ratings yet
- BSBHRM611 Learner Workbook Assignment 2023Document32 pagesBSBHRM611 Learner Workbook Assignment 2023Sudha BarahiNo ratings yet
- Impact of Reforms in Capital Market On Indian Capital MarketDocument30 pagesImpact of Reforms in Capital Market On Indian Capital MarketNiketu Shah0% (1)
- Repoprt On Loans & Advances PDFDocument66 pagesRepoprt On Loans & Advances PDFTitas Manower50% (4)
- Section D ACCA PM NotesDocument9 pagesSection D ACCA PM NotesCorrinaNo ratings yet
- Sabina Nepal CVDocument5 pagesSabina Nepal CVRakesh PradhanNo ratings yet
- Infosys Working CapitalDocument30 pagesInfosys Working CapitalSonali JoshiNo ratings yet
- Alzou Bi 2016Document22 pagesAlzou Bi 2016Denny PutriNo ratings yet
- Technopreneurship - EthicsDocument10 pagesTechnopreneurship - EthicsCamilogs100% (1)
- Sanraa Annual Report 08 09Document49 pagesSanraa Annual Report 08 09chip_blueNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document20 pagesCH 08Amaurrie ArpilledaNo ratings yet
- Problems On Operating CostingDocument2 pagesProblems On Operating Costingcoolstuf4uNo ratings yet
- Intenship ReportDocument43 pagesIntenship ReportManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Reference Letter ExamplesDocument7 pagesReference Letter ExamplesDufrain100% (1)
- Chapter-3: Job AnalysisDocument40 pagesChapter-3: Job AnalysisCabdixakiim-Tiyari Cabdillaahi AadenNo ratings yet
- Payment Step-By-Step: ZilingoDocument1 pagePayment Step-By-Step: ZilingoEKNo ratings yet
- Atlantic Pricing Case Study Submitted By: Ishali Kalsi Roll No: FT-21-539Document6 pagesAtlantic Pricing Case Study Submitted By: Ishali Kalsi Roll No: FT-21-539isha kalsiNo ratings yet
- SmartPlant Spoolgen Plus White Paper March 2012 PDFDocument40 pagesSmartPlant Spoolgen Plus White Paper March 2012 PDFrkarthikmtmrNo ratings yet