Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Roll No. 28 Eco
Uploaded by
Deepak0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views10 pagesThis document discusses price elasticity of demand, including:
1) It defines price elasticity of demand as a measure of how responsive the quantity demanded is to changes in price, with elasticity representing the responsiveness of consumers.
2) It provides definitions of price elasticity from various economists as the percentage or rate of change in quantity demanded relative to changes in price.
3) It outlines the different degrees of price elasticity - perfectly elastic, perfectly inelastic, relatively elastic, relatively inelastic, and unitary elastic - and provides examples and demand curve representations of each.
Original Description:
Original Title
ROLL NO. 28 ECO
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses price elasticity of demand, including:
1) It defines price elasticity of demand as a measure of how responsive the quantity demanded is to changes in price, with elasticity representing the responsiveness of consumers.
2) It provides definitions of price elasticity from various economists as the percentage or rate of change in quantity demanded relative to changes in price.
3) It outlines the different degrees of price elasticity - perfectly elastic, perfectly inelastic, relatively elastic, relatively inelastic, and unitary elastic - and provides examples and demand curve representations of each.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views10 pagesRoll No. 28 Eco
Uploaded by
DeepakThis document discusses price elasticity of demand, including:
1) It defines price elasticity of demand as a measure of how responsive the quantity demanded is to changes in price, with elasticity representing the responsiveness of consumers.
2) It provides definitions of price elasticity from various economists as the percentage or rate of change in quantity demanded relative to changes in price.
3) It outlines the different degrees of price elasticity - perfectly elastic, perfectly inelastic, relatively elastic, relatively inelastic, and unitary elastic - and provides examples and demand curve representations of each.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
TOPIC :- PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
: MEANING AND ITS DEGREE
FACULTY NAME :- Dr. Sofia khan STUDENT NAME :- DEEPAK GUPTA
ROLL NO. :- PG/25/028
Assistant professor
SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT SCIENCES
VARANASI
MEANING
Price elasticity of demand is a measure used in economics to show the
responsiveness, or elasticity, of the quantity demanded of a good or
service to increase in its price when nothing but the price changes.
Elasticity = responsiveness of consumer due to the price change of any
commodity.
DEFINITIONS
According to ALFRED MARSHALL: “Elasticity of demand may be
defined as the percentage change in quantity demanded to the percentage
change in price.”
According to A.K.CAIRNCROSS: “The elasticity of demand for a
commodity is the rate at which quantity bought changes as the price
changes.”
According to J.M.KEYNES: “ The elasticity of demand is a measure of
the relative changes in quantity to a relative change in price.”
According to KENNETH BOULDING: “ Elasticity of demand measures
the responsiveness of demand to changes in price.”
Degrees Of Price Elasticity Of
Demand
Perfectly elastic demand (e=∞)
Perfectly inelastic demand (e=0)
Relatively elastic demand (e>1)
Relatively inelastic demand (e<1)
Unitary elastic demand (e=1)
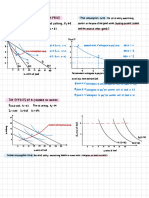
Perfectly elastic demand (e=∞)
When a small change in price of a product causes a major in its demand, it is
said to be perfectly elastic demand
Perfectly elastic demand is a theoretical concept and cannot be applied in the
real situation.
It can be applied in cases , such as perfectly competitive market and
homogeneity products.
In perfectly elastic demand , the demand
curve is represented as a horizontal straight
line , which is shown in figure.
Perfectly Inelastic Demand (ep=0)
A perfectly inelastic demand is one when there is no change produced in the
demand of a product with change in price.
The numerical value for perfectly inelastic demand is zero (ep=0).
In case of essential goods, such as salt , the demand does not change with
change in price.
In case of perfectly inelastic demand,
demand curve is represented as a
straight vertical line , which is shown
in figure.
Relatively elastic demand (ep>1)
Relatively elastic demand refers to the demand when the proportionate
change in demand is greater than the proportionate change in price of a
product.
The numerical value of relatively elastic demand ranges between one to
infinity. Mathematically, relatively elastic demand is know as more than
unit elastic demand(ep>1).
The demand curve of relatively
elastic demand is gradually
sloping as shown in figure
Relatively inelastic demand (e<1)
Relatively inelastic demand is one when the percentage change in demand
is less than the percentage in the price of a product.
The numerical value of relatively value of relatively elastic demand
ranges between zero to one (ep<1).
The demand curve of relatively
inelastic demand is rapidly
sloping as shown in figure.
Unitary elastic demand (e=1)
When the proportionate change in demand produces the same change in the price
of the product, the demand is referred as unitary elastic demand . The numerical
value for unitary elastic demand is equal to one (ep=1).
The demand curve for unitary
elastic demand is represented as a
rectangular hyperbola, as shown in
figure.
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Sample For Wedding Planner Business PlanDocument8 pagesSample For Wedding Planner Business PlanLmay Phang60% (5)
- Economics for CFA level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4From EverandEconomics for CFA level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- MKTG1199 Report Project (Final)Document39 pagesMKTG1199 Report Project (Final)xinyi angNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demandtypes: MeaningDocument3 pagesElasticity of Demandtypes: MeaningGoutham BindigaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument3 pagesProjectGoutham BindigaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument7 pagesElasticity of DemandNupur KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Perfectly Elasticity of Demand - Ed InfiniteDocument1 pagePerfectly Elasticity of Demand - Ed InfiniteDhruvSharmaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics and Financial Analysis: TopicDocument11 pagesManagerial Economics and Financial Analysis: TopicPatnana ArunaNo ratings yet
- Santosh Bhandari Assignment1Document18 pagesSantosh Bhandari Assignment1Santosh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument4 pagesElasticity of DemandAnkit Kumar0% (1)
- Elasticity of DemandDocument29 pagesElasticity of DemandabhishekNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand BBS1Document2 pagesElasticity of Demand BBS1BalNo ratings yet
- Elasticity-Of-Demand 8552087 PowerpointDocument21 pagesElasticity-Of-Demand 8552087 PowerpointChandan NNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument28 pagesElasticity of DemandAkankshya MishraNo ratings yet
- 5 Types of Price Elasticity of Demand - Explained!Document53 pages5 Types of Price Elasticity of Demand - Explained!Rounak BasuNo ratings yet
- Ecu 402-Lesson TwoDocument8 pagesEcu 402-Lesson TwoMksu GeniusNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument20 pagesElasticity of DemandManvendra Shahi100% (1)
- Naveena SamaDocument19 pagesNaveena SamaSägñîk KàtårïNo ratings yet
- 5 Degrees of Price Elasticity of DemandDocument17 pages5 Degrees of Price Elasticity of DemandSelenaNo ratings yet
- Demand AnalysisDocument11 pagesDemand AnalysisBenjamin YokeshNo ratings yet
- E Percentage Change in Quantity Demanded of A Commodity / Percentage Change in PriceDocument22 pagesE Percentage Change in Quantity Demanded of A Commodity / Percentage Change in PriceStephine BochuNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationDocument27 pagesNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentationravi_nyseNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand: Presented By: Hasan Shoukat Teacher: Sir Iqbal Panhwar Course: EconomicsDocument14 pagesElasticity of Demand: Presented By: Hasan Shoukat Teacher: Sir Iqbal Panhwar Course: EconomicsHasan Shoukat PathanNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument7 pagesElasticity of DemandLakshmiRengarajan100% (2)
- Unit-II ELASTICITY OF DEMAND (ALL)Document20 pagesUnit-II ELASTICITY OF DEMAND (ALL)stevesilasrockersNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and Its TypesDocument8 pagesElasticity of Demand and Its TypesCandy DollNo ratings yet
- CHP 3 (B) Elasticity of DemandDocument11 pagesCHP 3 (B) Elasticity of DemandRavi VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument29 pagesElasticity of Demandcyril george100% (1)
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pagesPrice Elasticity of DemandAymanTounsiNo ratings yet
- Concept of Elasticity of Demand - Types of Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pagesConcept of Elasticity of Demand - Types of Elasticity of Demandiarilangsyngkli0No ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics Bsit 5 Semester: Topic: Elasticity of Demand Teacher Name: Fizza ShaukatDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Economics Bsit 5 Semester: Topic: Elasticity of Demand Teacher Name: Fizza Shaukatwarda abbasNo ratings yet
- Types of Elasticity of DemandDocument13 pagesTypes of Elasticity of Demandwarda abbasNo ratings yet
- Notions of Elasticity: Prepared byDocument26 pagesNotions of Elasticity: Prepared byAndrea SiladanNo ratings yet
- Answer:: Course: Business Economics Internal Assignment Applicable For December 2020 ExaminationDocument5 pagesAnswer:: Course: Business Economics Internal Assignment Applicable For December 2020 Examinationjitendra.jgec8525No ratings yet
- The Price System PDFDocument5 pagesThe Price System PDFCommerce LineNo ratings yet
- Economics Assignment Q3Document3 pagesEconomics Assignment Q3jitendra.jgec8525No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3vinit sahooNo ratings yet
- Elasticity: Manzur AhmadDocument13 pagesElasticity: Manzur AhmadManzur AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument54 pagesUnit 3: Elasticity of Demand and SupplyNitesh BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocument10 pagesPrice Elasticity of DemandClaNo ratings yet
- Answer:: Course: Business Economics Internal Assignment ExaminationDocument3 pagesAnswer:: Course: Business Economics Internal Assignment ExaminationJitendraNo ratings yet
- 8.3.6 - Elasticity of DemandDocument3 pages8.3.6 - Elasticity of DemandJunior PyareNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 - Elasticity of DemandDocument12 pagesUnit-2 - Elasticity of DemandSachin Chimmalgi100% (1)
- Demand AnalysisDocument65 pagesDemand AnalysisJoshua Stalin SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of SupplyDocument15 pagesElasticity of SupplyAyas JenaNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics Assignment: Submitted To Mr. Raj KumarDocument12 pagesMicro Economics Assignment: Submitted To Mr. Raj Kumarpriyaleo_19894819No ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocument13 pagesPrice Elasticity of DemandeeeeNo ratings yet
- Types Ofelasticity of Demand: Presented By:-Sai Kiran Jasti (17k61e0025)Document19 pagesTypes Ofelasticity of Demand: Presented By:-Sai Kiran Jasti (17k61e0025)venkyNo ratings yet
- Economics Chapter 4Document14 pagesEconomics Chapter 4Sharif HassanNo ratings yet
- Elasticity - Measure of ResponsivenessDocument9 pagesElasticity - Measure of Responsivenesstegegn mogessieNo ratings yet
- Study Notes On Elasticity of Demand: Concept, Types and ImportanceDocument13 pagesStudy Notes On Elasticity of Demand: Concept, Types and ImportanceVickyNo ratings yet
- Types of Price Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pagesTypes of Price Elasticity of DemandNelluri Surendhar ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and Supply in 2022Document27 pagesElasticity of Demand and Supply in 2022mabsudNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument20 pagesManagerial Economics4PredicationNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocument12 pagesPrice Elasticity of DemandMasa MpoelengNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics-Sem 1-Unit 4Document46 pagesMicroeconomics-Sem 1-Unit 4Tejas PatilNo ratings yet
- Cross-Elasticity of DemandDocument11 pagesCross-Elasticity of DemandDivine Grace JasaNo ratings yet
- Elasticities of Demand and SupplyDocument18 pagesElasticities of Demand and SupplyAndre SoaresNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of Demand (PED or E: Economics Percent ChangeDocument3 pagesPrice Elasticity of Demand (PED or E: Economics Percent ChangemustafakarimNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii (C)Document6 pagesUnit Iii (C)Manisha SangwanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Demand Analysis FINAL COPY FOR ALLDocument89 pagesQuantitative Demand Analysis FINAL COPY FOR ALLHoyo VerseNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocument15 pagesPrice Elasticity of DemandGoransh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Strategic Choice-Bowmans Strategic ClockDocument7 pagesStrategic Choice-Bowmans Strategic ClockDeepakNo ratings yet
- Strategic IntentDocument7 pagesStrategic IntentDeepakNo ratings yet
- Surveys of Consumers: The University of Michigan Survey Research Center Institute For Social ResearchDocument13 pagesSurveys of Consumers: The University of Michigan Survey Research Center Institute For Social ResearchDeepakNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire 2Document13 pagesQuestionnaire 2DeepakNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Survey To Guage The Sentiments of WholesalersDocument5 pagesQuestionnaire On Survey To Guage The Sentiments of WholesalersDeepakNo ratings yet
- A Survey To Guage The Sentiments of Wholesalers: Electrical Tools / Appliances Market in VaranasiDocument9 pagesA Survey To Guage The Sentiments of Wholesalers: Electrical Tools / Appliances Market in VaranasiDeepakNo ratings yet
- Under The Mentorship Of: Mr. Amitabh Pandey (Assistant Professor) Submitted By:-Deepak Gupta ROLL NO.: - PG/25/028Document37 pagesUnder The Mentorship Of: Mr. Amitabh Pandey (Assistant Professor) Submitted By:-Deepak Gupta ROLL NO.: - PG/25/028DeepakNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics: TOPIC:-nominal Income and Real IncomeDocument5 pagesMacro Economics: TOPIC:-nominal Income and Real IncomeDeepakNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: TOPIC:-business and Problem Solving SkillsDocument6 pagesHuman Resource Management: TOPIC:-business and Problem Solving SkillsDeepakNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide - Consumer Behavior T323WSB 5Document14 pagesLearning Guide - Consumer Behavior T323WSB 5Stephen CelestineNo ratings yet
- Oferta y DemandaDocument9 pagesOferta y DemandaRosario Rivera NegrónNo ratings yet
- Summer Training ReportDocument54 pagesSummer Training ReportSyed Irfan Bin InayatNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour - Unit - 2Document5 pagesConsumer Behaviour - Unit - 2unknown_sm1No ratings yet
- PHD Thesis in India PDFDocument8 pagesPHD Thesis in India PDFmonicabogdaneverett100% (2)
- STARTEGIC FINAL .Docx Final - Docx FinalDocument62 pagesSTARTEGIC FINAL .Docx Final - Docx FinalDavid GeorgeNo ratings yet
- THE ROLE OF VALUE MAXIMIZATION IN CONSUMER BEHAVIOR 1314 (R)Document30 pagesTHE ROLE OF VALUE MAXIMIZATION IN CONSUMER BEHAVIOR 1314 (R)Saket jha100% (1)
- The Configuration of The University Image and Its Relationship With The Satisfaction of StudentsDocument26 pagesThe Configuration of The University Image and Its Relationship With The Satisfaction of StudentsMinh TrangNo ratings yet
- Thesis - Consumer Buying Behavior - Eastern Visayas - 22 June 2022Document89 pagesThesis - Consumer Buying Behavior - Eastern Visayas - 22 June 2022Crispin CalvezNo ratings yet
- 273 Simranjeet KaurDocument60 pages273 Simranjeet Kaurprathmesh666patilNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Test BankDocument13 pagesKnowledge Test BankShiv ShawarnNo ratings yet
- A Study On Jewellery Industry in Tamil Nadu: November 2019Document38 pagesA Study On Jewellery Industry in Tamil Nadu: November 2019Sreelatha ChakravarthulaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microeconomics 10th EditionDocument42 pagesTest Bank For Microeconomics 10th EditionAmandaReynoldsagfcy100% (28)
- Consumer BehaviourDocument400 pagesConsumer Behaviourtkesni100% (1)
- Customers Need For Uniqueness Theory PDFDocument11 pagesCustomers Need For Uniqueness Theory PDFGabriel VasquezNo ratings yet
- Consumer Demand Theory PDFDocument14 pagesConsumer Demand Theory PDFlovekumarchechiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Notes of Besanko Microeconomics TBDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Notes of Besanko Microeconomics TBsamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document34 pagesLecture 6Hoda AmrNo ratings yet
- Advance Business Research MethodsDocument31 pagesAdvance Business Research MethodsG.RameshNo ratings yet
- Marketing To The South African Consumer, 2021Document352 pagesMarketing To The South African Consumer, 2021sherly juuNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 BEEB1013Document20 pagesTopic 5 BEEB1013CyrilraincreamNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review of Consumer Buying Behavior of Milk ProductsDocument5 pagesA Systematic Review of Consumer Buying Behavior of Milk Productshaha babaNo ratings yet
- Disserr LitraDocument17 pagesDisserr LitraDisha GangwaniNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Consumer Behavior 6th Edition HoyerDocument17 pagesTest Bank For Consumer Behavior 6th Edition HoyerJoel Slama97% (32)
- SH AR E: Managerial EconomicsDocument29 pagesSH AR E: Managerial EconomicsG74GARV SETHINo ratings yet
- Consumer Decision Making and Beyond: Consumer Behavior, Schiffman & KanukDocument37 pagesConsumer Decision Making and Beyond: Consumer Behavior, Schiffman & KanukKhokhar ZadaNo ratings yet
- Male Skincare Buyer BehaviourDocument14 pagesMale Skincare Buyer BehaviourMuhammad AlJavaNo ratings yet
- Cobb Walgren1995Document17 pagesCobb Walgren1995MUHAMMAD NAUMAN KHANNo ratings yet