Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermodynamic Mind Map
Uploaded by
LEE LEE LAUOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermodynamic Mind Map
Uploaded by
LEE LEE LAUCopyright:
Available Formats
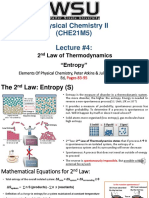
1st Law 2nd Law
• conservation of energy
• thermal equilibrium
• energy can be neither
• process occurs sponteneous
created nor destroyed
• in any cyclic process the
• ΔU=q+w
entropy will either increase or
• irreversible process: not in
remain the same
equilibrium changes
(wirreversible=-ʃPext.dV) ΔQ
• reversible process: Thermodynamic T1 heat transfer T2
infinitesimal changes • energy transfer (work/heat) Hot Cold
(w=-ʃPdV) • spontaneous direction of
• constant P, isobaric chemical process
(w=-PΔV) ΔS = Entropy = ΔQ/T
• equilibrium states
• constant V, isochoric (w=o) V1 Sf = Si (reversible)
Pext
• constant T, isothermal PS Sf > Si (irreversible)
• two different T, T1 and T2 V2
dw = F.dx
(w=-nR(T2-T1)) Volume = Area (A) × Distance (dx)
dV = A .dx
3rd Law
independent on the extensive properties
mass of system system
• open • a state of 0 entropy can only
surroundings exist in a perfectly pure
• closed
dependent on the • isolated boundary crystalline solid at absolute 0
intensive
mass of system
You might also like
- 4 0heat 130415001626 Phpapp01Document14 pages4 0heat 130415001626 Phpapp01sherlyn may lolNo ratings yet
- Science-9 Q4 Module5 Wk5 EditedDocument17 pagesScience-9 Q4 Module5 Wk5 EditedSean MatildoNo ratings yet
- Parallel and Series CircuitDocument13 pagesParallel and Series CircuitsafaNo ratings yet
- CH 16 Heat and TempDocument28 pagesCH 16 Heat and TempSaif SbaihaNo ratings yet
- Work Power EnergyDocument28 pagesWork Power Energymarife gupaalNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration PowerPointDocument20 pagesCellular Respiration PowerPointTasfia QuaderNo ratings yet
- Student Experiment ExplanationDocument59 pagesStudent Experiment ExplanationJimNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity and Latent Heat QuestionsDocument2 pagesHeat Capacity and Latent Heat QuestionstuvvacNo ratings yet
- Energy Activity - Exit TicketsDocument3 pagesEnergy Activity - Exit Ticketsapi-368213959No ratings yet
- Work Energy 1Document11 pagesWork Energy 1Bahril IlmiwanNo ratings yet
- Q1L7 ElectricityDocument61 pagesQ1L7 ElectricityCarmella Raguindin100% (1)
- Build A Submarine Part 5 Lesson Plan PDFDocument3 pagesBuild A Submarine Part 5 Lesson Plan PDFGrace Tolosa NitorNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic ProcessDocument2 pagesThermodynamic ProcessKaren Limpo ApostolNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity - Calorimetry Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesHeat Capacity - Calorimetry Worksheet AnswersCarlos ChNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolシューゴNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Report Sam, Mai and Zaid - 10B 1. IntroDocument9 pagesChemistry Lab Report Sam, Mai and Zaid - 10B 1. IntroSam SankarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document22 pagesChapter 03Abdullatif AlOmairNo ratings yet
- UNIT 9-PHY 131-Chapter 14-Heat-StudentsDocument32 pagesUNIT 9-PHY 131-Chapter 14-Heat-StudentscharlieNo ratings yet
- Dr. Pedro Julio Villegas AguilarDocument48 pagesDr. Pedro Julio Villegas AguilarCt0% (1)
- 3.2 Pressure in LiquidsDocument15 pages3.2 Pressure in Liquidssaeed akhtar100% (1)
- Energy, Energy Transfer, and General Energy Analysis: Fundamentals of Thermal-Fluid SciencesDocument33 pagesEnergy, Energy Transfer, and General Energy Analysis: Fundamentals of Thermal-Fluid SciencesJoelle KharratNo ratings yet
- Heat and TempDocument74 pagesHeat and TempPortia A. EgkenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Energy, Work and PowerDocument7 pagesLesson 5 Energy, Work and PowerCharles CristobalNo ratings yet
- 11.7 States of Matter Phet LabDocument3 pages11.7 States of Matter Phet Lababbymingus60% (1)
- Q4-WEEK 1-Boyle's LawDocument34 pagesQ4-WEEK 1-Boyle's LawAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Law of Conservation of EnergyDocument9 pagesLaw of Conservation of Energydiscoversenthil_9670No ratings yet
- 2.7 Impulsive Force 2020 AnswerDocument5 pages2.7 Impulsive Force 2020 Answer黎珮琴No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Worksheet Set ADocument2 pagesCBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Worksheet Set AlalitNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion Practice QuizDocument4 pagesCircular Motion Practice QuizAtria Paula NidarNo ratings yet
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument32 pagesSecond Law of ThermodynamicsLyndsay Jazmhere Madrilejos50% (2)
- Energy Transfer: Taking The Heat: PhysicsDocument18 pagesEnergy Transfer: Taking The Heat: PhysicsSaima HoqueNo ratings yet
- UG Gas Properties ActivityDocument7 pagesUG Gas Properties Activityardianti widoriniNo ratings yet
- Food Tests - Aiming For Grade 8Document5 pagesFood Tests - Aiming For Grade 8AleNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Force and Motion 1Document15 pages4.2 Force and Motion 1velavan0% (1)
- Energy Forms and ChangesDocument42 pagesEnergy Forms and Changesapi-271661638No ratings yet
- Physics Lab ReportDocument3 pagesPhysics Lab ReportnouraNo ratings yet
- Entropy A Detailed ExplanationDocument20 pagesEntropy A Detailed ExplanationgovindkaniNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q4 Week6Document14 pagesScience9 Q4 Week6MARIA JOSIE TUMLOSNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument32 pagesProjectile MotionSuresh100% (2)
- Lesson 3 - Charle's LawDocument11 pagesLesson 3 - Charle's LawTeacher JoanNo ratings yet
- Work - Energy - and PowerDocument14 pagesWork - Energy - and Powerraj78678No ratings yet
- Create By: Basic Physics IIDocument7 pagesCreate By: Basic Physics IIM Umar Said TyhnNo ratings yet
- But Can Change From One Form To Another Form of EnergyDocument19 pagesBut Can Change From One Form To Another Form of EnergyKhairiah SallehNo ratings yet
- 7 3seriesandparallelcircuits 121230035045 Phdpapp01Document19 pages7 3seriesandparallelcircuits 121230035045 Phdpapp01FerrolinoLouieNo ratings yet
- I Choose and Underline The Correct AnswerDocument6 pagesI Choose and Underline The Correct AnswerAshok Kumar DondatiNo ratings yet
- Ac & DC CurrentDocument11 pagesAc & DC CurrentAniketNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: Chemistry For EngineersDocument58 pagesThermochemistry: Chemistry For EngineersPaul Jhon Eugenio100% (1)
- DIAMOND BIOSENSOR-PPT Final SeminaDocument12 pagesDIAMOND BIOSENSOR-PPT Final SeminaGurmeet AroraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Scalar and VectorDocument25 pagesLesson 3 - Scalar and VectorEji AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry ExperimentDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry ExperimentMae TanNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Ionic BondsDocument27 pagesCH 7 Ionic Bondsapi-239855791No ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Chemical Foundations: Atoms, Ions, Compounds and MoleculesDocument39 pagesChapter 2. Chemical Foundations: Atoms, Ions, Compounds and MoleculesCalvin MakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Kinetics - Fast Facts: 6.1 Collision Theory and Rates of ReactionDocument2 pagesChapter 6: Kinetics - Fast Facts: 6.1 Collision Theory and Rates of ReactionChampbe Joo-LennoxNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Practice Test 1Document25 pagesKinetics Practice Test 1noelNo ratings yet
- Name: - Class: - DateDocument4 pagesName: - Class: - Dateaniahsefa11No ratings yet
- CH1201-TD-1st LawDocument20 pagesCH1201-TD-1st LawAbhroNo ratings yet
- The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument111 pagesThe First Law of ThermodynamicsJuan MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - 2nd Law of Thermodynamics - Entropy - 2022 PDFDocument18 pagesLecture 5 - 2nd Law of Thermodynamics - Entropy - 2022 PDFJey BlaQNo ratings yet
- Basics of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics Is The Science That Deals With The Study of and Its Relation To TheDocument22 pagesBasics of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics Is The Science That Deals With The Study of and Its Relation To Thenico NicoNo ratings yet
- 40 Minutes ThermodynamicsDocument20 pages40 Minutes ThermodynamicsDheeraj dixitNo ratings yet
- Tutor 7Document16 pagesTutor 7LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Final2017 180103163145Document14 pagesFinal2017 180103163145LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Y X y y X y y X Y: We Turn Now To The Solution of Differential Equations of Order Two or HigherDocument29 pagesY X y y X y y X Y: We Turn Now To The Solution of Differential Equations of Order Two or HigherLEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 2Document3 pagesExercise Chapter 2LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Linear Equations With Constant Coefficients (Second Order)Document22 pagesHomogeneous Linear Equations With Constant Coefficients (Second Order)LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Revisi Ekspres 7Document2 pagesRevisi Ekspres 7LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Revisi Ekspres 9Document3 pagesRevisi Ekspres 9LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Bab 4.3Document40 pagesBab 4.3LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Eigen VectorDocument12 pagesChapter 5 - Eigen VectorLEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document102 pagesChapter 3LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document65 pagesChapter 3LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Piperine From Black PepperDocument5 pagesIsolation of Piperine From Black PepperLEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document53 pagesChapter 2LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- The Main Steps of The Manufacturing Process: Synthetic Rubber GlovesDocument3 pagesThe Main Steps of The Manufacturing Process: Synthetic Rubber GlovesLEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document32 pagesChapter 3LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- 4 Diagram 4 Shows Experiments I and II in The Preparation of A Salt. Experiment MethodDocument2 pages4 Diagram 4 Shows Experiments I and II in The Preparation of A Salt. Experiment MethodLEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Weighing Scale Penimbang Glass Rod Rod Kaca NaohDocument3 pagesWeighing Scale Penimbang Glass Rod Rod Kaca NaohLEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Weighing Scale Penimbang Glass Rod Rod Kaca NaohDocument3 pagesWeighing Scale Penimbang Glass Rod Rod Kaca NaohLEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- 2 Diagram 2 Shows Two Sets of Experiments To Investigate The Chemical Properties ofDocument2 pages2 Diagram 2 Shows Two Sets of Experiments To Investigate The Chemical Properties ofLEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Notes 6.1Document3 pagesNotes 6.1LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
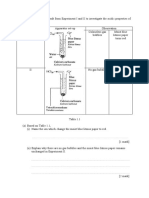
- 1 Table 1.1 Shows The Result From Experiment I and II To Investigate The Acidic Properties ofDocument2 pages1 Table 1.1 Shows The Result From Experiment I and II To Investigate The Acidic Properties ofLEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
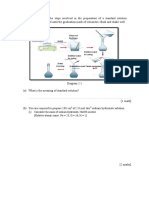
- What Is Standard Solution?Document2 pagesWhat Is Standard Solution?LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- 203 826 2 PBDocument15 pages203 826 2 PBTWW100% (1)
- Lecture 1Document46 pagesLecture 1Imtiyaaz MalickNo ratings yet
- Rohm Bu2090Document12 pagesRohm Bu2090Alberto Carrillo GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Angkur BetonDocument36 pagesAngkur BetonmhadihsNo ratings yet
- Spa 20008080VDocument1 pageSpa 20008080Vmichele DSNo ratings yet
- Bosvark ZL08F Front-End Loader: Key FeaturesDocument2 pagesBosvark ZL08F Front-End Loader: Key FeaturesJaco Coetzer100% (1)
- Gandolfi - L'Eclissi e L'orbe Magno Del LeoneDocument24 pagesGandolfi - L'Eclissi e L'orbe Magno Del LeoneberixNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Traditional Types of Building FoundationDocument14 pagesThe Evolution of Traditional Types of Building FoundationHenry Eduardo TorresNo ratings yet
- Tenda Catalogo 2020 PDFDocument24 pagesTenda Catalogo 2020 PDFTenda Región AndinaNo ratings yet
- Warning: Millennium Controller MC Series Installation and Operation ManualDocument28 pagesWarning: Millennium Controller MC Series Installation and Operation ManualHashemAliHashemNo ratings yet
- ) Wikipe: Types of Anemometer - : 1 - Cup AnemometerDocument4 pages) Wikipe: Types of Anemometer - : 1 - Cup Anemometermahmoud osamaNo ratings yet
- STP-27RD Press Kit MAY 2019: Launching On Electron Vehicle Six: 'Thats A Funny Looking Cactus'Document9 pagesSTP-27RD Press Kit MAY 2019: Launching On Electron Vehicle Six: 'Thats A Funny Looking Cactus'SrivasNo ratings yet
- OTC-10860-MS Overview of The Cantarell Field Development Program - GoodDocument9 pagesOTC-10860-MS Overview of The Cantarell Field Development Program - GoodGilbert OmittaNo ratings yet
- 1741 - Long Span Structures ReportDocument5 pages1741 - Long Span Structures ReportHuzefa SayyedNo ratings yet
- Ai in Health Care - Unit - IIDocument57 pagesAi in Health Care - Unit - IIvishnukaushikvarmaNo ratings yet
- Manual Generador 3100 600KWDocument58 pagesManual Generador 3100 600KWIsidro H Martin0% (1)
- LE Handicraft WEEK 3-4 GRADE 7 - 8Document6 pagesLE Handicraft WEEK 3-4 GRADE 7 - 8Michelle Llanes100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Transducer and Sensors Part 1Document46 pagesChapter 3 - Transducer and Sensors Part 1Zersh EthioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 Two Dimensional Problems in Elasticity - Ugural, FensterDocument50 pagesChapter 03 Two Dimensional Problems in Elasticity - Ugural, Fensteracanerk100% (6)
- TDS - Pidicryl 120V - UpdatedDocument1 pageTDS - Pidicryl 120V - Updatedhai nguyenNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - MINITASK - CapacitorDocument13 pagesActivity 3 - MINITASK - CapacitorEssi Marie FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Automatic Drainage Cleaning SystemDocument42 pagesAutomatic Drainage Cleaning SystemAnonymous j0aO95fg100% (2)
- Earth Pressure CalculationsDocument5 pagesEarth Pressure Calculationsnazeer_mohdNo ratings yet
- Unofficial Acs Practice Test 01 ADocument11 pagesUnofficial Acs Practice Test 01 AMaggie Zhang100% (1)
- Republic Act 8749 Salient FeaturesDocument34 pagesRepublic Act 8749 Salient Featuresdenr02legal88% (8)
- Course Task - Week 7Document34 pagesCourse Task - Week 7JoelynMacalintalNo ratings yet
- Decomposition of Diacetone AlcoholDocument3 pagesDecomposition of Diacetone Alcoholaryajs2017No ratings yet
- Chronic Pancreatitis: Causes ComplicationsDocument1 pageChronic Pancreatitis: Causes ComplicationsNikey LimNo ratings yet
- Niir Modern Technology Petroleum Greases Lubricants Petro Chemicals 2nd Revised EditionDocument8 pagesNiir Modern Technology Petroleum Greases Lubricants Petro Chemicals 2nd Revised EditionM.ASNo ratings yet
- Alcolyzer Beer Analyzing SystemDocument6 pagesAlcolyzer Beer Analyzing SystemAndrés MárquezNo ratings yet